Black History
COMMENTARY: Is Religious Freedom Free?
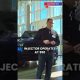
In 2019, a federal appeals court ruled that the school board in Washington State was correct when it fired Coach Joe Kennedy for praying publicly. A judge of the Ninth Circuit said, “A coach’s duty to serve as a good role model requires the coach to refrain from any manifestation of religious faith — even when the coach is plainly not on duty.” Where does freedom start and stop? Kennedy’s case has sparked controversy, landing in the Supreme Court this past week debating just how far can a person express religious freedom in public spaces.

By Rev. Dr. Martha C. Taylor, The Oakland Post
The late Fannie Lou Hamer said, “If I am truly free, who can tell me how much of my freedom I can have today?” That is the question that The United States Supreme Court wrestled with last week in the case of Joe Kennedy, who was fired by the school board in Washington State for praying at the 50-yard line after the high school football game ended.
Kennedy defended his position saying the school board violated his rights to free speech and the freedom to exercise his religion. Kennedy, a Christian, said he felt compelled to give thanks through a silent prayer at the conclusion of each game.
In 2019, a federal appeals court ruled that the school board in Washington State was correct when it fired Coach Joe Kennedy for praying publicly. A judge of the Ninth Circuit said, “A coach’s duty to serve as a good role model requires the coach to refrain from any manifestation of religious faith — even when the coach is plainly not on duty.”
Where does freedom start and stop? Kennedy’s case has sparked controversy, landing in the Supreme Court this past week debating just how far can a person express religious freedom in public spaces.
On June 25, 1962, the Supreme Court decided that praying in schools violated the First Amendment by constituting an establishment of religion. The following year, the Court disallowed Bible readings in public schools for similar reasons.
Long before the Supreme Court’s ruling in 1962 and the current Kennedy case, we are reminded of a very dark period in U.S. history; it was legal that enslaved Africans were forbidden to express religious freedom in any form including reading, writing and praying.
The late Dr. Albert J. Raboteau, an African American scholar, gave meaning to what Africans had to endure to worship. The hush harbors, known as the invisible church, was a secret worship place built with tree branches in the deep woods out of ear shot and eyesight of slave masters. The secret call to worship used codes. One such code was the spiritual, “Steal Away to Jesus.” If enslaved Africans were caught worshiping, they were subjected to vicious beatings or could be murdered for exercising religious freedom.
During the secret worship, the African preacher sermonized how God delivered the Hebrews from slavery to freedom. The ancestors believed and trusted that the same God who told Moses to go down in Egypt land and let my people go was the same God that was going to set them free. The enslaved Africans practiced their African rituals knowing the spirit of the ancestors was with them, encouraging them, that slavery was not their destiny. C. Eric Lincoln reminded us in the epic book “The Black Church in the African American Experience,” that “The term ‘freedom’ has found a deep religious resonance in the lives and hopes of African Americans.”
Colin Kaepernick refused to stand for the Star-Spangled Banner, National Anthem. He said he did so to protest police shootings of African American men and other social injustices faced by Black people in the United States. The Star-Spangled Banner is a lyrical prayer – “and this be our motto, “In God we trust.”
Kaepernick was punished for expressing his freedom by refusing to engage in what he sees as hypocrisy. Is it time for a new national anthem? Near the Rotunda of the Capitol, a room is set apart for prayer. In light of the controversy, should the prayer room be removed? In 2009, I gave the opening prayer as a Guest Chaplain for the U.S. House of Representatives that was aired on CNN and other networks.
Is the opening prayer possibly up for elimination? On April 17, 1952, President Harry Truman signed a bill proclaiming the National Day of Prayer into law in the United States. Will it be reversed? Tim Tebow often knelt and prayed at football games. Steph Curry has a line of tennis shoes with a biblical scripture, “I can do all things…”
Ms. Hamer raised a critical inquiry, how much of my freedom can I have today? Are you willing to contend for your faith?
Activism
Oakland Post: Week of April 24 – 30, 2024
The printed Weekly Edition of the Oakland Post: Week of April 24 – 30, 2024

To enlarge your view of this issue, use the slider, magnifying glass icon or full page icon in the lower right corner of the browser window. ![]()
Activism
Oakland Post: Week of April 17 – 23, 2024
The printed Weekly Edition of the Oakland Post: Week of April 17 – 23, 2024

