#NNPA BlackPress
Mysterious Vaping Lung Injuries May Have Flown Under Regulatory Radar
LOS ANGELES SENTINEL — It was the arrival of the second man in his early 20s gasping for air that alarmed Dr. Dixie Harris. Young patients rarely get so sick, so fast, with a severe lung illness, and this was her second case in a matter of days. Then she saw three more patients at her Utah telehealth clinic with similar symptoms. They did not have infections, but all had been vaping. When Harris heard several teenagers in Wisconsin had been hospitalized in similar cases, she quickly alerted her state health department.
By Sydney Lupkin and Anna Maria Barry-Jester
It was the arrival of the second man in his early 20s gasping for air that alarmed Dr. Dixie Harris. Young patients rarely get so sick, so fast, with a severe lung illness, and this was her second case in a matter of days.
Then she saw three more patients at her Utah telehealth clinic with similar symptoms. They did not have infections, but all had been vaping. When Harris heard several teenagers in Wisconsin had been hospitalized in similar cases, she quickly alerted her state health department.
As patients in hospitals across the country combat a mysterious illness linked to e-cigarettes, federal and state investigators are frantically trying to trace the outbreaks to specific vaping products that, until recently, were virtually unregulated.
As of Aug. 22, 193 potential vaping-related illnesses in 22 states had been reported to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. California is investigating 22 cases. Wisconsin, which first put out an alert in July, has at least 16 confirmed and 15 suspected cases. Illinois has reported 34 patients, one of whom has died. Indiana is investigating 24.
Lung doctors said they had seen warning signs for years that vaping could be hazardous, as they treated patients. Medically it seemed problematic, since it often involved inhaling chemicals not normally inhaled into the lungs. Despite that, assessing the safety of a new product storming the market fell between regulatory cracks, leaving doctors unsure where to register concerns before the outbreak. The Food and Drug Administration took years to regulate e-cigarettes once a court determined it had the authority to do so.
“You don’t know what you’re putting into your lungs when you vape,” said Harris, a critical care pulmonologist at Intermountain Healthcare in Salt Lake City. “It’s purported to be safe, but how do you know if it’s safe? To me, it’s a very dangerous thing.”
Dr. Laura Crotty Alexander, a pulmonologist and researcher with the University of California-San Diego, said she saw her first case about two years ago. A young man had been vaping for months with the same device but developed acute lung injury when he switched flavors. She strongly suspected a link but did not report the illness anywhere.
“It wasn’t that I didn’t want to report it, it’s that there’s no pathway” to do so, Alexander said.
She said she’s concerned that many physicians haven’t been asking patients about e-cigarette use and that there’s no way to document a case like this in the medical coding system.
Off The Radar
When electronic cigarettes came to market about a decade ago, they fell into a regulatory no man’s land. They are not a food, not a drug and not a medical device, any of which would have put them immediately in the FDA’s purview. And, until a few years ago, they weren’t even lumped in with tobacco products.
As a result, billions of dollars of vaping products have been sold online, at big-box retailers and in corner stores without going through the FDA’s rigorous review process to assess their safety. Companies like Blu, NJoy and Juul, which is based in San Francisco, quickly established their brands of devices and cartridges, or pods. And thousands of related products are sold, sometimes on the black market over the internet or beyond.
“It makes it really tough because we don’t know what we’re looking for,” said Dr. Ruth Lynfield, the state epidemiologist for Minnesota, where several patients were admitted to the intensive care unit as a result of the illness. She added that if it turns out that the products in question were sold by unregistered retailers and manufacturers “on the street,” outbreak sleuths will have a harder time figuring out exactly what is in them.
With e-cigarettes, people can vape — or smoke — nicotine products, selecting flavorings like mint, mango, blueberry crème brûlée or cookies and milk. They can also inhale cannabis products. Many are hopeful that e-cigarettes might be useful smoking cessation tools, but some research has called that into question.
The mysterious pulmonary disease cases have been linked to vaping, but it’s unclear whether there is a common device or chemical. In some states, including California and Utah, all of the patients had vaped cannabis products. One or more substances could be involved, health officials have said. The products used by several victims are being tested to see what they contained.
