World
Liberia Cautiously Marks End of Ebola with 4,700 Deaths

In this photo taken on Friday, May 8, 2015, Mercy Kennedy, left, sits with her caregiver Martu Weefor, right, after school at her home in Monrovia, Liberia. (AP Photo/ Abbas Dulleh)
Jonathan Paye-Layleh and Krista Larson, ASSOCIATED PRESS
MONROVIA, Liberia (AP) — On the day Mercy Kennedy lost her mother to Ebola, it was hard to imagine a time when Liberia would be free from one of the world’s deadliest viruses. It had swept through the 9-year-old’s neighborhood, killing people house by house.
Neighbors were so fearful that Mercy, too, might be sick that no one would touch her to comfort her as tears streamed down her face. She had only a tree to lean on as she wept.
Now seven months later, Liberia on Saturday officially marked the end of the epidemic that claimed more than 4,700 lives here, and Mercy is thriving in the care of a family friend not far from where she used to live.
“What we went through here was terrifying,” said Martu Weefor, 39, who is now raising Mercy alongside her three biological children and Mercy’s older brother. “Nobody wanted to pass on our road or have anything to do with us, everybody was afraid of the community. I thank God that Liberia is free from Ebola.”
Saturday marks 42 days since Liberia’s last Ebola case — the benchmark used to declare the outbreak over because it represents two incubation periods of 21 days for new cases to emerge. The World Health Organization on Saturday called the milestone a “monumental achievement for a country that reported the highest number of deaths in the largest, longest, and most complex outbreak since Ebola first emerged in 1976.”
The statistics of loss, though, are enormous in Liberia: 189 health workers dead. Some 3,290 children lost one or both parents to the disease, though most have been placed with other relatives or in foster care.
While praising the international community’s help in getting Liberia to zero cases, Liberian President Ellen Johnson Sirleaf on Saturday criticized the slow initial response to the epidemic in West Africa that cost many lives.
“This Ebola outbreak is a scar on the conscious of the world. For some the pain and grief will take a generation to heal,” she said. “Therefore, let today’s announcement be a call to arms that we will build a better world for those Ebola could not reach … It is the least the memories of our dearly departed deserve.”
Elsewhere in West Africa, new cases were still being reported this week in both Sierra Leone and in Guinea, where five of the new victims were only diagnosed after death. The fact they had never even sought treatment for Ebola means health officials lost critical time to track their relatives and other contacts.
“It’s important to remember the next case is only a canoe ride away across the river or across a forest path, so we still have an element of risk here and we all need to be very conscious of that,” said Sheldon Yett, UNICEF’s Representative in Liberia, who emphasized that the recovery needs also remain enormous.
At the height of the crisis back in August and September, Saturday’s milestone seemed far from reach. Liberia had between 300 and 400 new cases every week. People pushed victims in wheelbarrows down the streets of Monrovia, with only cheap plastic bags to protect their sandaled feet from possible exposure to Ebola. Scores of people too sick to stand waited outside Ebola treatment centers with the hope that enough people had died overnight so there would be beds for them and a chance at life.
The disastrous epidemic in Monrovia and the capitals of Guinea and Sierra Leone marked the first time the Ebola virus had infiltrated major urban areas where it could spread quickly through densely populated, impoverished neighborhoods. The outbreak caused its first deaths in December 2013 but only made headlines in March 2014 in Guinea before soon spreading to Liberia and Sierra Leone.
Worldwide panic heightened in late September when a man from Liberia tested positive for Ebola in the United States while visiting relatives in Texas. The disease also broke out in Senegal, Mali and Nigeria where officials managed to quickly isolate and quash their Ebola cases but the virus became deeply entrenched particularly in Liberia’s capital. Ultimately, social mobilization helped turn the tide.
“Communities here did the right thing: They isolated people who were sick, they reported people who were sick. Every street corner had stations for washing hands, and this made a difference,” Yett said.
