Activism
California NAACP Conference Honors 1968 Olympics Heroes
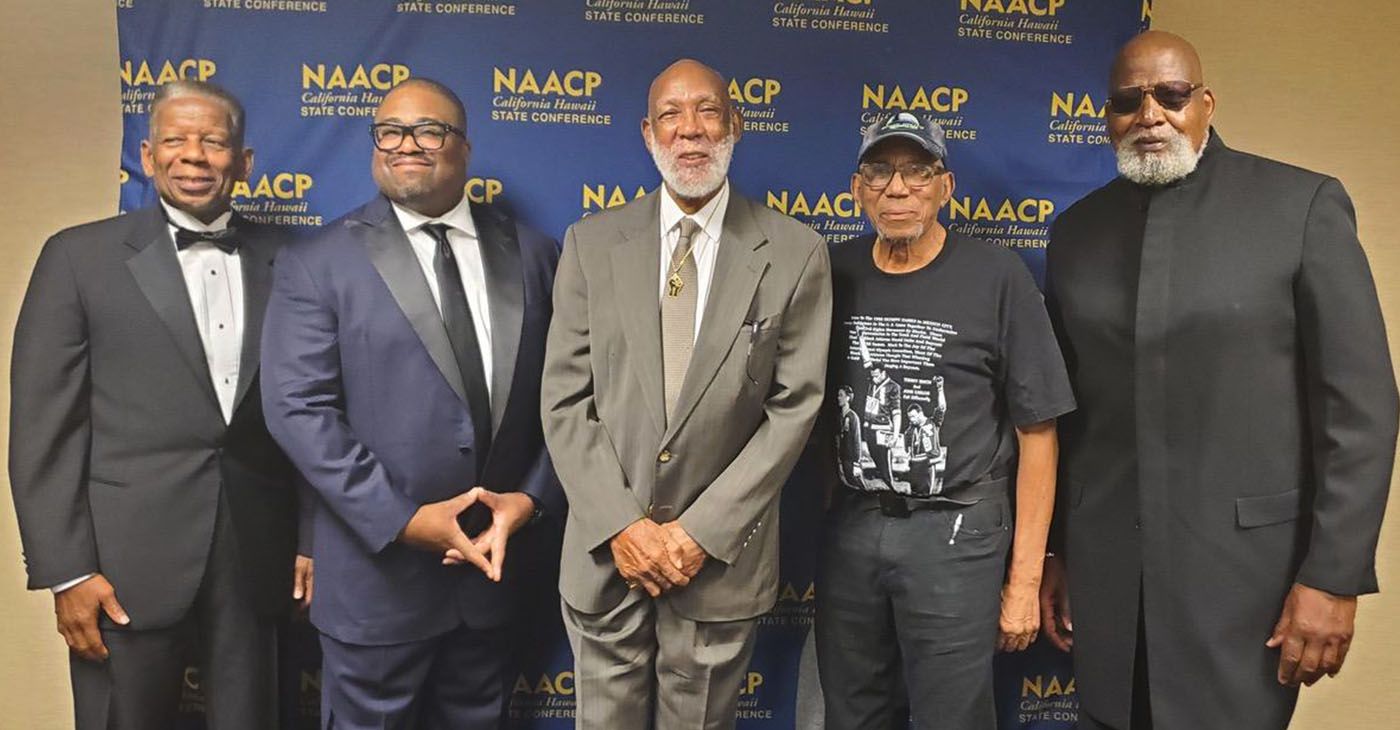
The California Hawaii State Conference of the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (CA/HI NAACP) held its 11th annual Legacy Hall of Fame induction ceremony. The event took place on June 24 at the Sheraton Hotel in downtown Sacramento.