Because e-cigarettes aren’t classified as drugs or medical devices, which have well-established FDA databases to track adverse events, doctors say there has been no clear way to report and track health problems related to vaping products.
And this has apparently been the case for years.
Multiple doctors described seeing earlier cases of severe lung problems linked to vaping that were not officially reported or included in the current CDC count.
Dr. John E. Parker of West Virginia University said he saw his first patient with pneumonia tied to vaping in 2015. Doctors there were intrigued enough to report on the case at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians. Parker and his team didn’t contact a federal agency, and Parker said it was unclear whom to call.
Numerous other cases have been reported in medical journals and at professional conferences in the years since. The FDA’s voluntary system for reporting tobacco-related health problems included 96 seizures and only one lung ailment tied to e-cigarettes from April through June of this year. The system appears to be utilized most by concerned citizens, rather than manufacturers or health care professionals.
But several lung specialists said that due to the patchwork nature of regulatory oversight over the years, the true scope of the problem is yet to be identified.
“We do know that e-cigarettes do not emit a harmless aerosol,” said Brian King, a deputy director in the Office on Smoking and Health at the CDC in a call with media on Aug. 23 about the outbreak. “It is possible that some of these cases were already occurring but we were not picking them up.”
Regulatory Limits
The FDA has had limited authority to regulate e-cigarettes over the years.
In 2009, Congress passed the Family Smoking Prevention and Tobacco Control Act, empowering the FDA to oversee the safety and sale of tobacco products. But e-cigarettes, still new, were not top of mind.
Later that year, the FDA tried to block imports of e-cigarettes, saying the combination drug-device products were unapproved and therefore illegal for sale in the United States. Two vaping companies, Smoking Everywhere and NJoy, sued, and a federal judge ruled in 2010 that the FDA should regulate e-cigarettes as tobacco products.
It took the agency six years to finalize what’s become known as the “deeming rule,” in which it formally began regulating e-cigarettes and e-liquids.
By then, it was May 2016. The e-cigarette market had swelled to an estimated $4.1 billion, Wells Fargo Securities analyst Bonnie Herzog said at the time. Market researchers now project that the global industry could reach $48 billion by 2023.
Critics say the FDA took too long to act.
“I think the fact that FDA has been dillydallying [has made] figuring out what’s going on [with this outbreak] much harder,” said Stanton Glantz, a University of California-San Francisco professor in its Center for Tobacco Control Research and Education. “No question.”
The agency began by banning e-cigarette sales to minors and requiring all new vaping products to submit applications for authorization before they could come to market. Companies and retailers with thousands of products already on the market were granted two years to submit applications, and the FDA would get an additional year to evaluate the applications. Meanwhile, existing products could still be sold.
But when Dr. Scott Gottlieb arrived as the new FDA commissioner in 2017, the rule hadn’t been implemented and there was no formal guidance for companies to file applications, he said. As a result, he pushed the deadline back to 2022, drawing ire from public health advocates, who called foul over his previous ties to an e-cigarette retailer called Kure.
“I thought e-cigarettes at the time — and I still believe — that they represent an opportunity for currently addicted adult smokers to transition off of combustible tobacco,” he said in an interview, adding that other parts of the deeming rule went into effect as planned. “All I did was delay the application deadline.”
Gottlieb’s thinking changed the following year, when a national survey showed a sharp rise in teen vaping, which he called an “epidemic.” He announced that the agency would rethink the extended deadline and weigh whether to take flavors that appeal to kids off the market.
A judge ruled last month that e-cigarette makers would have only 10 more months to submit applications to the FDA. They’re now due in May 2020.
Asked about the lung injuries appearing now, Gottlieb, who left the FDA in April, said he suspected counterfeit pods are to blame, given the geographic clustering of cases and the fact that, overall, the FDA is inspecting registered e-cigarette makers and retailers to make sure they’re complying with existing regulations.
“I think the manufacturers are culpable if their products are being used, whether the liquids are counterfeit or real,” he said. “Ultimately, they’re responsible for keeping their products out of the hands of kids.”