To enlarge your view of this issue, use the slider, magnifying glass icon or full page icon in the lower right corner of the browser window. ![]()
Black History
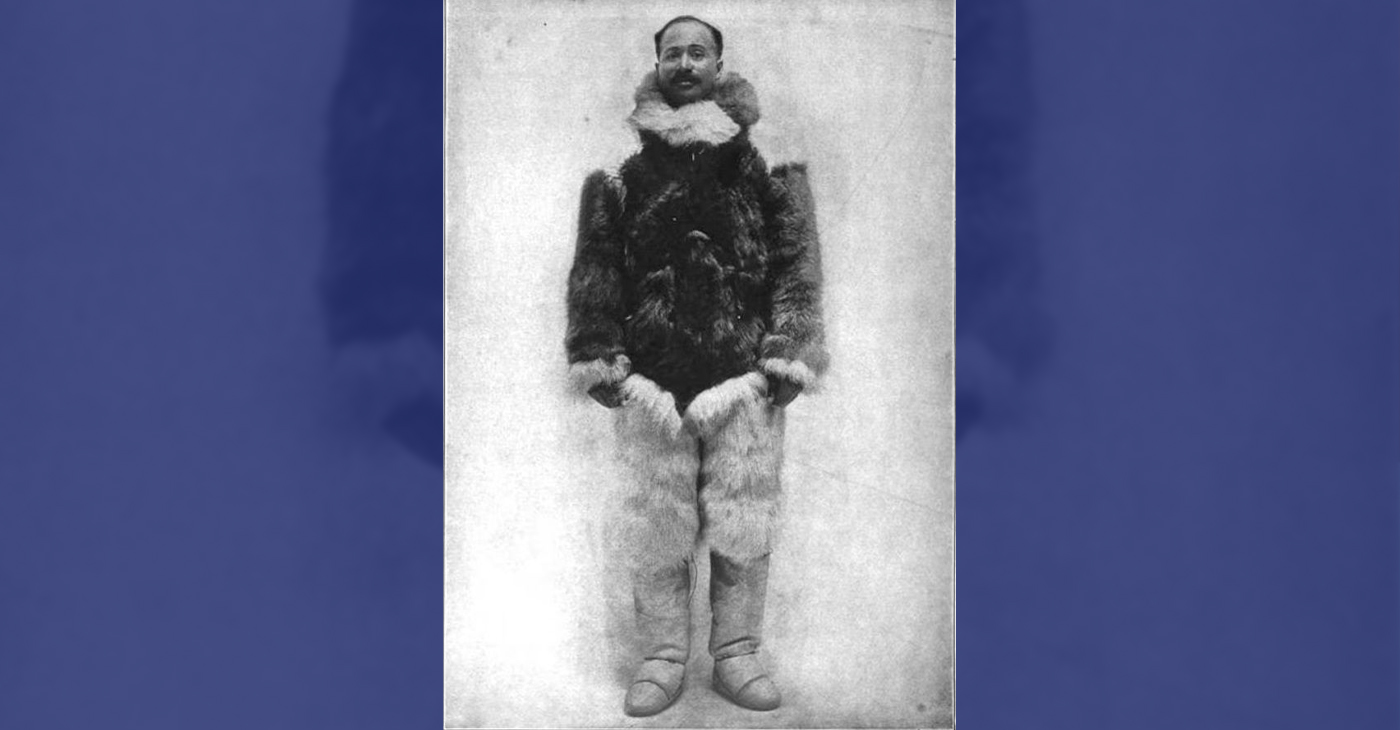
Matthew Henson: Explorer Extraordinaire
Matthew Henson, a trailblazing explorer who overcame countless obstacles to leave an incredible mark on history. Born on August 8, 1866, in Charles County, Maryland, his journey is a testament to the power of determination and the spirit of adventure.

By Tamara Shiloh
Matthew Henson, a trailblazing explorer who overcame countless obstacles to leave an incredible mark on history. Born on August 8, 1866, in Charles County, Maryland, his journey is a testament to the power of determination and the spirit of adventure.
Henson’s life began amidst the backdrop of post-Civil War America, where opportunities for African Americans were scarce. From a young age, he possessed an insatiable curiosity about the world beyond his small town. At the age of 12, he embarked on a journey that would change the course of his life forever when he joined a merchant ship as a cabin boy.
His most famous expedition was his journey to the Arctic with renowned explorer Robert E. Peary. In 1887, Henson joined Peary’s crew as a seaman and quickly proved himself to be invaluable with his skills as a navigator and craftsman. Over the course of several expeditions, Matthew endured extreme cold, treacherous terrain, and grueling conditions as he and Peary sought to reach the elusive North Pole.
In 1908–09, Peary set out on his eighth attempt to reach the North Pole. It was a big expedition, with Peary planning to leave supplies along the way. When he and Henson boarded their ship, the Roosevelt, leaving Greenland on August 18, 1909, they were joined by a large group. This included 22 Inuit men, 17 Inuit women, 10 children, 246 dogs, 70 tons of whale meat, blubber from 50 walruses, hunting gear, and tons of coal.
In February, Henson and Peary left their anchored ship at Ellesmere Island’s Cape Sheridan, along with the Inuit men and 130 dogs. They worked together to set up a trail and supplies along the way to the Pole.
Peary picked Henson and four Inuit people to join him in the final push to the Pole. However, before they reached their destination, Peary couldn’t walk anymore and had to ride in a dog sled. He sent Henson ahead to scout the way. In a later interview with a newspaper, Henson recalled being in the lead and realizing they had gone too far. The group turned back, and Henson noticed his footprints helped guide them to their destination. At that location, Henson planted the American flag.
Henson’s legacy extends far beyond his expeditions to the Arctic. He shattered racial barriers in the world of exploration and inspired countless individuals, regardless of race, to dream big and pursue their passions. In 1937, he was finally recognized for his achievements when he was inducted into The Explorers Club, an organization dedicated to promoting scientific exploration and field research.
Matthew Henson died in the Bronx, New York, on March 9, 1955, at the age of 88.
-

 Activism4 weeks ago
Activism4 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of March 27 – April 2, 2024
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoBeloved Actor and Activist Louis Cameron Gossett Jr. Dies at 87
-

 Community1 week ago
Community1 week agoFinancial Assistance Bill for Descendants of Enslaved Persons to Help Them Purchase, Own, or Maintain a Home
-

 Activism3 weeks ago
Activism3 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of April 3 – 6, 2024
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoV.P. Kamala Harris: Americans With Criminal Records Will Soon Be Eligible for SBA Loans
-

 Activism2 weeks ago
Activism2 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of April 10 – 16, 2024
-

 Community1 week ago
Community1 week agoAG Bonta Says Oakland School Leaders Should Comply with State Laws to Avoid ‘Disparate Harm’ When Closing or Merging Schools
-

 Community6 days ago
Community6 days agoOakland WNBA Player to be Inducted Into Hall of Fame