Business
Tobacco Company Lawsuit Alleges FDA Overstepping Authority

This Tuesday, July 15, 2014 photo shows the tobacco in cigarettes in Philadelphia. A study ties a host of new diseases to smoking, and says an additional 60,000 to 120,000 deaths each year in the United States are probably due to tobacco use. (AP Photo/Matt Rourke)
MATTHEW PERRONE, AP Health Writer
WASHINGTON (AP) — The nation’s largest tobacco companies are suing the Food and Drug Administration over recent guidelines that they claim overstep the agency’s authority over labeling and packaging for cigarettes and other tobacco products.
Units of R.J. Reynolds Tobacco, Altria Group Inc. and Lorillard Tobacco filed the lawsuit Tuesday in the U.S. District Court for the District of Columbia, claiming the FDA’s guidance infringes on their commercial speech.
The FDA gained authority to regulate tobacco in 2009, including the power to pre-review new tobacco products that are significantly different from older ones already on the market.
Last month the agency issued guidelines intended to help manufacturers determine which new products require FDA review.
But the tobacco makers allege that the FDA is asserting overly-broad authority to approve or deny any labeling change that would make a product “distinct.” Their lawsuit argues that the FDA only has prior-review authority for labels on tobacco products claiming to represent a “modified risk,” or to be less harmful than other tobacco products.
FDA guidelines are considered suggestions and are not legally binding. But the tobacco companies say the FDA document “creates specific legal obligations with clear and draconian consequences for violations.”
The FDA said it does not comment on litigation.
The agency issued a draft version of the guidelines in September 2011 and took comments from industry and the public on the proposal.
In an explanation accompanying the final guidelines issued last month, the FDA said that certain labeling changes effectively create a new product “if consumers are likely to perceive it as ‘new’ by virtue of the different label.” Regulators listed examples such as changing a product’s logo, packaging color or product description.
The U.S. tobacco industry has repeatedly challenged FDA authority in court since Congress passed the Tobacco Control Act of 2009.
In 2011, some of the industry’s largest companies sued the FDA to block an order that would have required cigarette packages to carry large, graphic warning labels illustrating the dangers of smoking. But an appeals court decision ruled that the labels violated the First Amendment’s free speech protections and the government abandoned the plan in 2013.
Tobacco companies rely on their packaging to build brand loyalty and grab consumers. It’s one of few advertising levers left to them after the government curbed their presence in magazines, billboards and TV.
Copyright 2015 The Associated Press. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.
Bay Area
State Controller Malia Cohen Keynote Speaker at S.F. Wealth Conference
California State Controller Malia Cohen delivered the keynote speech to over 50 business women at the Black Wealth Brunch held on March 28 at the War Memorial and Performing Arts Center at 301 Van Ness Ave. in San Francisco. The Enterprising Women Networking SF Chapter of the American Business Women’s Association (ABWA) hosted the Green Room event to launch its platform designed to close the racial wealth gap in Black and Brown communities.