Juul, the leading e-cigarette maker, agreed that children shouldn’t be able to vape its products, and said curtailing access should be done “through significant regulation” and “enforcement.”
“When people say ‘Why aren’t these being regulated?’ They actually are all being regulated,” Gottlieb said.
For example, companies are required to label their products as potentially addictive, sell only to adults and comply with manufacturing standards. The agency has conducted thousands of inspections of e-cigarette manufacturers and retailers and taken enforcement actions against companies selling e-cigarettes that look like juice boxes, and a company that was putting the ingredients found in erectile dysfunction drugs into its vape liquid.
Health departments investigating the outbreak told Kaiser Health News that e-cigarettes’ niche as a tobacco product instead of a drug has presented challenges. Most weren’t aware that adverse events could be reported to a database that tracks problems with tobacco products. And, because e-cigarettes never went through the FDA’s “gold standard” approval process for drugs, doctors can’t readily look up a detailed list of known side effects.
But like other arms of the FDA, the tobacco office has tools and a team to investigate a public health threat just as the teams for drugs and devices do, Gottlieb said. It may even be better equipped because of its funding.
“I don’t think FDA is operating in any way with hands tied behind its back because of the way that the statute is set up,” he said.
Teen vaping has exploded during this regulatory tussle. In 2011, 1.5% of high school students reported vaping. By 2018, it was 20.8%, according to a CDC report.
Unknown Components
Still, doctors and researchers are concerned about the ingredients in e-cigarettes, and how little the public knows about the risks of vaping.
In Juul’s terms and conditions, posted on its website, it says, “We encourage consumers to do their own research regarding vapor products and what is right for them.” Many ingredients in e-cigarette products, however, are protected as trade secrets.
Since at least 2013, the flavor industry has expressed concern about the use of flavoring chemicals in vaping products.
The vast majority of the chemicals have been tested only by ingesting them in small quantities, as they’re encountered in foods. For most of these chemicals, there have been no tests to determine whether it is safe to inhale them, as happens daily by millions when they use e-cigarettes.
“Many of the ingredients of vaping products, including flavoring substances, have not been tested for … the exposure one would get from using a vaping device,” said John Hallagan, a senior adviser to the Flavor and Extract Manufacturers Association. The group has sent cease-and-desist letters to e-cigarette companies in previous years for using the food safety certification of the flavor industry to imply that the chemicals are also safe in e-cigarettes.
Some flavor chemicals are thought to be harmful when inhaled in high doses. Research suggests that cinnamaldehyde, the main component of many cinnamon flavors, may impair lung function when inhaled. Sven-Eric Jordt, a professor at Kaiser Health News, says he presented evidence of its dangers at an FDA meeting in 2015 — and its relative abundance in many e-cigarette vaping liquids. In response, one major e-cigarette liquid seller, Tasty Vapor, voluntarily took its cinnamon-flavored liquid off the shelves.
In 2017, when Gottlieb delayed the FDA application deadline, the product was back. A company email to its customers put it this way:
“Two years ago, Tasty Vapor allowed itself to be intimidated by scaremongering tactics. … We lost a lot of sales as well as a good number of long time customers. We no long see reason to disappoint our customers hostage for these shady tactics.”
At the time of publication, Tasty Vapor’s owner did not reply to a request for comment.
Jordt said he is frustrated by the delays in the regulatory approval process.
“As a parent, I would say that the government has not acted on this,” he said. “You’re basically left to act alone with your addicted kid. It’s kind of terrifying that this was allowed to happen. The industry needs to be held to account.”
Kaiser Health News correspondents Cara Anthony, Markian Hawryluk and Lauren Weber and reporter Victoria Knight contributed to this report.
This story was produced by Kaiser Health News, an editorially independent program of the Kaiser Family Foundation.
This article originally appeared in The Los Angeles Sentinel.
