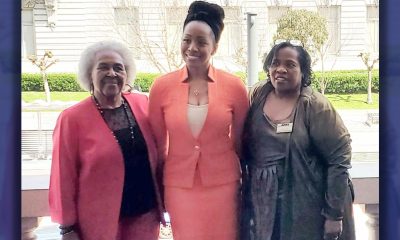Activism
Free School Meals for All Here to Stay in California
With 1 in every 6 children facing hunger in the U.S., California is the first state to promise that every public school student — all 6 million of them – will get free school meals.

With 1 in every 6 children facing hunger in the U.S., California is the first state to promise that every public school student — all 6 million of them – will get free school meals.
The universal school meals program, which will launch in the 2022-2023 school year, is part of the landmark state budget agreement reached between Gov. Gavin Newsom and the Legislature last month. Days later, Maine became the second state to commit to offering a universal school meals program with the signing of its budget.
The program ensures that all students will be offered breakfast and lunch at their school, which state Sen. Nancy Skinner, D-Berkeley, said is “essential to learning.” Skinner has led the effort to establish a universal school meal program.
“We know that many California children are food insecure, and if you’re hungry you cannot learn well,” Skinner said. “The whole point of school is learning, and everything we can do to create an environment that allows children to thrive and learn is what we need to do.”
Skinner introduced a bill in March that would have established a universal school meal program. After the program garnered bipartisan support and the California Department of Finance forecast unexpectedly large projected revenues, lawmakers opted to include it in the state budget rather than as a separate bill.
The final agreement between Newsom and the Legislature calls for $650 million through the Proposition 98 fund each year to reimburse school districts starting in 2022, as well as $54 million in the 2021-22 fiscal year to supplement state meal reimbursements. Proposition 98 is the formula that determines what portion of the general fund goes to community colleges and K-12 schools.
The state program is set to begin in the 2022-23 school year because the U.S. Department of Agriculture has already committed to paying for school meals for all students through the 2021-22 school year.
The USDA has reimbursed districts for providing free meals to all students since the start of the pandemic. Before the pandemic, districts were only reimbursed for feeding students who were enrolled in the National School Lunch Program. Advocates said being able to feed students without having to check whether they qualified for free lunches allowed districts to serve more families at a time when many faced hunger and hardship.
Waiving the eligibility requirements allowed the Oakland Unified School District, for example, to distribute as many as 18,000 grab-and-go meals a day during the pandemic, said spokesman John Sasaki.
“That just goes to show the need that was there,” Sasaki said.
Previously, as part of the National School Lunch Program application process, families had to disclose their household income, how many people lived in the household, their children’s immigration status or if their children were homeless or runaways. Some families feared giving out that information, and students may have felt embarrassed to receive a free meal while others paid for it.
Schools in New York City began serving free meals to all students in 2017 after finding that some students would rather go hungry than admit they didn’t have enough money to pay for lunch. The decision followed a national outcry over “lunch shaming” — publicly shaming students for unpaid school meal bills, or even school staff throwing away their lunches rather than allowing them to eat.
Advocates believed that though 3.9 million students – 63% of California’s student body — participated in the program, the need was actually much higher.
“It’s such good news that everybody gets food with no strings attached, but to be able to do it in a way that nobody is called out is the best thing about this,” Sasaki said. “We want to make sure kids are never given a hard time for being who they are or being in the situation they are in.”
Districts will still be asking families to fill out household income eligibility forms, however. That’s because the number of families in the district that make so little that they qualify for the federal free and reduced-price lunch program remains a key factor in the state’s Local Control Funding Formula. The formula gives additional state funds to districts based on the number of low-income students, English learners, foster children and homeless youth they serve.
Tony Wold, the West Contra Costa Unified associate superintendent of business services, said the district was concerned that fewer families would fill out the household income eligibility forms because they didn’t have to in order to receive free meals. That could have potentially led to a reduction in supplemental funds for the cash-strapped district. To help solve the problem, the district had outreach workers call families directly, explaining why it was important for families to submit the information.
The outreach workers’ “big lift” resulted in more families filling out the forms than the previous year, Wold said, which kept the district’s unduplicated pupils percentage constant. That statistic measures the share of a district’s students who are low-income, homeless, foster youth or English learners — all of which drive the Local Control Funding Formula.
Outreach workers at Oakland Unified emphasize to families who are skeptical about the forms that they determine how much money goes to the classroom, Sasaki said.
California School Boards Association spokesman Troy Flint said the organization anticipates it will be harder for districts to collect income eligibility forms with the new universal meals program. The association hopes the state will provide some support to schools’ “diligent and creative efforts” to collect the forms, though the group isn’t calling for any specific change.
“This administration has prioritized steering additional money toward high-need students, particularly into concentration grants, so there’s reason to believe they might be willing to work toward a modification here,” Flint said.
Activism
Oakland Post: Week of April 17 – 23, 2024
The printed Weekly Edition of the Oakland Post: Week of April 17 – 23, 2024