Many of the treatment centers built with help from the United States finished construction after the height of the epidemic — some of the tarp and wood constructed facilities will be repurposed but many will be taken down. Communities scarred by the looming threat of death can’t imagine visiting them even months later, even if the clinics never treated a single Ebola case, experts say.
“Even today (when) we hear an ambulance siren, we have to shake a little bit, seeing if this normal or are we facing something again,” Liberia’s president said recently at an event marking the end of an American-built Ebola treatment center for exposed health workers.
There are also concerns about the long-term effects on survivors, including questions about how long the virus remains present in the body. On Friday, WHO updated advice and testing guidelines for male survivors of Ebola because of the “strong possibility” that the virus could be spread through sex months later.
And medical study this week found Ebola inside the eye of a patient months after the virus was gone from his blood. Tears and tissue around the outside of the eye, though, did not. That suggests it poses little public health risk, experts said.
It’s been nearly a year since Korlia Bonarwolo helped care for a co-worker at Redemption Hospital who later died from Ebola. The physician’s assistant had no protective suit and no special gloves.
The 26-year-old ultimately got treatment in the country’s first Ebola treatment center and now leads a network of more than 800 survivors across Liberia. He too was marking Saturday cautiously.
“We should instead be happy in our hearts,” said Bonarwolo, “and pray for the other countries to be freed.”
___
Larson reported from Dakar, Senegal.
Copyright 2015 The Associated Press. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.
###
Barbara Lee
Congresswoman Barbara Lee Issues Statement on Deaths of Humanitarian Aid Volunteers in Gaza
On April 2, a day after an Israeli airstrike erroneously killed seven employees of World Central Kitchen (WCK), a humanitarian organization delivering aid in the Gaza Strip, a statement was release by Rep. Barbara Lee (D-CA-12). “This is a devastating and avoidable tragedy. My prayers go to the families and loved ones of the selfless members of the World Central Kitchen team whose lives were lost,” said Lee.

By California Black Media
On April 2, a day after an Israeli airstrike erroneously killed seven employees of World Central Kitchen (WCK), a humanitarian organization delivering aid in the Gaza Strip, a statement was release by Rep. Barbara Lee (D-CA-12).
“This is a devastating and avoidable tragedy. My prayers go to the families and loved ones of the selfless members of the World Central Kitchen team whose lives were lost,” said Lee.
The same day, it was confirmed by the organization that the humanitarian aid volunteers were killed in a strike carried out by Israel Defense Forces (IDF). Prior to the incident, members of the team had been travelling in two armored vehicles marked with the WCF logo and they had been coordinating their movements with the IDF. The group had successfully delivered 10 tons of humanitarian food in a deconflicted zone when its convoy was struck.
“This is not only an attack against WCK. This is an attack on humanitarian organizations showing up in the direst situations where food is being used as a weapon of war. This is unforgivable,” said Erin Gore, chief executive officer of World Central Kitchen.
The seven victims included a U.S. citizen as well as others from Australia, Poland, the United Kingdom, Canada, and Palestine.
Lee has been a vocal advocate for a ceasefire in Gaza and has supported actions by President Joe Biden to airdrop humanitarian aid in the area.
“Far too many civilians have lost their lives as a result of Benjamin Netanyahu’s reprehensible military offensive. The U.S. must join with our allies and demand an immediate, permanent ceasefire – it’s long overdue,” Lee said.
Bay Area
Nigerian Bank Chief Killed in Helicopter Crash on Way to Superbowl XVIII
According to the San Bernardino County Sheriff’s Dept., the crash occurred near Nipton, on the edge of the Mojave Desert Preserve. The poor weather conditions — rain, wind and snow showers—may have contributed to the accident, although the investigation is not complete. All six aboard were killed. Herbert Wigwe, 57, founded Access Bank in 1989, and it became the country’s largest competitor, Diamond Bank in 2018.