#NNPA BlackPress
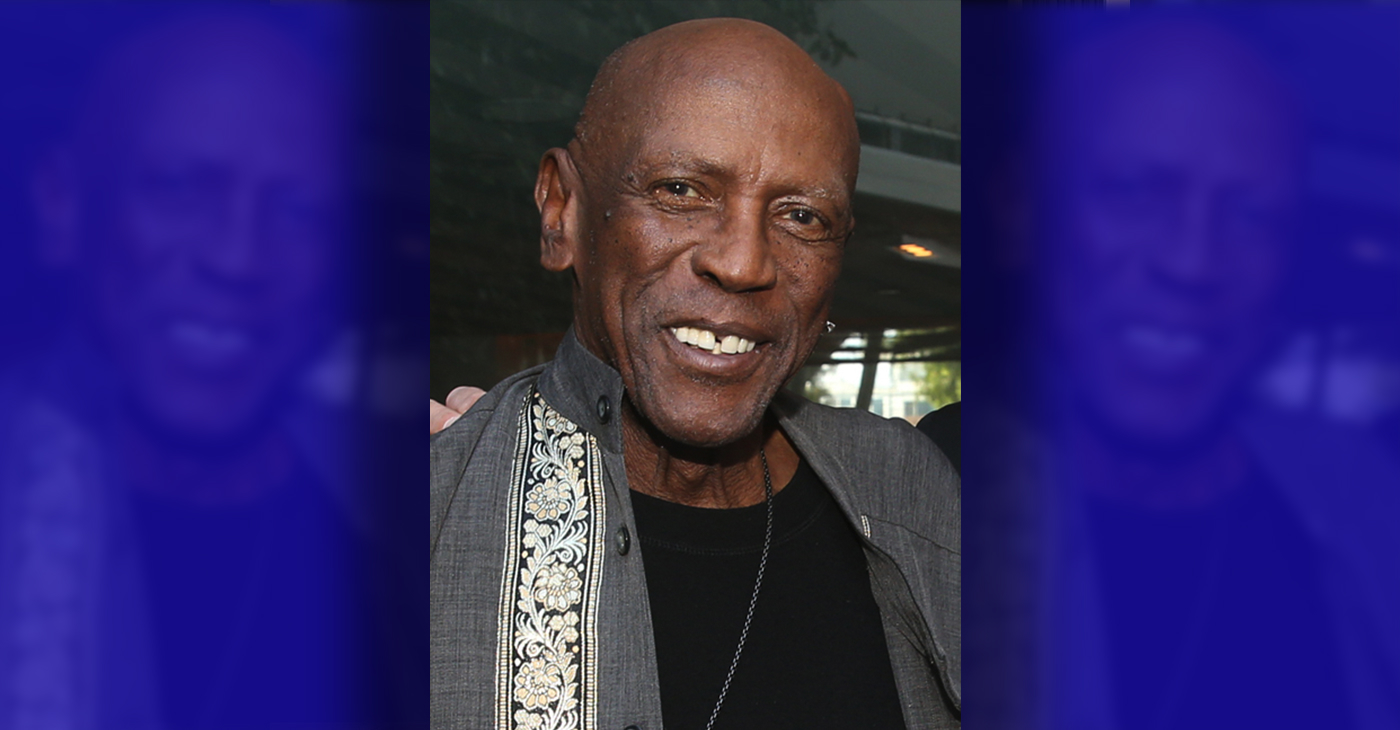
Beloved Actor and Activist Louis Cameron Gossett Jr. Dies at 87
NNPA NEWSWIRE — Louis Gossett Jr., the groundbreaking actor whose career spanned over five decades and who became the first Black actor to win an Academy Award as Best Supporting Actor for his memorable role in “An Officer and a Gentleman,” has died. Gossett, who was born on May 27, 1936, in Brooklyn, N.Y., was 87. Recognized early on for his resilience and nearly unmatched determination, Gossett arrived in Los Angeles in 1967 after a stint on Broadway.
The post Beloved Actor and Activist Louis Cameron Gossett Jr. Dies at 87 first appeared on BlackPressUSA.

By Stacy M. Brown
NNPA Newswire Senior National Correspondent
@StacyBrownMedia
Louis Gossett Jr., the groundbreaking actor whose career spanned over five decades and who became the first Black actor to win an Academy Award as Best Supporting Actor for his memorable role in “An Officer and a Gentleman,” has died. Gossett, who was born on May 27, 1936, in Brooklyn, N.Y., was 87. Recognized early on for his resilience and nearly unmatched determination, Gossett arrived in Los Angeles in 1967 after a stint on Broadway.