To enlarge your view of this issue, use the slider, magnifying glass icon or full page icon in the lower right corner of the browser window. ![]()
Activism
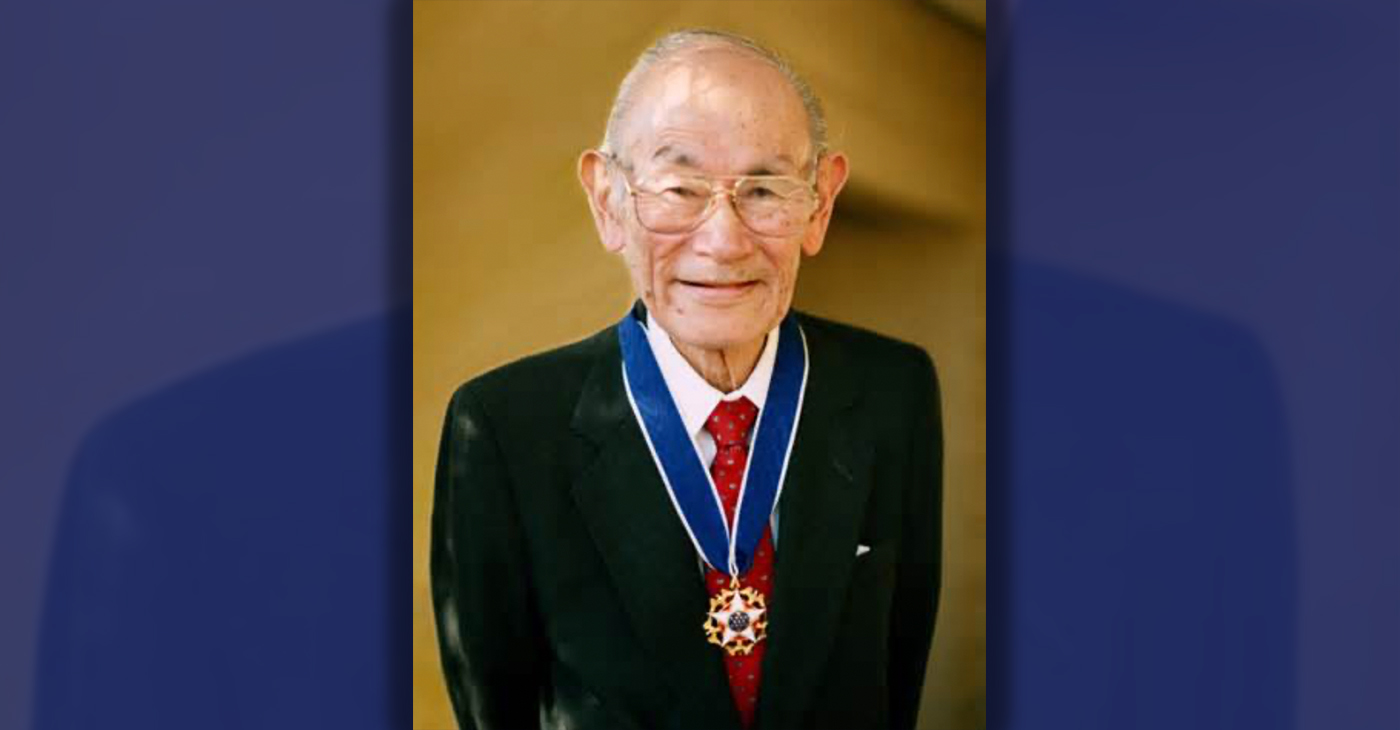
Oakland Schools Honor Fred Korematsu Day of Civil Liberties
Every Jan. 30, OUSD commemorates the legacy of Fred Korematsu, an Oakland native, a Castlemont High School graduate, and a national symbol of resistance, resilience, and justice. His defiant stand against racial injustice and his unwavering commitment to civil rights continue to inspire the local community and the nation. Tuesday was “Fred Korematsu Day of Civil Liberties and the Constitution” in the state of California and a growing number of states across the country.

