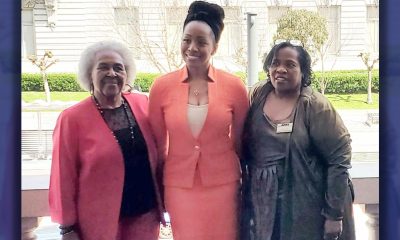#NNPA BlackPress
Historically Black Colleges give graduates a wage boost
LOUISIANA WEEKLY — Increased wages were strongest for the elite HBCUs: Hampton, Howard, Morehouse, Spelman and Xavier. But the effect persisted 10 years after graduation for graduates of all 59 HBCUs – more than half of the 100 or so HBCUs in the nation – that were included in the sample. Other HBCUs were not included because of lack of data.
By Gregory N. Price
(Special from theconversation.com) — In 2010, two economists claimed that graduates of Historically Black Colleges and Universities, or HBCUs, suffer a “wage penalty” – that is, they earn relatively less than they would had they gone to a non-HBCU.
In an early draft of the paper, the economists – one from Harvard and the other from MIT – argued that while HBCUs may have served a useful purpose back in the 1970s, they were now, by some measures, serving to “retard black progress.” The reason why, they suggested, is that traditionally white institutions may have gotten better at educating Black students and that there might be value in “cross-racial connections” when it came time to get a job.
The paper, which relied on data from the 1950s through the early 2000s, generated negative headlines for HBCUs. For instance, The Wall Street Journal called HBCUs “academically inferior.” The New York Times warned readers about the “declining payoff from black colleges.”
As a scholar who has researched HBCUs, my colleagues and I have found contrary evidence: Students who went to HBCUs do not suffer a relative wage penalty. In fact, we found that they typically and on average earn more than similar students who went to non-HBCUs. Our findings are based on comparing HBCUs to other schools with a sizable Black student population.
Producers of black doctors, engineers
Largely established to serve Black people after the Civil War and in the Jim Crow era of racial segregation, HBCUs were the only higher education option for many Black Americans up through the mid-1960s during the push for integration. Since then, HBCUs have served a declining share of Black students. For instance, HBCUs served 17.3 percent of Black college students in 1980, but by 2015 the figure had fallen to 8.5 percent.
HBCUs have been in a constant struggle for their financial survival because of declining enrollment, among other things. In fact, some college finance experts predict that many HBCUs will disappear in the next 20 years.
HBCUs currently serve about 298,000 students and rank among the highest producers of black doctors. HBCUs also play an outsized role in the production of Black graduates in science, technology, engineering and mathematics, or STEM.
A wage premium
Our study included 1,364 nonprofit colleges and universities, both public and private, that award at least a baccalaureate degree.
Increased wages were strongest for the elite HBCUs: Hampton, Howard, Morehouse, Spelman and Xavier. But the effect persisted 10 years after graduation for graduates of all 59 HBCUs – more than half of the 100 or so HBCUs in the nation – that were included in the sample. Other HBCUs were not included because of lack of data.
And it wasn’t a small amount of money, either. In our study, we found that HBCU students from the elite universities earn 32 percent more six years after attendance than students with similar characteristics who attended other colleges and universities.
But before anyone celebrates our findings as a clear victory for HBCUs, a few caveats are in order.
Penalties exist
First, all HBCU graduates don’t earn more than all non-HBCU graduates all the time. In fact, much like Freyer and Greenstone did a decade ago, we found that early in their careers – extending to six years after graduation – typical HBCU graduates do in fact suffer a wage penalty.
The HBCU study in 2010 found grads earned 20 percent less than peers from other colleges in the 1990s, although it’s not known how long after graduation this occurred.
We found that there’s an 11 percent wage penalty after six years but then it disappears after 10 years, and in fact turns into an advantage. So while typical HBCU graduates may be earning less money than non-HBCU graduates in their late 20s, by their early 30s, they are earning more.
We also found that the wage advantage for HBCUs remained no matter what the major. In my view as an economist, the relative gains for HBCU attendees after six years suggest, that on average, HBCU graduates are better able to find jobs that match their skill and capabilities.
Demographic factors
Just what is it that makes HBCUs more effective as escalators for labor market earnings and income mobility? Earlier research my colleagues and I conducted at Howard University found that a high proportion of Black students in a college or university serves as a boost to Black identity and self-esteem. That boost, we found, translates into labor market skill acquisition that results in an earnings advantage.
Given the history of HBCUs receiving unequal resources, our results suggest that government and philanthropy could consider more funding for HBCUs. That could enable them to be even more successful at what they do, particularly when it comes to enabling students from households that earn the least money to move up economically.
Gregory Pine is Professor, Economics, University of New Orleans.
This article originally published in the September 16, 2019 print edition of The Louisiana Weekly newspaper.
This article originally appeared in The Louisiana Weekly.
#NNPA BlackPress
IN MEMORIAM: Ramona Edelin, Influential Activist and Education Advocate, Dies at 78
NNPA NEWSWIRE — Born on September 4, 1945, in Los Angeles, California, activist Ramona Edelin’s early years were marked by a commitment to education and social justice. According to her HistoryMakers biography, after graduating from Fisk University with a Bachelor’s degree in 1967, she pursued further studies at the University of East Anglia in England. She earned her master’s degree before completing her Ph.D. at Boston University in 1981.
The post IN MEMORIAM: Ramona Edelin, Influential Activist and Education Advocate, Dies at 78 first appeared on BlackPressUSA.