He sometimes spoke of being pulled over by law enforcement en route to Beverly Hills, once being handcuffed to a tree, which he remembered as a jarring introduction to the racial tensions of Hollywood. In his memoir “An Actor and a Gentleman,” Gossett recounted the ordeal, noting the challenges faced by Black artists in the industry. Despite the hurdles, Gossett’s talent shone brightly, earning him acclaim in groundbreaking productions such as “A Raisin in the Sun” alongside Sidney Poitier. His Emmy-winning portrayal of Fiddler in “Roots” solidified his status as a trailblazer, navigating a landscape fraught with racial prejudice.
According to the HistoryMakers, which interviewed him in 2005, Gossett’s journey into the limelight began during his formative years at PS 135 and Mark Twain Junior High School, where he demonstrated early leadership as the student body president. His passion for the arts blossomed when he starred in a “You Can’t Take It With You” production at Abraham Lincoln High School, catching the attention of talent scouts who propelled him onto Broadway’s stage in “Take A Giant Step.” His stellar performance earned him the prestigious Donaldson Award for Best Newcomer to Theatre in 1952. Though initially drawn to sports, Gossett’s towering 6’4” frame and athletic prowess led him to receive a basketball scholarship at New York University. Despite being drafted by the New York Knicks in 1958, Gossett pursued his love for acting, honing his craft at The Actors Studio under the tutelage of luminaries like John Sticks and Peggy Fury.
In 1961, Gossett’s talent caught the eye of Broadway directors, leading to roles in acclaimed productions such as “Raisin in the Sun” and “The Blacks,” alongside legends like James Earl Jones, Cicely Tyson, Roscoe Lee Brown, and Maya Angelou. Transitioning seamlessly to television, Gossett graced small screens with appearances in notable shows like “The Bush Baby” and “Companions in Nightmare.” Gossett’s silver screen breakthrough came with his role in “The Landlord,” paving the way for a prolific filmography that spanned over 50 movies and hundreds of television shows. From “Skin Game” to “Lackawanna Blues,” Gossett captivated audiences with his commanding presence and versatile performances.
However, his portrayal of “Fiddler” in Alex Haley’s groundbreaking miniseries “Roots” earned Gossett critical acclaim, including an Emmy Award. The HistoryMakers noted that his golden touch extended to the big screen, where his role as Sergeant Emil Foley in “An Officer and a Gentleman” earned him an Academy Award for Best Supporting Actor, making him a trailblazer in Hollywood history.
Beyond the glitz and glamour of Hollywood, Gossett was deeply committed to community activism. In 1964, he co-founded a theater group for troubled youth alongside James Earl Jones and Paul Sorvino, setting the stage for his lifelong dedication to mentoring and inspiring the next generation. Gossett’s tireless advocacy for racial equality culminated in the establishment of Eracism, a nonprofit organization dedicated to combating racism both domestically and abroad. Throughout his illustrious career, Gossett remained a beacon of strength and resilience, using his platform to uplift marginalized voices and champion social change. Gossett is survived by his children, Satie and Sharron.
The post Beloved Actor and Activist Louis Cameron Gossett Jr. Dies at 87 first appeared on BlackPressUSA.
#NNPA BlackPress
COMMENTARY: D.C. Crime Bill Fails to Address Root Causes of Violence and Incarceration
WASHINGTON INFORMER — The D.C. crime bill and so many others like it are reminiscent of the ‘94 crime bill, which produced new and harsher criminal sentences, helped deploy thousands of police and surveilling methods in Black and brown communities, and incentivized more states to build prisons through a massive infusion of federal funding. While it is not at the root of mass incarceration, it significantly accelerated it, forcing a generation of Black and brown families into a never-ending cycle of state-sanctioned violence and incarceration.
The post COMMENTARY: D.C. Crime Bill Fails to Address Root Causes of Violence and Incarceration first appeared on BlackPressUSA.