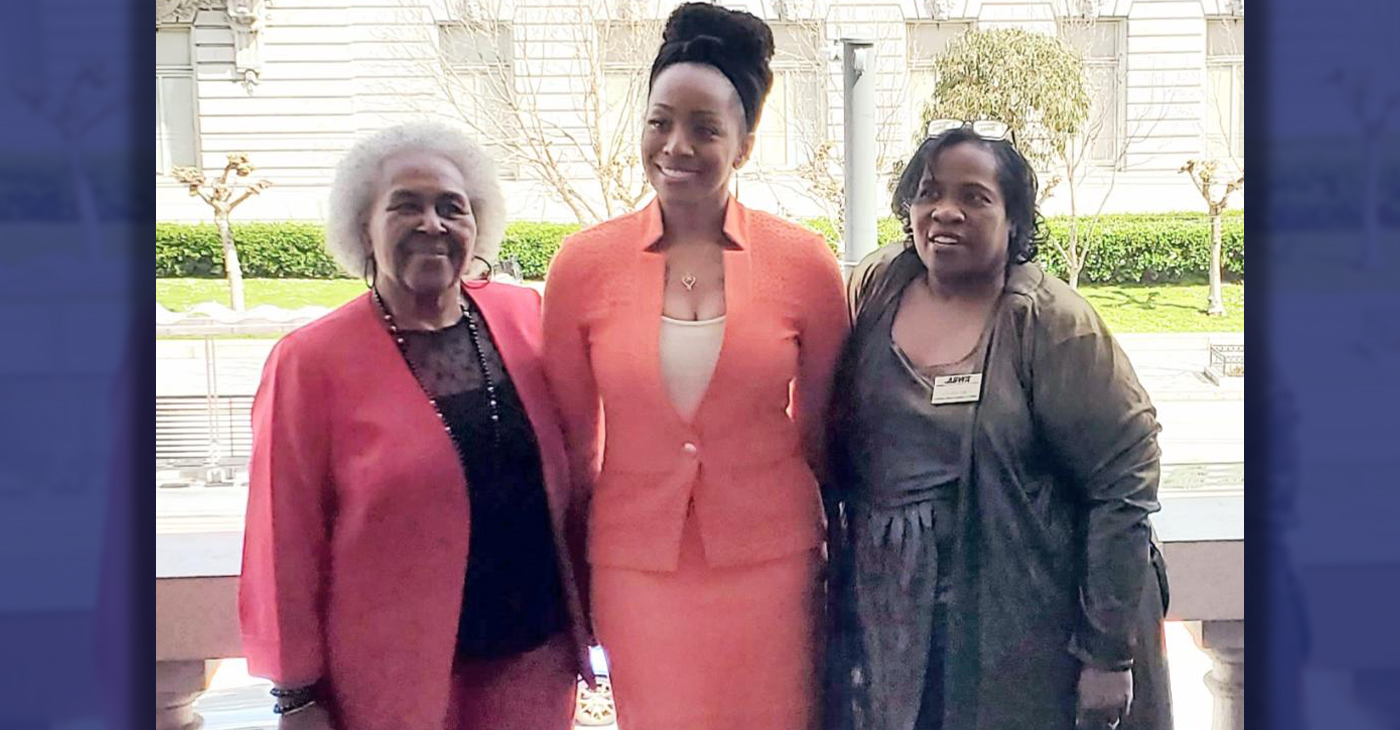
By Carla Thomas
California State Controller Malia Cohen delivered the keynote speech to over 50 business women at the Black Wealth Brunch held on March 28 at the War Memorial and Performing Arts Center at 301 Van Ness Ave. in San Francisco.
The Enterprising Women Networking SF Chapter of the American Business Women’s Association (ABWA) hosted the Green Room event to launch its platform designed to close the racial wealth gap in Black and Brown communities.
“Our goal is to educate Black and Brown families in the masses about financial wellness, wealth building, and how to protect and preserve wealth,” said ABWA San Francisco Chapter President LaRonda Smith.
ABWA’s mission is to bring together businesswomen of diverse occupations and provide opportunities for them to help themselves and others grow personally and professionally through leadership, education, networking support, and national recognition.
“This day is about recognizing influential women, hearing from an accomplished woman as our keynote speaker and allowing women to come together as powerful people,” said ABWA SF Chapter Vice President Velma Landers.
More than 60 attendees dined on the culinary delights of Chef Sharon Lee of The Spot catering, which included a full soul food brunch of skewered shrimp, chicken, blackened salmon, and mac and cheese.
Cohen discussed the many economic disparities women and people of color face. From pay equity to financial literacy, Cohen shared not only statistics, but was excited about a new solution in motion which entailed partnering with Californians for Financial Education.
“I want everyone to reach their full potential,” she said. “Just a few weeks ago in Sacramento, I partnered with an organization, Californians for Financial Education.
“We gathered 990 signatures and submitted it to the [California] Secretary of State to get an initiative on the ballot that guarantees personal finance courses for every public school kid in the state of California.
“Every California student deserves an equal opportunity to learn about filing taxes, interest rates, budgets, and understanding the impact of credit scores. The way we begin to do that is to teach it,” Cohen said.
By equipping students with information, Cohen hopes to close the financial wealth gap, and give everyone an opportunity to reach their full financial potential. “They have to first be equipped with the information and education is the key. Then all we need are opportunities to step into spaces and places of power.”
Cohen went on to share that in her own upbringing, she was not guided on financial principles that could jump start her finances. “Communities of color don’t have the same information and I don’t know about you, but I did not grow up listening to my parents discussing their assets, their investments, and diversifying their portfolio. This is the kind of nomenclature and language we are trying to introduce to our future generations so we can pivot from a life of poverty so we can pivot away and never return to poverty.”
Cohen urged audience members to pass the initiative on the November 2024 ballot.