By Post Staff
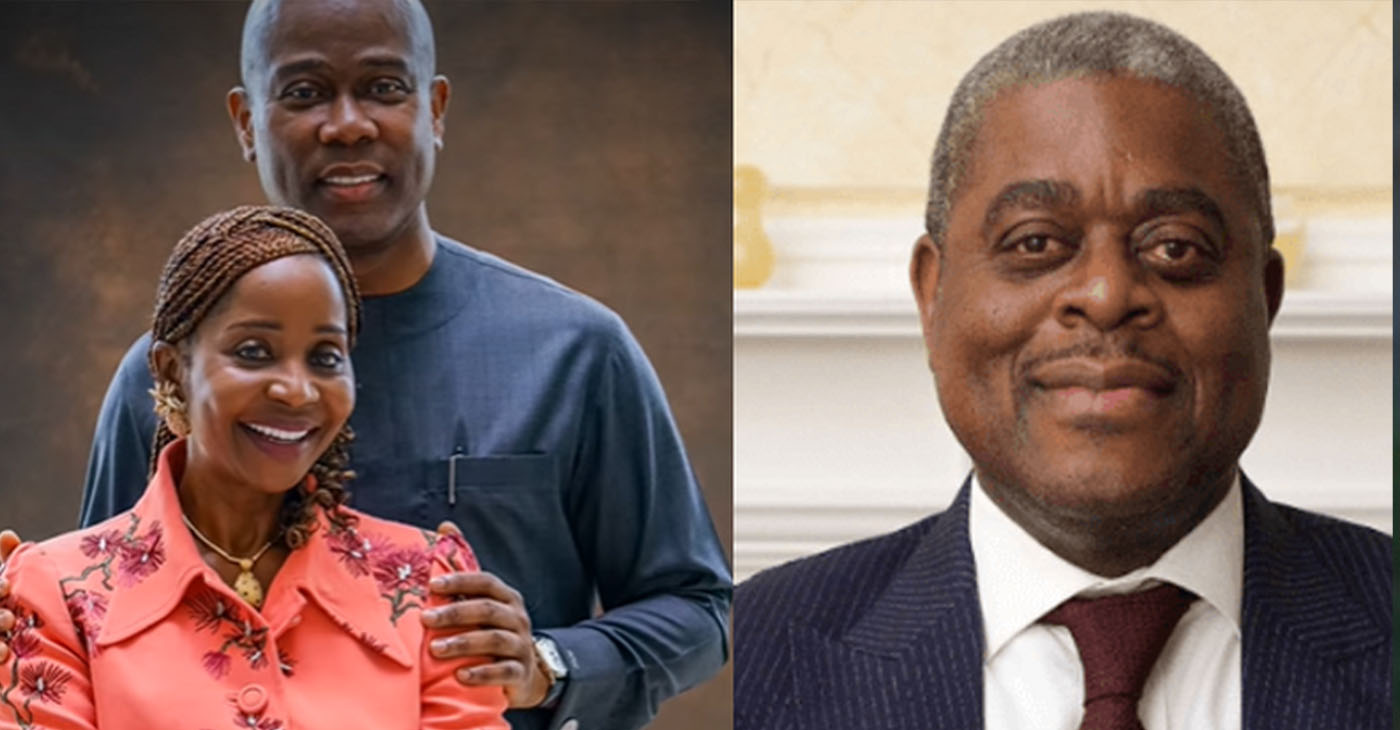
The co-founder of one of Nigeria’s largest banks died with his wife, son and three others when the helicopter transporting them from Palm Springs, Ca., to Boulder City, Nev. to attend the fifty-eighth SuperBowl at the stadium outside Las Vegas crashed on Feb. 9.
According to the San Bernardino County Sheriff’s Dept., the crash occurred near Nipton, on the edge of the Mojave Desert Preserve. The poor weather conditions — rain, wind and snow showers—may have contributed to the accident, although the investigation is not complete. All six aboard were killed
Herbert Wigwe, 57, founded Access Bank in 1989, and it became the country’s largest competitor, Diamond Bank in 2018.