By Kaili Moss and Jillian Burford | Washington Informer
Mayor Bowser has signed the “Secure DC” omnibus bill passed by the D.C. Council last month. But we already know that this bill will be disastrous for all of D.C., especially for Black and brown residents.
While proponents claim that this legislation “will make D.C. residents safer and more secure,” it actually does nothing to address the root of the harm in the first place and instead maintains a cycle of violence, poverty, and broken community ties. The omnibus bill calls for increased surveillance, drug-free zones, and will expand pre-trial detention that will incarcerate people at a significantly higher rate and for an indeterminate amount of time before they are even tried. This bill will roll back decades of nationwide policy reform efforts and initiatives to keep our communities safe and whole, which is completely contradictory to what the “Secure” D.C. bill claims it will do.
What is unfolding in Washington, D.C., is part of a dangerous national trend. We have seen a resurrection of bad crime bills in several jurisdictions across the country — a phenomenon policy experts have named “zombie laws,” which are ineffective, costly, dangerous for communities of color and, most importantly, will not create public safety. Throwing more money into policing while failing to fund preventative measures does not keep us safe.
The D.C. crime bill and so many others like it are reminiscent of the ‘94 crime bill, which produced new and harsher criminal sentences, helped deploy thousands of police and surveilling methods in Black and brown communities, and incentivized more states to build prisons through a massive infusion of federal funding. While it is not at the root of mass incarceration, it significantly accelerated it, forcing a generation of Black and brown families into a never-ending cycle of state-sanctioned violence and incarceration. Thirty years later, despite spending billions each year to enforce these policies with many of these provisions remaining in effect, it has done very little to create long-term preventative solutions. Instead, it placed a permanent moving target on the backs of Black people, and the D.C. crime bill will do the same.
The bill calls for more pretrial detention. When our loved ones are held on pretrial detention, they are held on the presumption of guilt for an indeterminate amount of time before ever seeing a judge, which can destabilize people and their families. According to experts at the Malcolm Weimer Center for Social Policy at Harvard University, just one day in jail can have “devastating consequences.” On any given day, approximately 750,000 people are held in jails across the nation — a number that beats our nation’s capital population by about 100,000. Once detained, people run the risk of losing wages, jobs, housing, mental and health treatments, and time with their families. Studies show that pretrial detention of even a couple of days makes it more likely for that person to be rearrested.
The bill also endangers people by continuing a misguided and dangerous War on Drugs, which will not get drugs off the street, nor will it deter drug use and subsequent substance use disorders (SUDs). Drug policies are a matter of public health and should be treated as such. Many states such as Alabama, Iowa and Wisconsin are treating the current fentanyl crisis as “Crack 2.0,” reintroducing a litany of failed policies that have sent millions to jails and prisons instead of prioritizing harm reduction. Instead, we propose a simple solution: listen to members of the affected communities. Through the Decrim Poverty D.C. Coalition, community members, policy experts and other stakeholders formed a campaign to decriminalize drugs and propose comprehensive legislation to do so.
While there are many concerning provisions within the omnibus bill, car chases pose a direct physical threat to our community members. In July 2023, NBC4 reported that the D.C. Council approved emergency legislation that gave MPD officers the ability to engage in vehicular pursuits with so-called “limited circumstances.” Sgt. Val Barnes, the head of MPD’s carjacking task force, even expressed concern months before the decision, saying, “The department has a pretty strict no-chase policy, and obviously for an urban setting and a major metropolitan city, that’s understandable.” If our law enforcement officers themselves are operating with more concern than our elected officials, what does it say about the omnibus bill’s purported intention to keep us safe?
And what does it mean when the risk of bodily harm is posed by the pursuit itself? On Saturday, Feb. 10, an Eckington resident had a near-miss as a stolen car barreled towards her and her dog on the sidewalk with an MPD officer in pursuit. What responsibility does the city hold if this bystander was hit? What does restitution look like? Why are our elected officials pushing for MPD officers to contradict their own policies?