By Antonio Ray Harvey
California Black Media
The California Hawaii State Conference of the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (CA/HI NAACP) held its 11th annual Legacy Hall of Fame induction ceremony. The event took place on June 24 at the Sheraton Hotel in downtown Sacramento.
At the event, the NAACP paid tribute to 1968 Olympic medalists Dr. Tommie Smith and Dr. John Carlos, and 1967 Olympic Project for Human Rights co-organizers Dr. Harry Edwards and Dr. Kenneth Noel. These men were honored for their contributions to the civil rights movement in the 1960s.
All the honorees except Smith were present at the ceremony. Smith’s friend Darrell Goode accepted the award on his behalf.
“If you receive this award, it exemplifies greatness of your career whether it’s in politics, whether it’s in business, or whether it be activism,” said Rick Callender, president of the CA/HI NAACP.
“I’m sure you can see why now our current inductees are receiving this honor. It just shows you what an incredible impact they had on the lives of everyone in their fight for civil rights,” he added.
After placing first and third in the 200-meter dash at the Olympic Games in Mexico City in 1968, sprinters Smith and Carlos ascended the medal stand to receive their respective gold and bronze metals with second-place silver medalist Peter Norman of Australia. During that historic moment, the men led a protest to draw attention to racial discrimination and other negative conditions affecting Black people in America and across the globe.
Shoeless, donning black socks to represent Black poverty, and wearing beads to protest violence against African Americans, the athletes raised a black-gloved fist to show support for Black and oppressed people. Smith wore a black scarf around his neck to show Black pride.
The iconic image of their stance on the podium and their bold display of the Black power movement’s most recognizable symbol (the raised fist) was seen around the world. That moment changed the racial dynamics of international sports forever.
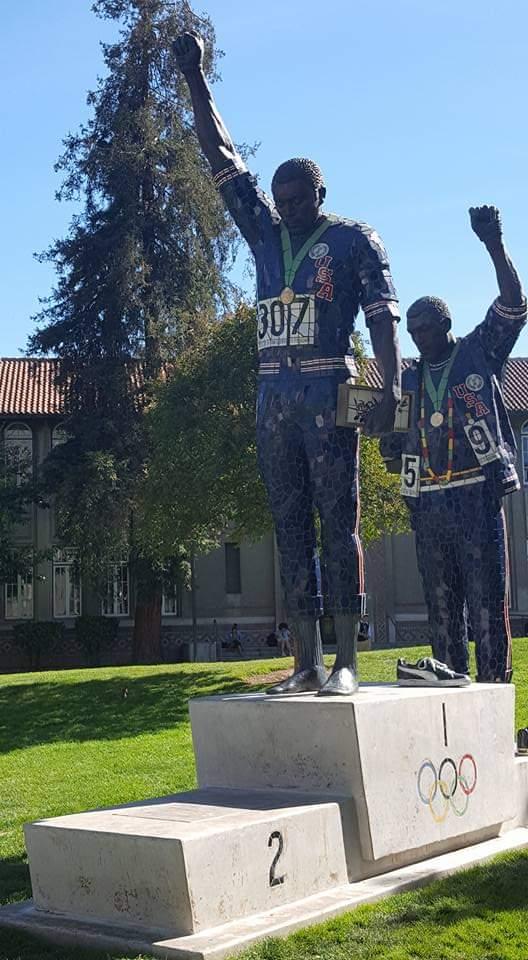

On the morning of Oct. 16, 1968, African American athletes Tommie Smith and John Carlos each raised a black-gloved fist while the U.S. national anthem, “The Star-Spangled Banner,” played during their medal ceremony at the Olympics in Mexico City. CBM photo by Antonio Ray Harvey was taken at their alma mater on Oct.6, 2016 on the campus of San Jose State University. Statue designed by artist Rigo 23 in 2005.
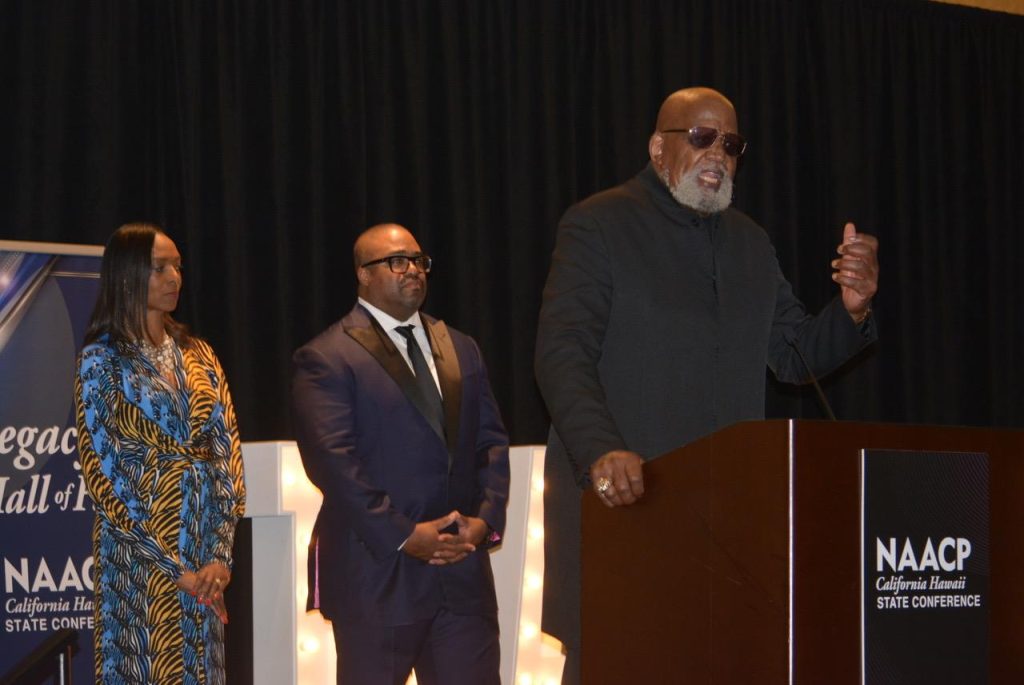

