Black History
Granville Woods: The Black Edison
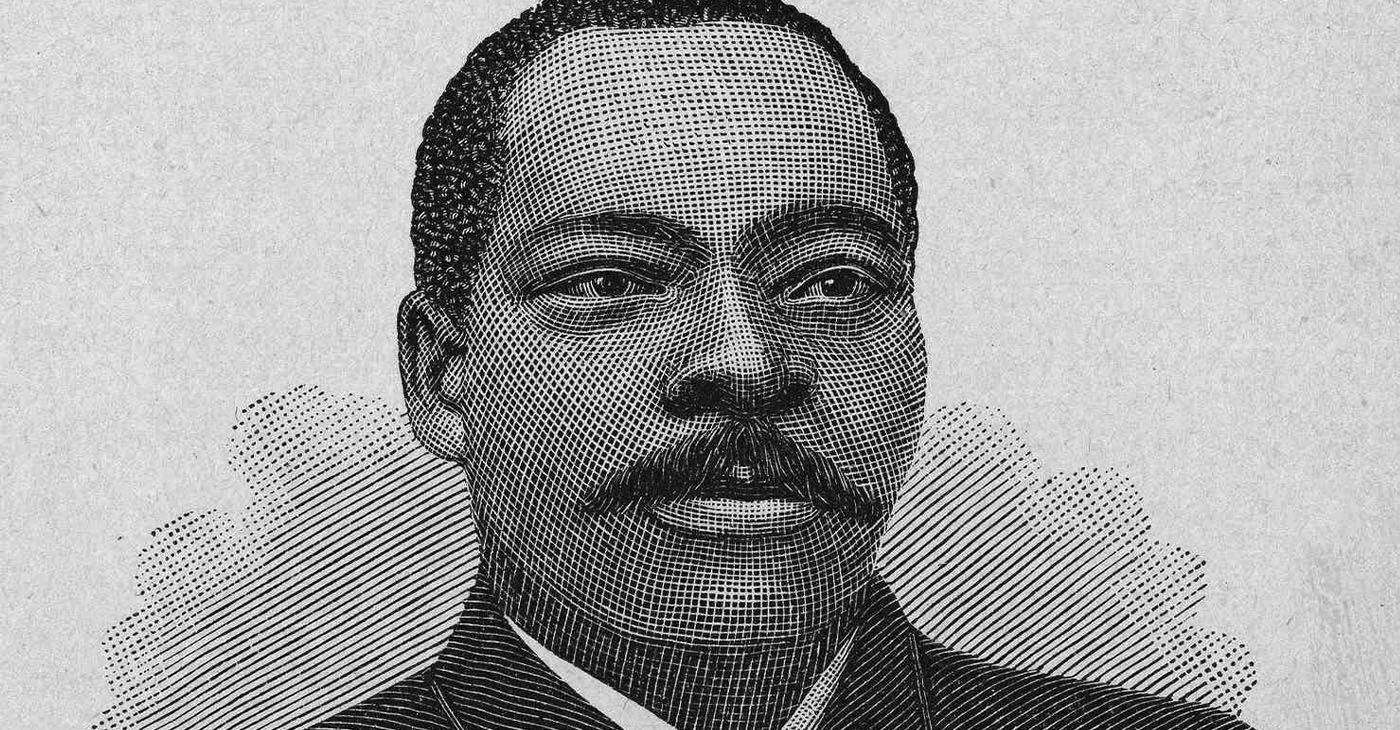
Granville T. Woods, a name that reverberates through the annals of technological innovation, was a trailblazing inventor whose contributions transformed the world. Born before the U.S. Civil War, Woods overcame significant obstacles to become one of the most prolific inventors of his time.