“When we come together as women, uplift women, and support women, we all win. By networking and learning together, we can continue to build generational wealth,” said Landers. “Passing a powerful initiative will ensure the next generation of California students will be empowered to make more informed financial decisions, decisions that will last them a lifetime.”
Business
Black Business Summit Focuses on Equity, Access and Data
The California African American Chamber of Commerce hosted its second annual “State of the California African American Economy Summit,” with the aim of bolstering Black economic influence through education and fellowship. Held Jan. 24 to Jan. 25 at the Westin Los Angeles Airport Hotel, the convention brought together some of the most influential Black business leaders, policy makers and economic thinkers in the state. The discussions focused on a wide range of economic topics pertinent to California’s African American business community, including policy, government contracts, and equity, and more.

By Solomon O. Smith, California Black Media
The California African American Chamber of Commerce hosted its second annual “State of the California African American Economy Summit,” with the aim of bolstering Black economic influence through education and fellowship.
Held Jan. 24 to Jan. 25 at the Westin Los Angeles Airport Hotel, the convention brought together some of the most influential Black business leaders, policy makers and economic thinkers in the state. The discussions focused on a wide range of economic topics pertinent to California’s African American business community, including policy, government contracts, and equity, and more.
Toks Omishakin, Secretary of the California State Transportation Agency (CALSTA) was a guest at the event. He told attendees about his department’s efforts to increase access for Black business owners.
“One thing I’m taking away from this for sure is we’re going to have to do a better job of connecting through your chambers of all these opportunities of billions of dollars that are coming down the pike. I’m honestly disappointed that people don’t know, so we’ll do better,” said Omishakin.
Lueathel Seawood, the president of the African American Chamber of Commerce of San Joaquin County, expressed frustration with obtaining federal contracts for small businesses, and completing the process. She observed that once a small business was certified as DBE, a Disadvantaged Business Enterprises, there was little help getting to the next step.
Omishakin admitted there is more work to be done to help them complete the process and include them in upcoming projects. However, the high-speed rail system expansion by the California High-Speed Rail Authority has set a goal of 30% participation from small businesses — only 10 percent is set aside for DBE.
The importance of Diversity, Equity and Inclusion (DEI) in economics was reinforced during the “State of the California Economy” talk led by author and economist Julianne Malveaux, and Anthony Asadullah Samad, Executive Director of the Mervyn Dymally African American Political and Economic Institute (MDAAPEI) at California State University, Dominguez Hills.
Assaults on DEI disproportionately affect women of color and Black women, according to Malveaux. When asked what role the loss of DEI might serve in economics, she suggested a more sinister purpose.
“The genesis of all this is anti-blackness. So, your question about how this fits into the economy is economic exclusion, that essentially has been promoted as public policy,” said Malveaux.
The most anticipated speaker at the event was Janice Bryant Howroyd known affectionately to her peers as “JBH.” She is one of the first Black women to run and own a multi-billion-dollar company. Her company ActOne Group, is one of the largest, and most recognized, hiring, staffing and human resources firms in the world. She is the author of “Acting Up” and has a profile on Forbes.
Chairman of the board of directors of the California African American Chamber of Commerce, Timothy Alan Simon, a lawyer and the first Black Appointments Secretary in the Office of the Governor of California, moderated. They discussed the state of Black entrepreneurship in the country and Howroyd gave advice to other business owners.
“We look to inspire and educate,” said Howroyd. “Inspiration is great but when I’ve got people’s attention, I want to teach them something.”
Activism
Oakland Post: Week of April 17 – 23, 2024
The printed Weekly Edition of the Oakland Post: Week of April 17 – 23, 2024

To enlarge your view of this issue, use the slider, magnifying glass icon or full page icon in the lower right corner of the browser window. ![]()
-

 Activism4 weeks ago
Activism4 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of March 27 – April 2, 2024
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoCOMMENTARY: D.C. Crime Bill Fails to Address Root Causes of Violence and Incarceration
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoFrom Raids to Revelations: The Dark Turn in Sean ‘Diddy’ Combs’ Saga
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoCOMMENTARY: Lady Day and The Lights!
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoMayor, City Council President React to May 31 Closing of Birmingham-Southern College
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoBaltimore Key Bridge Catastrophe: A City’s Heartbreak and a Nation’s Alarm
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoBaltimore’s Key Bridge Struck by Ship, Collapses into Water
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoBeloved Actor and Activist Louis Cameron Gossett Jr. Dies at 87