Dr. Harry Edwards (Legacy Hall of Fame recipient), at the podium, and Dr. Kenneth Noel organized the protest at the 1968 Olympics in Mexico City. He is shown here with CA/HI NAACP President Rick Callendar and Carolyn Veal-Hunter (CA/HI NAACP treasurer) at the Legacy Hall of Fame induction ceremony in Sacramento, June 24, 2023. CBM photo by Antonio Ray Harvey.
After their stand against racial injustice, Smith and Carlos never relinquished their medals even though the International Olympic Committee (IOC) prohibits protests at the games. They were immediately asked to leave the games in Mexico City.
Carlos said it was a widespread myth for decades that the IOC took his and Smith’s medals.
“They never took our medals. It was pure propaganda,” Carlos told California Black Media. “They were saying for years that they took our medals but what it really was was a fear factor. They said it to try to instill fear into every Black athlete after 1968.”
Carlos, Smith, Edwards, and Noel were associated with San Jose State College’s track and field team in the mid-1960s. Facing discrimination as students on the campus, Edwards and Noel orchestrated rallies, protests and social justice events to attract African American student-athletes and fellow campus activists.
Noel and Edwards started The United Black Students for Action (UBSA). They both noticed that Black student-athletes could use their fame to elevate civil rights issues. They both converted UBSA into the Olympic Project for Human Rights (OPHR), a civil rights organization created to boycott the 1968 Summer Olympics.
On Oct. 16, 1968, Smith won the 200-meter race in a world-record time of 19.83 seconds. Norman finished second with a time of 20.06 seconds, and Carlos was third with a time of 20.10 seconds.
“There were several other people who were really important in our lives and involved in the struggle too,” said Noel, who was known as a gifted middle-distance runner. “One of the things that I will say about the fight for human rights is we endeavored to change the paradigm of what it means to be a champion athlete. Not only to perform on the field but to get involved in politics, and support activities in our communities.”
Edwards, an emeritus professor of Sociology at the University of California, Berkeley, and former scholar-athlete at San Jose State College (today San Jose State University), encouraged African American athletes to protest the 1968 summer Olympics in Mexico City with the support of the Project for Human Rights.
Edwards, a long-time consultant for the San Francisco 49ers, is a proud and committed social activist.
In 2016, Edwards supported then-49ers quarterback Colin Kaepernick’s controversial protest against excessive use of force by police officers.
Kaepernick took a knee during the playing of the National Anthem before each game, as a way of bringing attention to police brutality against Black people in the United States.
After the first time Kaepernick knelt, Edwards told him to give him his uniform immediately because his action would be a monumental moment in sports and representative of the new wave of civil rights. Edwards sent the garment to the National Museum of African American History and Culture in Washington, D.C., to be displayed alongside Carlos, Smith, and Muhammad Ali’s exhibits.
“He felt strong enough about it to put his career and life on the line. Look at the number of death threats and other things that happened to him. He put it all on the line in order to make that statement,” Edwards said. “He was saying we are better than this. He started a movement that swept the world.”
The Legacy Hall of Fame honors outstanding community leaders who have fought tirelessly to advance the Civil Rights Movement while also creating vital funding for local unit capacity building, youth leadership programs, and NextGen Leadership programs and initiatives, according to the CA/HI NAACP.
Activism
Oakland Post: Week of April 24 – 30, 2024
The printed Weekly Edition of the Oakland Post: Week of April 24 – 30, 2024