By Tamara Shiloh
Granville T. Woods, a name that reverberates through the annals of technological innovation, was a trailblazing inventor whose contributions transformed the world. Born before the U.S. Civil War, Woods overcame significant obstacles to become one of the most prolific inventors of his time.
He was born on April 23, 1856, in Columbus, Ohio. Coming of age during the era of racial segregation, Woods faced immense challenges in pursuing his passion for engineering. Denied formal education, he taught himself through relentless self-study and practical experience. Despite racial discrimination, Woods went on to establish a successful career as an inventor, leaving an indelible mark on American technological advancements.
He left school at the age of 10 due to his parents’ poverty and apprenticed in a machine shop learning the trades of a machinist and blacksmith. At 18, he worked as a fireman on a railroad in Missouri, moving to Springfield, Illinois, where he worked at a mill. From 1876-78, some sources say he attended college and studied mechanical and electrical engineering.
He worked on a steamship and rose to the position of chief engineer before returning to Ohio where he became an engineer with the Dayton and Southwestern Railroad. He established a business as an electrical engineer and inventor in 1880 in Cincinnati, reorganized it as the Woods Electric Co. and 12 years later, moved research operations to New York City where he worked with his brother, Lyates, who was also an inventor.
Granville Woods’ most significant contributions were in the field of railway technology. He invented numerous devices that revolutionized the safety and efficiency of railroad systems. One of his notable inventions was the “Synchronous Multiplex Railway Telegraph,” which allowed communication between trains, reducing the risk of accidents.
Additionally, Woods developed the “Induction Telegraph System,” enabling moving trains to communicate with station operators. His inventions played a pivotal role in enhancing the safety, reliability, and coordination of train operations, earning him the nickname “The Black Edison.”
Beyond the railroad industry, Woods made groundbreaking advancements in electrical engineering and communication. He invented the “Telegraphony,” a device that combined the telegraph and telephone, allowing voice communication over long distances.
Woods also developed the “Multiplex Railway Telegraph,” which allowed simultaneous communication on multiple telegraph lines. His inventions greatly influenced the development of telegraph and telephone technology, leading to improved communication systems.
One invention that is still used today is the safety dimmer, allowing theaters to decrease their electricity use by 10%.
Before he died of a cerebral hemorrhage in Harlem on Jan. 30, 1910, he had sold a number of his devices to Westinghouse, General Electric and American Engineering.
Woods held over 60 patents for his inventions, leaving an enduring legacy in the field of engineering. Woods’ contributions were posthumously recognized, and in 2006, he was inducted into the National Inventors Hall of Fame.
Activism
Oakland Post: Week of April 24 – 30, 2024
The printed Weekly Edition of the Oakland Post: Week of April 24 – 30, 2024

To enlarge your view of this issue, use the slider, magnifying glass icon or full page icon in the lower right corner of the browser window. ![]()
Activism
Oakland Post: Week of April 17 – 23, 2024
The printed Weekly Edition of the Oakland Post: Week of April 17 – 23, 2024

To enlarge your view of this issue, use the slider, magnifying glass icon or full page icon in the lower right corner of the browser window. ![]()
Black History
Matthew Henson: Explorer Extraordinaire
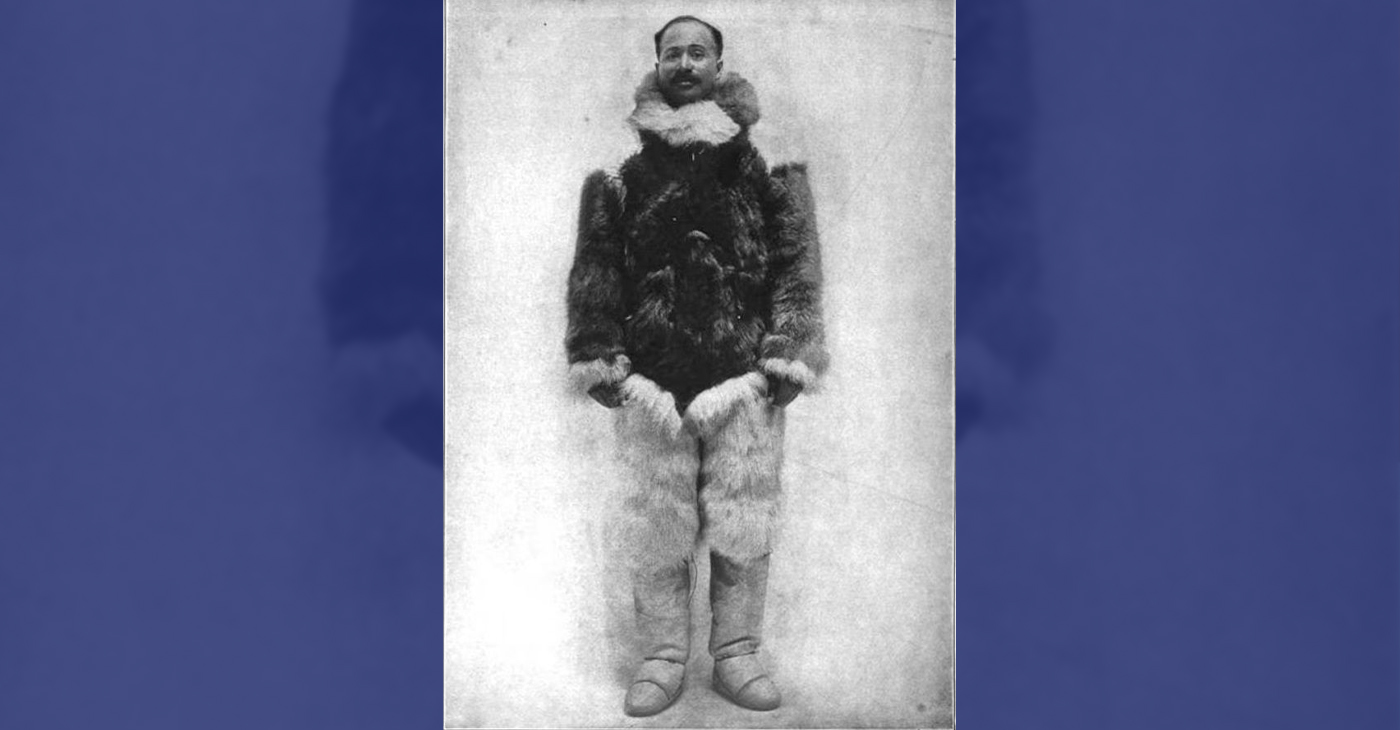
Matthew Henson, a trailblazing explorer who overcame countless obstacles to leave an incredible mark on history. Born on August 8, 1866, in Charles County, Maryland, his journey is a testament to the power of determination and the spirit of adventure.