By Post Staff
Every Jan. 30, OUSD commemorates the legacy of Fred Korematsu, an Oakland native, a Castlemont High School graduate, and a national symbol of resistance, resilience, and justice.
His defiant stand against racial injustice and his unwavering commitment to civil rights continue to inspire the local community and the nation. Tuesday was “Fred Korematsu Day of Civil Liberties and the Constitution” in the state of California and a growing number of states across the country.
One OUSD school is named in his honor: Fred T. Korematsu Discovery Academy (KDA) elementary in East Oakland.
Several years ago, founding KDA Principal Charles Wilson, in a video interview with anti-hate organization “Not In Our Town,” said, “We chose the name Fred Korematsu because we really felt like the attributes that he showed in his work are things that the children need to learn … that common people can stand up and make differences in a large number of people’s lives.”
Fred Korematsu was born in Oakland on Jan. 30, 1919. His parents ran a floral nursery business, and his upbringing in Oakland shaped his worldview. His belief in the importance of standing up for your rights and the rights of others, regardless of race or background, was the foundation for his activism against racial prejudice and for the rights of Japanese Americans during World War II.
At the start of the war, Korematsu was turned away from enlisting in the National Guard and the Coast Guard because of his race. He trained as a welder, working at the docks in Oakland, but was fired after the bombing of Pearl Harbor in 1941. Fear and prejudice led to federal Executive Order 9066, which forced more than 120,000 Japanese Americans out of their homes and neighborhoods and into remote internment camps.
The 23-year-old Korematsu resisted the order. He underwent cosmetic surgery and assumed a false identity, choosing freedom over unjust imprisonment. His later arrest and conviction sparked a legal battle that would challenge the foundation of civil liberties in America.
Korematsu’s fight culminated in the Supreme Court’s initial ruling against him in 1944. He spent years in a Utah internment camp with his family, followed by time living in Salt Lake City where he was dogged by racism.
In 1976, President Gerald Ford overturned Executive Order 9066. Seven years later, the 9th Circuit Court of Appeals in San Francisco vacated Korematsu’s conviction. He said in court, “I would like to see the government admit that they were wrong and do something about it so this will never happen again to any American citizen of any race, creed, or color.”
Korematsu’s dedication and determination established him as a national icon of civil rights and social justice. He advocated for justice with Rosa Parks. In 1998, President Bill Clinton gave him the Presidential Medal of Freedom saying, “In the long history of our country’s constant search for justice, some names of ordinary citizens stand for millions of souls … To that distinguished list, today we add the name of Fred Korematsu.”
After Sept. 11, 2001, Korematsu spoke out against hatred and discrimination, saying what happened to Japanese Americans should not happen to people of Middle Eastern descent.
Korematsu’s roots in Oakland and his education in OUSD are a source of great pride for the city, according to the school district. His most famous quote, which is on the Korematsu elementary school mural, is as relevant now as ever, “If you have the feeling that something is wrong, don’t be afraid to speak up.”
Activism
WOMEN IMPACTING THE CHURCH AND COMMUNITY
Juanita Matthews, better known as “Sister Teacher,” is a walking Bible scholar. She moved to California from the great state of Arkansas in 1971. Sister Teacher has a passion for teaching. She has been a member of Bible Fellowship Missionary Baptist Church since 1971.

Sister Juanita Matthews
55 Years with Oakland Public School District
The Teacher, Mother, Community Outreach Champion, And Child of God
Juanita Matthews, better known as “Sister Teacher,” is a walking Bible scholar. She moved to California from the great state of Arkansas in 1971. Sister Teacher has a passion for teaching. She has been a member of Bible Fellowship Missionary Baptist Church since 1971. She followed her passion for teaching, and in 1977 became the lead teacher for Adult Class #6. Her motto still today is “Once My Student, Always My Student”.
Beyond her remarkable love for the Lord, Sister Teacher has showcased her love for teaching by working for the Oakland Unified School District for 55 years, all but four of those years spent at Emerson Elementary and Child Development School. She truly cares about her students, making sure they have the tools/supplies needed to learn either at OUSD or Bible Fellowship Missionary Baptist Church.
She’s also had a “Clothes Closet Ministry” for 51 years, making sure her students have sufficient clothing for school. The Clothes Closet Ministry extends past her students, she has been clothing the community for over 50 years as well. She loves the Lord and is a servant on a mission. She is a loving mother to two beautiful children, Sandra and Andre. This is the impact this woman of God has on her church and the community.
-

 Activism4 weeks ago
Activism4 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of March 27 – April 2, 2024
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoCOMMENTARY: D.C. Crime Bill Fails to Address Root Causes of Violence and Incarceration
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoMayor, City Council President React to May 31 Closing of Birmingham-Southern College
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoBeloved Actor and Activist Louis Cameron Gossett Jr. Dies at 87
-

 Community1 week ago
Community1 week agoFinancial Assistance Bill for Descendants of Enslaved Persons to Help Them Purchase, Own, or Maintain a Home
-

 Activism3 weeks ago
Activism3 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of April 3 – 6, 2024
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoV.P. Kamala Harris: Americans With Criminal Records Will Soon Be Eligible for SBA Loans
-

 Activism2 weeks ago
Activism2 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of April 10 – 16, 2024