To enlarge your view of this issue, use the slider, magnifying glass icon or full page icon in the lower right corner of the browser window. ![]()
Activism
Oakland Post: Week of April 17 – 23, 2024
The printed Weekly Edition of the Oakland Post: Week of April 17 – 23, 2024

To enlarge your view of this issue, use the slider, magnifying glass icon or full page icon in the lower right corner of the browser window. ![]()
Activism
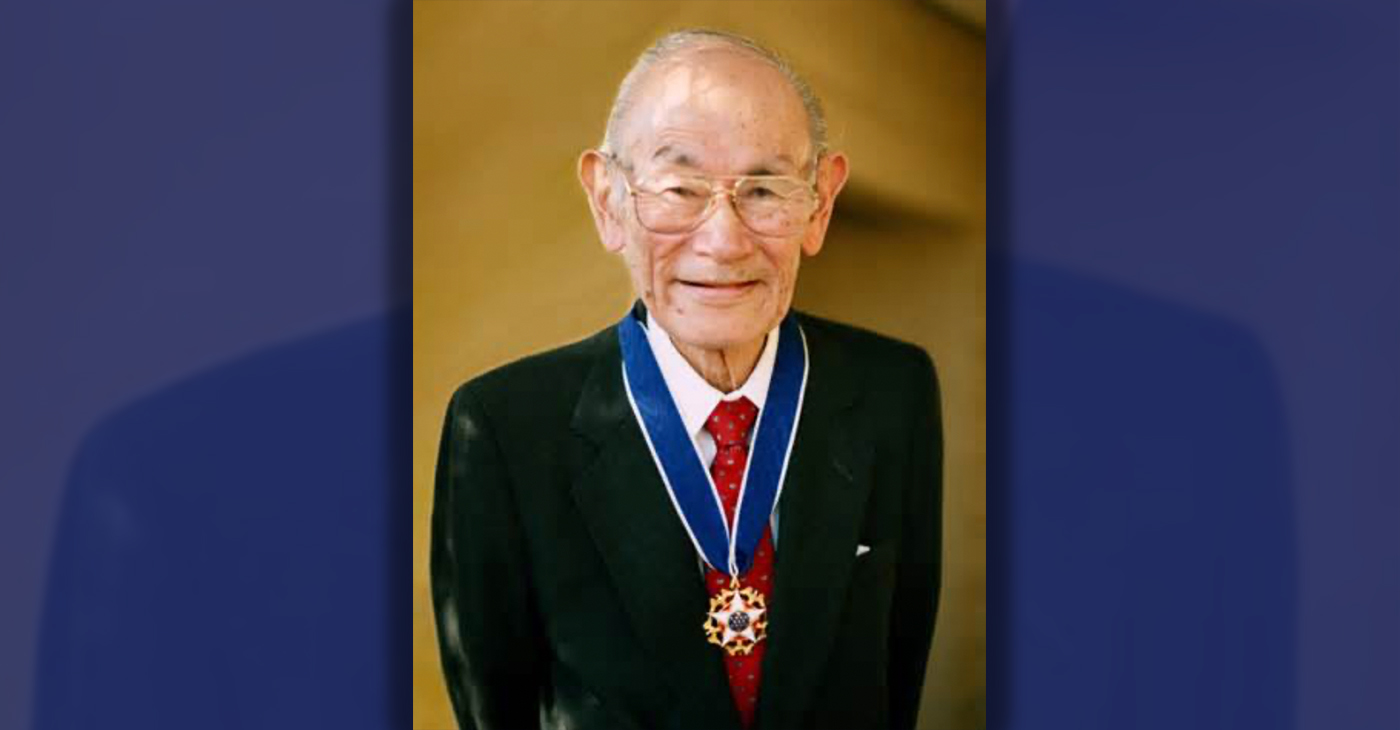
Oakland Schools Honor Fred Korematsu Day of Civil Liberties
Every Jan. 30, OUSD commemorates the legacy of Fred Korematsu, an Oakland native, a Castlemont High School graduate, and a national symbol of resistance, resilience, and justice. His defiant stand against racial injustice and his unwavering commitment to civil rights continue to inspire the local community and the nation. Tuesday was “Fred Korematsu Day of Civil Liberties and the Constitution” in the state of California and a growing number of states across the country.