More recently, Wigwe was planning to open a banking service in Asia this year after making successful expansions to other parts of Africa, including South Africa, Kenya, and Botswana.
Nigerian President Bola Tinubu described Wigwe’s death as an ‘overwhelming tragedy.”
Oakland resident and Nigerian immigrant Kayode Gbadebo agrees with Tinubu. He met Wigwe in Nigeria but crossed paths with him in London in 2006. Wigwe, he said, “took risks.”
He was young and people thought he couldn’t do what he intended, which was not so much about money but community.
“He was more like Jesus in washing the feet of the poor– Wigwe was culturizing community,” Gbadebo said.
“There will never be another like him. This is a deep, deep loss” and he hopes everyone will eventually “be comforted.”
He was also disappointed that a replacement has already been named even before Wigwe is buried. “It is not reasonable. You don’t want a vacuum, but it’s” not fair to the family, Gbadebo observed.
Wigwe had also been working to solve the migration issues from African countries, believing that “investing in higher education was key to controlling mass migration, which “is destabilising countries across the world,” BBC News reported.
“We need to take a holistic approach to address global migration, starting with our traditional framework for international development,” Wigwe wrote.
To that end, according to BBC News, Wigwe was preparing to open Wigwe University in Niger, where he was from.
“The best place to limit migration is not in the middle of the Mediterranean or the English Channel or the Rio Grande. It is in the home countries that so many migrants are so desperate to leave,” he wrote, saying his university was an opportunity for him “to give back to society.”
Besides Wigwe and his wife, Chizoba Nwuba Wigwe, and one son, two crew members and Bimbo Ogunbanjo, former group chairman of the Nigerian Exchange Group Plc, were also killed in the crash.
According to Wikipedia, three other children survive Wigwe.
In his statement reported in People magazine, Tinubu described Wigwe as “a distinguished banker, humanitarian, and entrepreneur.”
“I pray for the peaceful repose of the departed and ask God Almighty to comfort the multitude of Nigerians who are grieving and the families of the deceased at this deeply agonizing moment,” the president said.
He added, “Their passing is an overwhelming tragedy that is shocking beyond comprehension.”
Besides feeling the tremendous loss, Gbadebo fears the disorder and greed that will follow. “It’s a mess,” he said.
People magazine, BBC News and Wikipedia were the sources for this report.
Activism
No Valid Reason for Failing to Condemn Hamas’ Act of Terrorism
On Oct. 7, 2023, Hamas terrorists crossed the Israel-Gaza border and indiscriminately slaughtered Israeli civilians in their homes. They killed nearly 300 young people at a music festival and took at least 200 hostages including 30 children. The atrocities they committed included massacres of families, abduction of the elderly and children, burning of babies and rapes of women.

By Joe W. Bowers Jr.
California Black Media
OPINION
On Oct. 7, 2023, Hamas terrorists crossed the Israel-Gaza border and indiscriminately slaughtered Israeli civilians in their homes.
They killed nearly 300 young people at a music festival and took at least 200 hostages including 30 children. The atrocities they committed included massacres of families, abduction of the elderly and children, burning of babies and rapes of women.
The horrific surprise attack deserves universal and unequivocal condemnation. President Joe Biden called what Hamas did “an act of sheer evil” and pledged to defend the lives of Israelis and Jewish Americans.
He said, “Let there be no doubt. The United States has Israel’s back. We’ll make sure the Jewish and democratic state of Israel can defend itself today, tomorrow, as we always have.”
Hamas killed approximately 1,400 people including 32 Americans. Citizens from 40 different countries including the United Kingdom, France, Mexico, and Thailand were killed or reported missing.
Hamas fighters breached Israel’s border defenses on the final day of Sukkot while soldiers were away due to the holiday and launched attacks on 22 towns outside the Gaza Strip. This security lapse has been described as a catastrophic failure of Israel’s intelligence agencies..
