Activism
Black Leaders: Redistricting Process Is “Rushed, Inconsistent, Incomplete”
According to the California Citizens Redistricting Commission, because the proposed maps chop up and split districts where African Americans live, Black political power will be diluted in Los Angeles County, San Diego County, the Central Valley, the Bay Area and the Inland Empire. To address the problem, they have submitted proposed maps to the redistricting commission that will protect Black political power and representation.

By Tanu Henry | California Black Media
African American leaders in California are keeping a close eye on the commission drafting congressional, state Senate, state Assembly and Board of Equalization voting maps. They are concerned about the outcome of the redistricting process.
On November 10, the California Citizens Redistricting Commission released the first draft maps of the redrawn lines for the state’s voting districts. By state law, the finalized versions of the new political districts have to be completed by December 27.
But advocates like James Woodson, the policy director of the California Black Census and Redistricting Hub (CBCRH), are asking the commission to press pause and re-evaluate the maps they have come up with so far.
The CBCRH, also called “the Black Hub” is a statewide coalition focused on “racial equity” and “fairness” in the redistricting process.
“The Black Hub appreciates the commission’s hard work and its early release of the maps for public input. At the same time, the Black Hub is deeply concerned that the process for developing the maps has been rushed, inconsistent, and incomplete,” said Woodson. “It has resulted in maps that have ignored the interests of many Black communities and millions of residents in the state’s most populated areas.”
For example, draft maps released by the commission last month collapsed the only two congressional districts in Los Angeles County represented by Black U.S. Congressmembers, Maxine Waters (D-CA-43) and Karen Bass (D-CA-37), into one district. After advocates and activists complained about African Americans losing political power, the commission separated the single district it was proposing into two constituencies again.
But because California lost one seat in the U.S. Congress due to an overall drop in the state’s population, according to the U.S. 2020 Census numbers, advocates worry that it will cause a ripple effect, which will change the racial and political composition of districts across the state.
The “Black Hub” leaders and other advocates in the state are urging Black Californians to speak up and provide input to ensure their communities do not lose representation or resources.
“It’s not just about us losing political power. It’s also about us losing assets,” said Kellie Todd Griffin, a resident of the Los Angeles County city of Carson, where the number of Black residents accounts for more than 25% of the city’s total population. Los Angeles County, where California is expected to lose one congressional seat, is home to about 40% of African Americans in the state.
Griffin, who is an organizer and entrepreneur, is known in California’s political circles for her outspoken advocacy on behalf of Black Californians. She says with the Olympics coming to Los Angeles in 2028, there will be a lot of development and an increase in revenue for government and businesses in Carson. Redrawn political districts, she fears, could hurt her city and others nearby economically.
“When you look at the maps, you see that our congressional district in Carson has been attached more to Redondo Beach and Rancho Palos Verdes instead of being connected to cities like Long Beach and Compton and places like that,” Griffin said. “There is also an assumption that Blacks and other minorities in the area vote the same on issues. As we know, that is not always true. We have specific issues that affect us Blacks differently. So, we vote differently on them – from some criminal justice reforms to the Crown Act.”
One of the realities driving the leaders’ concern is the possibility that the Black vote in five different regions of California will be diluted.
“Rather than adhere to map priorities from BIPOC communities, we are concerned that, in an effort to prioritize all voices, some commissioners have mistakenly and unknowingly elevated voices from less diverse, affluent communities in the process, and at the expense of BIPOC communities,” said Woodson.
According to CBCRH, because the proposed maps chop up and split districts where African Americans live, Black political power will be diluted in Los Angeles County, San Diego County, the Central Valley, the Bay Area and the Inland Empire. To address the problem, they have submitted proposed maps to the redistricting commission that will protect Black political power and representation.
Another major concern is the compressed timeline on which the commission is working, which limits the time for citizens to influence the line-drawing process. This year, due to pandemic-related federal delays, census data the commission relies on to redraw maps was delayed. Instead of its usual release in March, the U.S. Census Bureau did not provide that information until September 21.
“The Black Hub is deeply concerned that the process for developing the maps has been rushed, inconsistent, and incomplete. It has resulted in maps that have ignored the interests of many Black communities and millions of residents in the state’s most populated areas,” said a statement released by CBCRH last week.
Every 10 years, California appoints a new redistricting commission after the U.S. Census. It is tasked with mapping or re-drawing the state’s electoral lines based on population shifts in the state population over the decade between census counts.
According to Census 2020 numbers, California’s Black population decreased from about 2.5 to nearly 2.2 million over the last decade. However, there was a dramatic increase in the number of Californians who identify as more than one race — from 4.9% in 2010 to 14.6% in 2020.
In 2008, California voters approved the Citizens Redistricting Commission through a constitutional amendment called The Voters First Act or Proposition 11. It handed the function of drawing electoral maps to citizens. The policy was set up to avoid the political influence of government officials or special interest groups on the redistricting process.
Before the passage of Prop 11, the state Legislature was responsible for drawing its own electoral districts. There are five Democrats, five Republicans, and four members who are not affiliated with any political party on the committee.
When redrawing maps, the number of voters in all districts across the state has to be equal. That is roughly 761,000 people in each congressional district. For all state Senate districts that number is 988,000, and 494,000 people in Assembly districts.