Just a few summers ago during the uprisings of 2020, we saw a shift in public perspectives on policing and led to legislation aimed at limiting police power after the highly-publicized murders of loved ones Breonna Taylor and George Floyd — both victims of War on Drugs policing and the powers gained from the ’94 crime bill. And yet here we are. These measures do not keep us safe and further endanger the health of our communities. Studies show that communities that focus on harm reduction and improving material conditions have a greater impact on public safety and community health. What’s missing in mainstream conversations about violent crime is the violence that stems from state institutions and structures that perpetuate racial and class inequality. The people of D.C. deserve to feel safe, and that includes feeling safe from the harms enacted by the police.
Kaili Moss is a staff attorney at Advancement Project, a national racial justice and legal organization, and Jillian Burford is a policy organizer at Harriet’s Wildest Dreams.
The post COMMENTARY: D.C. Crime Bill Fails to Address Root Causes of Violence and Incarceration first appeared on BlackPressUSA.
#NNPA BlackPress
Mayor, City Council President React to May 31 Closing of Birmingham-Southern College
THE BIRMINGHAM TIMES — “This is a tragic day for the college, our students, our employees, and our alumni, and an outcome so many have worked tirelessly to prevent,” Rev. Keith Thompson, chairman of the BSC Board of Trustees said in an announcement to alumni. “We understand the devastating impact this has on each of you, and we will now direct our efforts toward ensuring the smoothest possible transition for everyone involved.”
The post Mayor, City Council President React to May 31 Closing of Birmingham-Southern College first appeared on BlackPressUSA.

By Barnett Wright | The Birmingham Times
Birmingham-Southern College will close on May 31, after more than a century as one of the city’s most respected institutions.
“This is a tragic day for the college, our students, our employees, and our alumni, and an outcome so many have worked tirelessly to prevent,” Rev. Keith Thompson, chairman of the BSC Board of Trustees said in an announcement to alumni. “We understand the devastating impact this has on each of you, and we will now direct our efforts toward ensuring the smoothest possible transition for everyone involved.”
There are approximately 700 students enrolled at BSC this semester.
“Word of the decision to close Birmingham Southern College is disappointing and heartbreaking to all of us who recognize it as a stalwart of our community,” Birmingham Mayor Randall Woodfin said in a statement. “I’ve stood alongside members of our City Council to protect this institution and its proud legacy of shaping leaders. It’s frustrating that those values were not shared by lawmakers in Montgomery.”
Birmingham City Council President Darrell O’Quinn said news of the closing was “devastating” on multiple levels.
“This is devastating for the students, faculty members, families and everyone affiliated with this historic institution of higher learning,” he said. “It’s also profoundly distressing for the surrounding community, who will now be living in close proximity to an empty college campus. As we’ve seen with other institutions that have shuttered their doors, we will be entering a difficult chapter following this unfortunate development … We’re approaching this with resilience and a sense of hope that something positive can eventually come from this troubling chapter.”
The school first started as the merger of Southern University and Birmingham College in 1918.
The announcement comes over a year after BSC officials admitted the institution was $38 million in debt. Looking to the Alabama Legislature for help, BSC did not receive any assistance.
This past legislative session, Sen. Jabo Waggoner sponsored a bill to extend a loan to BSC. However, the bill subsequently died on the floor.
Notable BSC alumni include former New York Times editor-in-chief Howell Raines, former U.S. Sen. Howell Heflin and former Alabama Supreme Court Chief Justice Perry O. Hooper Sr.
This story will be updated.
The post Mayor, City Council President React to May 31 Closing of Birmingham-Southern College first appeared on BlackPressUSA.
-

 Activism3 weeks ago
Activism3 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of March 27 – April 2, 2024
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoCOMMENTARY: D.C. Crime Bill Fails to Address Root Causes of Violence and Incarceration
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoFrom Raids to Revelations: The Dark Turn in Sean ‘Diddy’ Combs’ Saga
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoCOMMENTARY: Lady Day and The Lights!
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoMayor, City Council President React to May 31 Closing of Birmingham-Southern College
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoBaltimore Key Bridge Catastrophe: A City’s Heartbreak and a Nation’s Alarm
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoBaltimore’s Key Bridge Struck by Ship, Collapses into Water
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoBeloved Actor and Activist Louis Cameron Gossett Jr. Dies at 87