Hamas is an extremist Islamist militant organization that has governed the Gaza Strip since 2007. It is recognized as an Iranian-backed terrorist group by the U.S. and the European Union and has a long history of violence against Jews and Palestinians, the latter of whom they often use as human shields.
While there have been plenty of groups who have unequivocally condemned the massacres, there are a number who haven’t, including organizations such as the Democratic Socialists of America (DSA), Black Alliance for Peace, Red Nation, and independent Black Lives Matter (BLM) chapters (excluding the national Black Lives Matter Global Network Foundation).
The DSA San Francisco chapter put out a statement on Oct. 9 that said, “Socialists support the Palestinian people’s, and all people’s, right to resist and fight for their own liberation. This weekend’s events are no different.”
Student organizations at a number of universities and colleges in California signed a solidarity statement titled “Resistance Uprising in Gaza” from Students for Justice in Palestine (SJP). The statement attributes the violence of the Hamas attack to what it refers to as Israeli apartheid and occupation.
The SJP statement written by Bears for Palestine at UC Berkeley says, “We support the resistance, we support the liberation movement, and we indisputably support the Uprising.” Essentially, these students are indirectly associating themselves with Hamas’ barbaric acts under the guise of “resistance.”
Signing the statement were 51 student organizations including those from Stanford, UC Berkeley, UCLA, UC Davis, UC San Diego, CSU Sacramento, and USC.
A statement signed by 34 Harvard student organizations said, “We, the undersigned student organizations, hold the Israeli regime entirely responsible for all unfolding violence.”
Many university leaders, where these students are enrolled, have been guilty of failing to unequivocally condemn Hamas and for inadequately addressing their students’ expressed support for Hamas.
Several Stanford faculty members, including three Nobel laureates, condemned Stanford’s administrators’ weak response to acts of terrorism and the expression of pro-Hamas sentiments by students on campus.
Israel unilaterally withdrew from Gaza in 2005. It dismantled 21 Israeli settlements in the territory and handed them over to the Palestinian Authority.
The assault by Hamas on Oct. 7 was not an ordinary clash with Israel. Hamas’ actions resulted in the deadliest single day for Jews since the Holocaust.
While there are valid reasons for protesting Israel’s treatment of Palestinians and a real reckoning with the Israeli government on its policies is long overdue, nothing justifies Hamas’ attack.
Israelis who were killed largely had nothing to do with the conditions of Palestinians in Gaza. Some of the victims weren’t even Israeli — they were just tourists.
The students blaming Israel for the atrocities committed by Hamas have faced criticism. Some groups have withdrawn their endorsements because of the backlash aimed at them. Others have doubled down on their activism. SJP held a “National Day of Resistance” on several campuses.
Several CEOs have asked Harvard to disclose a list of members from the organizations assigning responsibility to Israel to insure they do not hire any of their members. A Berkeley law professor has also urged firms not to hire his students who have publicly blamed Israel for the war.
This California Black Media report was supported in whole or in part by funding provided by the State of California, administered by the California State Library.
-

 Activism4 weeks ago
Activism4 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of March 27 – April 2, 2024
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoCOMMENTARY: D.C. Crime Bill Fails to Address Root Causes of Violence and Incarceration
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoMayor, City Council President React to May 31 Closing of Birmingham-Southern College
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoBeloved Actor and Activist Louis Cameron Gossett Jr. Dies at 87
-

 Community1 week ago
Community1 week agoFinancial Assistance Bill for Descendants of Enslaved Persons to Help Them Purchase, Own, or Maintain a Home
-

 Activism3 weeks ago
Activism3 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of April 3 – 6, 2024
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoV.P. Kamala Harris: Americans With Criminal Records Will Soon Be Eligible for SBA Loans
-

 Community1 week ago
Community1 week agoAG Bonta Says Oakland School Leaders Should Comply with State Laws to Avoid ‘Disparate Harm’ When Closing or Merging Schools