By Post Staff
Every Jan. 30, OUSD commemorates the legacy of Fred Korematsu, an Oakland native, a Castlemont High School graduate, and a national symbol of resistance, resilience, and justice.
His defiant stand against racial injustice and his unwavering commitment to civil rights continue to inspire the local community and the nation. Tuesday was “Fred Korematsu Day of Civil Liberties and the Constitution” in the state of California and a growing number of states across the country.
One OUSD school is named in his honor: Fred T. Korematsu Discovery Academy (KDA) elementary in East Oakland.
Several years ago, founding KDA Principal Charles Wilson, in a video interview with anti-hate organization “Not In Our Town,” said, “We chose the name Fred Korematsu because we really felt like the attributes that he showed in his work are things that the children need to learn … that common people can stand up and make differences in a large number of people’s lives.”
Fred Korematsu was born in Oakland on Jan. 30, 1919. His parents ran a floral nursery business, and his upbringing in Oakland shaped his worldview. His belief in the importance of standing up for your rights and the rights of others, regardless of race or background, was the foundation for his activism against racial prejudice and for the rights of Japanese Americans during World War II.
At the start of the war, Korematsu was turned away from enlisting in the National Guard and the Coast Guard because of his race. He trained as a welder, working at the docks in Oakland, but was fired after the bombing of Pearl Harbor in 1941. Fear and prejudice led to federal Executive Order 9066, which forced more than 120,000 Japanese Americans out of their homes and neighborhoods and into remote internment camps.
The 23-year-old Korematsu resisted the order. He underwent cosmetic surgery and assumed a false identity, choosing freedom over unjust imprisonment. His later arrest and conviction sparked a legal battle that would challenge the foundation of civil liberties in America.
Korematsu’s fight culminated in the Supreme Court’s initial ruling against him in 1944. He spent years in a Utah internment camp with his family, followed by time living in Salt Lake City where he was dogged by racism.
In 1976, President Gerald Ford overturned Executive Order 9066. Seven years later, the 9th Circuit Court of Appeals in San Francisco vacated Korematsu’s conviction. He said in court, “I would like to see the government admit that they were wrong and do something about it so this will never happen again to any American citizen of any race, creed, or color.”
Korematsu’s dedication and determination established him as a national icon of civil rights and social justice. He advocated for justice with Rosa Parks. In 1998, President Bill Clinton gave him the Presidential Medal of Freedom saying, “In the long history of our country’s constant search for justice, some names of ordinary citizens stand for millions of souls … To that distinguished list, today we add the name of Fred Korematsu.”
After Sept. 11, 2001, Korematsu spoke out against hatred and discrimination, saying what happened to Japanese Americans should not happen to people of Middle Eastern descent.
Korematsu’s roots in Oakland and his education in OUSD are a source of great pride for the city, according to the school district. His most famous quote, which is on the Korematsu elementary school mural, is as relevant now as ever, “If you have the feeling that something is wrong, don’t be afraid to speak up.”
-

 Activism4 weeks ago
Activism4 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of March 27 – April 2, 2024
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoBeloved Actor and Activist Louis Cameron Gossett Jr. Dies at 87
-

 Community1 week ago
Community1 week agoFinancial Assistance Bill for Descendants of Enslaved Persons to Help Them Purchase, Own, or Maintain a Home
-

 Activism3 weeks ago
Activism3 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of April 3 – 6, 2024
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoV.P. Kamala Harris: Americans With Criminal Records Will Soon Be Eligible for SBA Loans
-

 Activism2 weeks ago
Activism2 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of April 10 – 16, 2024
-

 Community1 week ago
Community1 week agoAG Bonta Says Oakland School Leaders Should Comply with State Laws to Avoid ‘Disparate Harm’ When Closing or Merging Schools
-

 Community6 days ago
Community6 days agoOakland WNBA Player to be Inducted Into Hall of Fame