By Stacy M. Brown, NNPA Newswire Senior National Correspondent
@StacyBrownMedia
Once upon a time, Black Americans were simply known as colored people, or Negroes. That is until Ramona Edelin came along. The activist, renowned for her pivotal roles in advancing civil rights, education reform, and community empowerment, died at her D.C. residence last month at the age of 78. Her death, finally confirmed this week by Barnaby Towns, a communications strategist who collaborated with Dr. Edelin, was attributed to cancer.
Born on September 4, 1945, in Los Angeles, California, Edelin’s early years were marked by a commitment to education and social justice. According to her HistoryMakers biography, after graduating from Fisk University with a Bachelor’s degree in 1967, she pursued further studies at the University of East Anglia in England. She earned her master’s degree before completing her Ph.D. at Boston University in 1981.
Edelin’s contributions to academia and activism were manifold. She was pivotal in popularizing the term “African American” alongside Rev. Jesse L. Jackson in the late 1980s.
Jackson had announced the preference for “African American,” speaking for summit organizers that included Dr. Edelin. “Just as we were called Colored, but were not that, and then Negro, but not that, to be called Black is just as baseless,” he said, adding that “African American” “has cultural integrity” and “puts us in our proper historical context.”
Later, Edelin told Ebony magazine, “Calling ourselves African Americans is the first step in the cultural offensive,” while linking the name change to a “cultural renaissance” in which Black Americans reconnected with their history and heritage.
“Who are we if we don’t acknowledge our motherland?” she asked later. “When a child in a ghetto calls himself African American, immediately he’s international. You’ve taken him from the ghetto and put him on the globe.”
The HistoryMakers bio noted that Edelin’s academic pursuits led her to found and chair the Department of African American Studies at Northeastern University, where she established herself as a leading voice.
Transitioning from academia to advocacy, Edelin joined the National Urban Coalition in 1977, eventually ascending to president and CEO. During her tenure, she spearheaded initiatives such as the “Say Yes to a Youngster’s Future” program, which provided crucial support in math, science, and technology to youth and teachers of color in urban areas. Her biography noted that Edelin’s efforts extended nationwide through partnerships with organizations like the National Science Foundation and the United States Department of Education.
President Bill Clinton recognized Edelin’s expertise by appointing her to the Presidential Board on Historically Black Colleges and Universities in 1998. She also co-founded and served as treasurer of the Black Leadership Forum, solidifying her standing as a respected leader in African American communities.
Beyond her professional achievements, Edelin dedicated herself to numerous boards and committees, including chairing the District of Columbia Educational Goals 2000 Panel and contributing to the Federal Advisory Committee for the Black Community Crusade for Children.
Throughout her life, Edelin received widespread recognition for her contributions. Ebony magazine honored her as one of the 100 Most Influential Black Americans, and she received prestigious awards such as the Southern Christian Leadership Award for Progressive Leadership and the IBM Community Executive Program Award.
The post IN MEMORIAM: Ramona Edelin, Influential Activist and Education Advocate, Dies at 78 first appeared on BlackPressUSA.
#NNPA BlackPress
Tennessee State University Board Disbanded by MAGA Loyalists as Assault on DE&I Continues
NNPA NEWSWIRE — Recent legislative actions in Tennessee, such as repealing police reform measures enacted after the killing of Tyre Nichols, underscore a troubling trend of undermining local control and perpetuating racist agendas. The new law preventing local governments from restricting police officers’ authority disregards community efforts to address systemic issues of police violence and racial profiling.
The post Tennessee State University Board Disbanded by MAGA Loyalists as Assault on DE&I Continues first appeared on BlackPressUSA.