By Tamara Shiloh
Matthew Henson, a trailblazing explorer who overcame countless obstacles to leave an incredible mark on history. Born on August 8, 1866, in Charles County, Maryland, his journey is a testament to the power of determination and the spirit of adventure.
Henson’s life began amidst the backdrop of post-Civil War America, where opportunities for African Americans were scarce. From a young age, he possessed an insatiable curiosity about the world beyond his small town. At the age of 12, he embarked on a journey that would change the course of his life forever when he joined a merchant ship as a cabin boy.
His most famous expedition was his journey to the Arctic with renowned explorer Robert E. Peary. In 1887, Henson joined Peary’s crew as a seaman and quickly proved himself to be invaluable with his skills as a navigator and craftsman. Over the course of several expeditions, Matthew endured extreme cold, treacherous terrain, and grueling conditions as he and Peary sought to reach the elusive North Pole.
In 1908–09, Peary set out on his eighth attempt to reach the North Pole. It was a big expedition, with Peary planning to leave supplies along the way. When he and Henson boarded their ship, the Roosevelt, leaving Greenland on August 18, 1909, they were joined by a large group. This included 22 Inuit men, 17 Inuit women, 10 children, 246 dogs, 70 tons of whale meat, blubber from 50 walruses, hunting gear, and tons of coal.
In February, Henson and Peary left their anchored ship at Ellesmere Island’s Cape Sheridan, along with the Inuit men and 130 dogs. They worked together to set up a trail and supplies along the way to the Pole.
Peary picked Henson and four Inuit people to join him in the final push to the Pole. However, before they reached their destination, Peary couldn’t walk anymore and had to ride in a dog sled. He sent Henson ahead to scout the way. In a later interview with a newspaper, Henson recalled being in the lead and realizing they had gone too far. The group turned back, and Henson noticed his footprints helped guide them to their destination. At that location, Henson planted the American flag.
Henson’s legacy extends far beyond his expeditions to the Arctic. He shattered racial barriers in the world of exploration and inspired countless individuals, regardless of race, to dream big and pursue their passions. In 1937, he was finally recognized for his achievements when he was inducted into The Explorers Club, an organization dedicated to promoting scientific exploration and field research.
Matthew Henson died in the Bronx, New York, on March 9, 1955, at the age of 88.
-

 Activism4 weeks ago
Activism4 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of March 27 – April 2, 2024
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoBeloved Actor and Activist Louis Cameron Gossett Jr. Dies at 87
-

 Community1 week ago
Community1 week agoFinancial Assistance Bill for Descendants of Enslaved Persons to Help Them Purchase, Own, or Maintain a Home
-

 Activism3 weeks ago
Activism3 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of April 3 – 6, 2024
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoV.P. Kamala Harris: Americans With Criminal Records Will Soon Be Eligible for SBA Loans
-

 Activism2 weeks ago
Activism2 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of April 10 – 16, 2024
-

 Community1 week ago
Community1 week agoAG Bonta Says Oakland School Leaders Should Comply with State Laws to Avoid ‘Disparate Harm’ When Closing or Merging Schools
-

 Community6 days ago
Community6 days agoOakland WNBA Player to be Inducted Into Hall of Fame