Film
Robert Townsend to visit Twin Cities for Gordon Parks film series kick-off
MINNESOTA SPOKESMAN-RECORDER — Screenings and curated events will serve as a bridge between the Twin Cities community and noteworthy artists and media-makers who drew inspiration from Parks’ legacy.
#NNPA BlackPress
IN MEMORIAM: Legendary Funk Pioneer Sly Stone Dies at 82
Sly Stone’s musical approach radically reshaped popular music. He transcended genre boundaries and empowered a new generation of artists. The band’s socially conscious message and infectious rhythms sparked a wave of influence, reaching artists as diverse as Miles Davis, George Clinton, Prince, Dr. Dre, and the Roots.

Arts and Culture
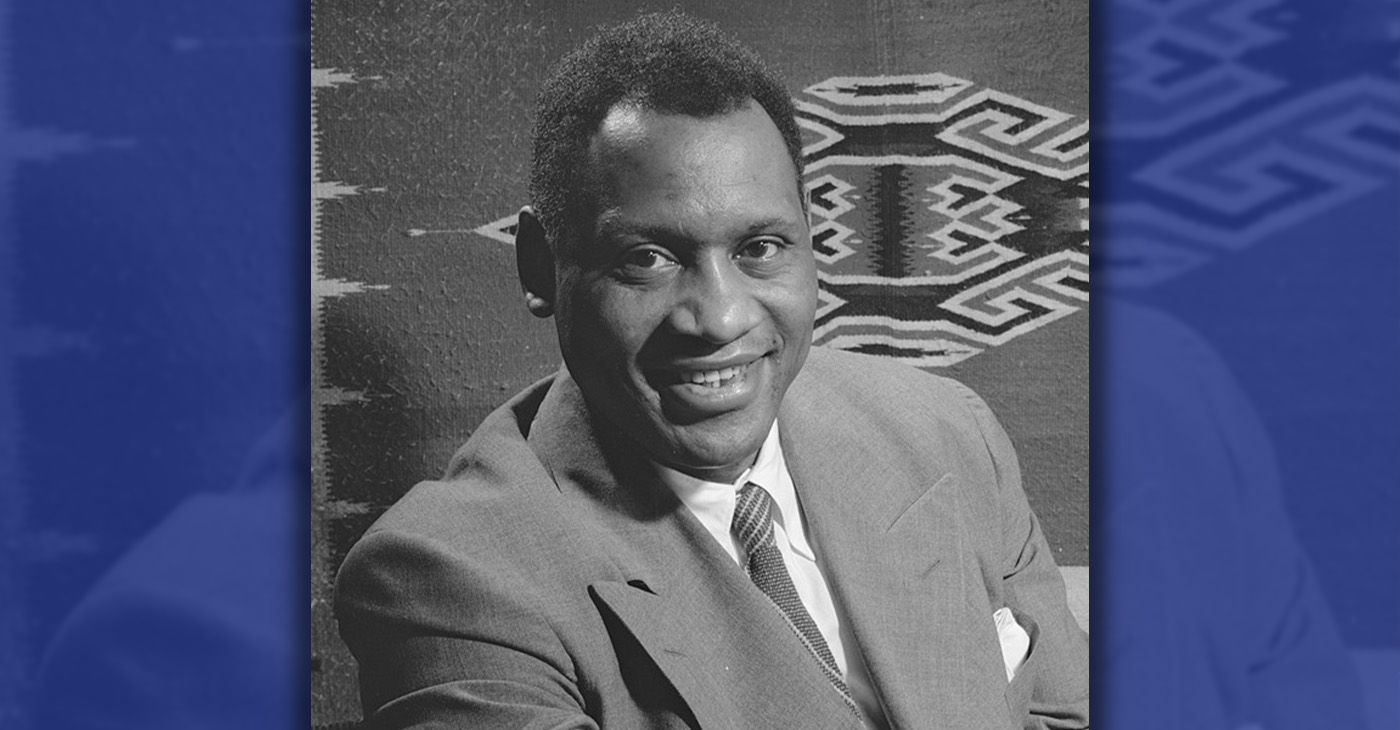
Paul Robeson: A Voice for the Ages, A Champion for Justice
Robeson first gained widespread recognition on stage and screen, delivering commanding performances that captivated audiences. Yet, it was his voice in concert halls that sealed his legacy. His repertoire was vast, spanning spirituals, classical compositions, global folk traditions, and songs of struggle — music that carried the weight of the oppressed and the hopes of the marginalized.
Activism
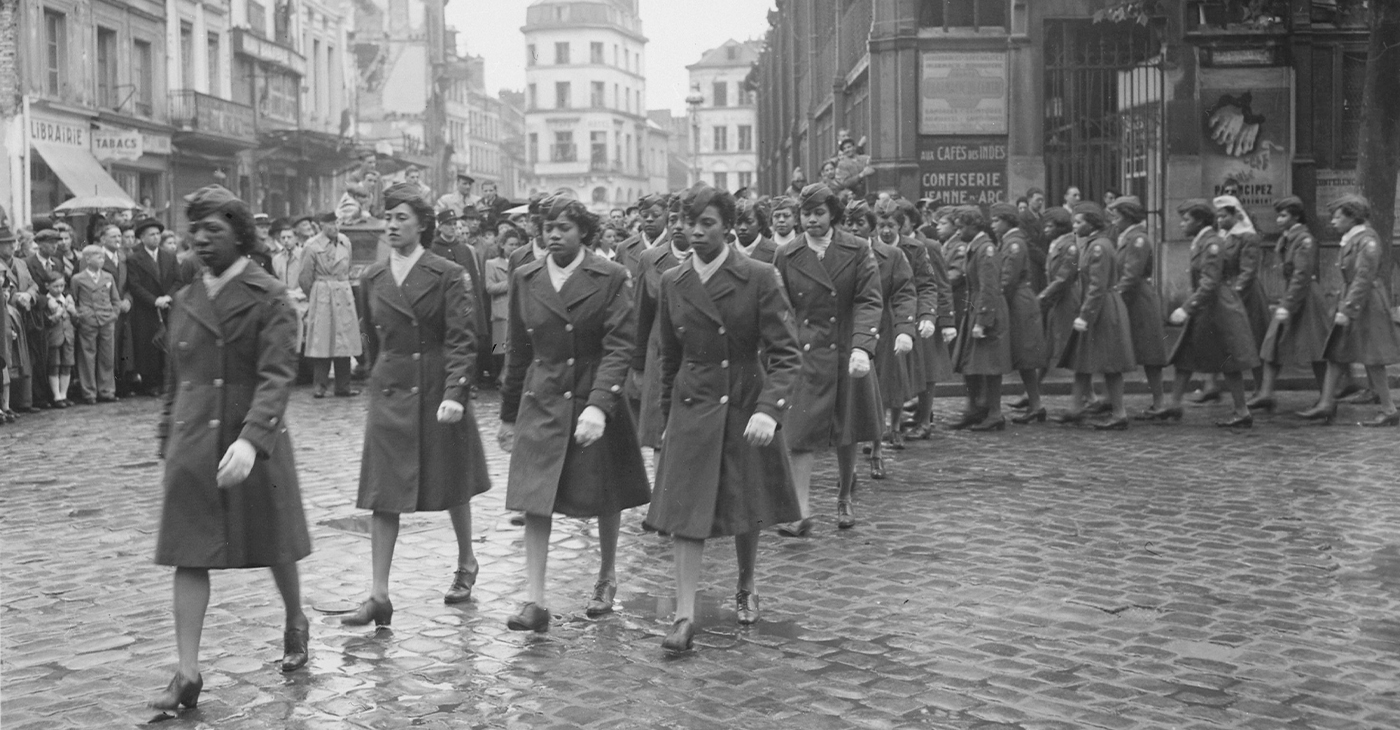
The SixTripleEight: “No Mail, Low Morale”
Women were recruited and trained until May 1942. The Women’s Auxiliary Army Corps was formed, and women of all races were officially allowed to serve. In July of that same year, women were given full benefits in the military, and the word “auxiliary” was removed from their name. The Corps then became known as the Women’s Army Corps (WACs).
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoOP-ED: The Dream Cannot be Realized Without Financial Freedom
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoTravis Scott Teaches Us How to Give Forward
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoFour Stolen Futures: Will H-E-B Do The Right Thing?
-

 Activism2 weeks ago
Activism2 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of January 28, 2025 – February 3, 2026
-

 Activism3 weeks ago
Activism3 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of January 21 – 27, 2026
-

 Activism2 weeks ago
Activism2 weeks agoLife Expectancy in Marin City, a Black Community, Is 15-17 Years Less than the Rest of Marin County
-
Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Homegoing Service for Education Advocate Oscar Wright, 101
-

 Activism2 weeks ago
Activism2 weeks agoMedi-Cal Cares for You and Your Baby Every Step of the Way