By Stacy M. Brown, NNPA Newswire Senior National Correspondent
@StacyBrownMedia
Tennessee State University (TSU), the state’s only public historically Black college and university (HBCU), faces a tumultuous future as Gov. Bill Lee dissolved its board, a move supported by racist conservatives and MAGA Republicans in the Tennessee General Assembly, who follow the lead of the twice-impeached, four-times indicted, alleged sexual predator former President Donald Trump. Educators and others have denounced the move as an attack on diversity, equity, and inclusion (DE&I) and a grave setback for higher education.
Critics argue that TSU’s purported financial mismanagement is a manufactured crisis rooted in decades of underinvestment by the state government. They’ve noted that it continues a trend by conservatives and the racist MAGA movement to eliminate opportunities for Blacks in education, corporate America, and the public sector.
Gevin Reynolds, a former speechwriter for Vice President Kamala Harris, emphasizes in an op-ed that TSU’s financial difficulties are not the result of university leadership because a recent audit found no evidence of fraud or malfeasance.
Reynolds noted that the disbanding of TSU’s board is not an isolated incident but part of a broader assault on DE&I initiatives nationwide. Ten states, including Tennessee, have enacted laws banning DE&I policies on college campuses, while governors appointing MAGA loyalists to university trustee positions further undermine efforts to promote inclusivity and equality.
Moreover, recent legislative actions in Tennessee, such as repealing police reform measures enacted after the killing of Tyre Nichols, underscore a troubling trend of undermining local control and perpetuating racist agendas. The new law preventing local governments from restricting police officers’ authority disregards community efforts to address systemic issues of police violence and racial profiling.
The actions echo historical efforts to suppress Black progress, reminiscent of the violent backlash against gains made during the Reconstruction era. President Joe Biden warned during an appearance in New York last month that Trump desires to bring the nation back to the 18th and 19th centuries – in other words, to see, among other things, African Americans back in the chains of slavery, women subservient to men without any say over their bodies, and all voting rights restricted to white men.
The parallels are stark, with white supremacist ideologies used to justify attacks on Black institutions and disenfranchise marginalized communities, Reynolds argued.
In response to these challenges, advocates stress the urgency of collective action to defend democracy and combat systemic racism. Understanding that attacks on institutions like TSU are symptomatic of broader threats to democratic norms, they call for increased civic engagement and voting at all levels of government.
The actions of people dedicated to upholding the principles of inclusivity, equity, and justice for all will determine the outcome of the ongoing fight for democracy, Reynolds noted. “We are in a war for our democracy, one whose outcome will be determined by every line on every ballot at every precinct,” he stated.
The post Tennessee State University Board Disbanded by MAGA Loyalists as Assault on DE&I Continues first appeared on BlackPressUSA.
#NNPA BlackPress
Braxton Haulcy and the Expansion of Walker|West Music Academy
May 24, 2023 – Walker West Music Academy gets an early start on expansion. Join us for a Wednesday episode of The …
The post Braxton Haulcy and the Expansion of Walker|West Music Academy first appeared on BlackPressUSA.

May 24, 2023 – Walker West Music Academy gets an early start on expansion. Join us for a Wednesday episode of The …
The post Braxton Haulcy and the Expansion of Walker|West Music Academy first appeared on BlackPressUSA.
-

 Activism4 weeks ago
Activism4 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of March 27 – April 2, 2024
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoCOMMENTARY: D.C. Crime Bill Fails to Address Root Causes of Violence and Incarceration
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoMayor, City Council President React to May 31 Closing of Birmingham-Southern College
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoBeloved Actor and Activist Louis Cameron Gossett Jr. Dies at 87
-

 Community1 week ago
Community1 week agoFinancial Assistance Bill for Descendants of Enslaved Persons to Help Them Purchase, Own, or Maintain a Home
-

 Activism3 weeks ago
Activism3 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of April 3 – 6, 2024
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoV.P. Kamala Harris: Americans With Criminal Records Will Soon Be Eligible for SBA Loans
-

 Activism2 weeks ago
Activism2 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of April 10 – 16, 2024