In California, Blacks make up a little over 5% of the state’s population of about 40 million people. There are 52 congressional districts; 80 Assembly districts; and 40 Senate districts. For the state Board of Equalization, the body responsible for representing taxpayer interests and “equalizing” county-by-county tax assessments across California, there are four districts.
The commission has to comply with a number of constitutional mandates, including Voting Rights Act provisions that all minority groups must be able to elect a representative of their choice; a district must be whole or contiguous (connected geographically); among other rules.
Starting November 17 there will be a series of meetings during which the public will be able to provide their input to commissioners. Another round of map drawing sessions will commence November 30.
“We need to lift our voices and make sure we have said something. That we didn’t just sit by and let these lines be redrawn without us fighting for our interests. We have to define what community means to us,” said Griffin. “We have to make sure we are submitting written comments and letting people know the things that work for us and the things that don’t.”
To make a public comment to the commission, email votersfirstact@crc.ca.gov or complete the Community Feedback Form.
____________________________________________________________
Photo Caption:
Website Tags and Keywords:
Twitter Tags/Handles:
@Tanu_Henry @CaliforniaBlack2 @RepMaxineWaters @RepKarenBass @CACalls @jdublu44 @BlackPressUSA @NNPA_BlackPress
Activism
Oakland Post: Week of April 17 – 23, 2024
The printed Weekly Edition of the Oakland Post: Week of April 17 – 23, 2024

To enlarge your view of this issue, use the slider, magnifying glass icon or full page icon in the lower right corner of the browser window. ![]()
Activism
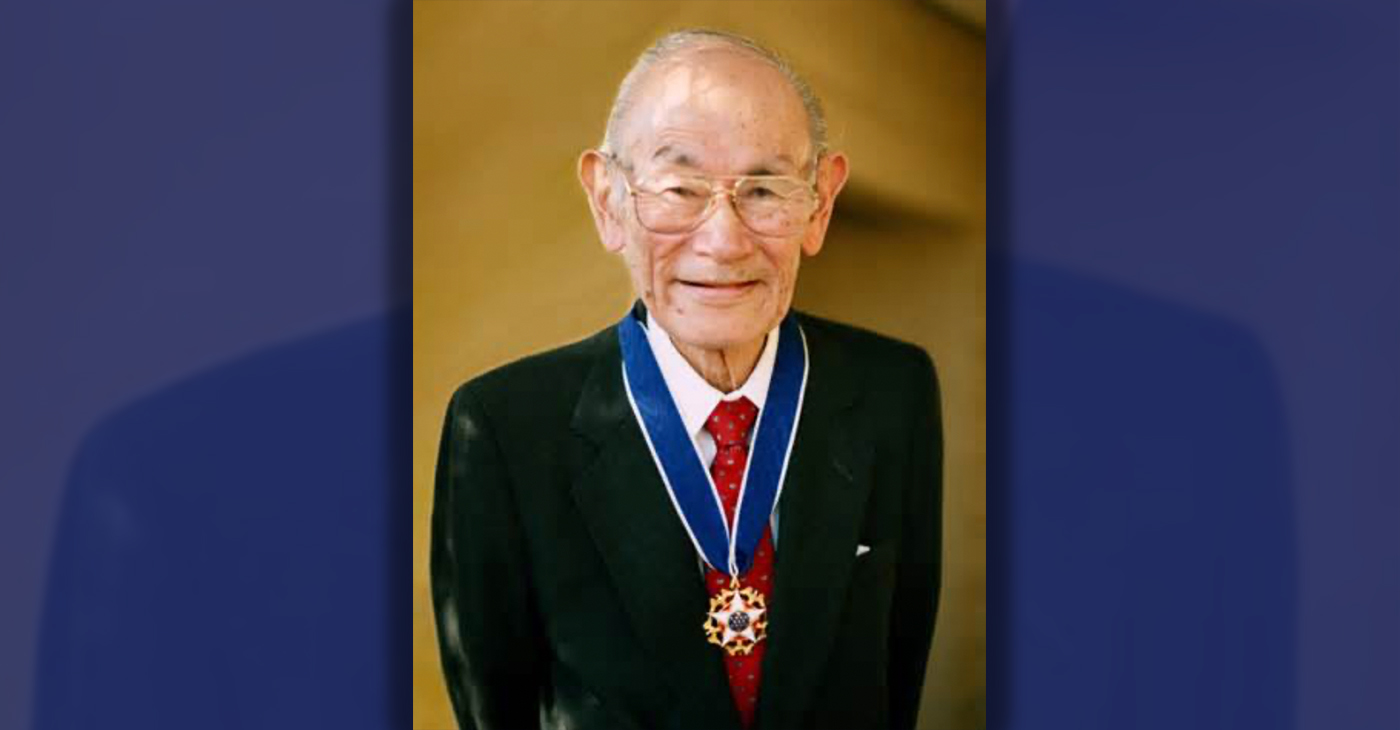
Oakland Schools Honor Fred Korematsu Day of Civil Liberties
Every Jan. 30, OUSD commemorates the legacy of Fred Korematsu, an Oakland native, a Castlemont High School graduate, and a national symbol of resistance, resilience, and justice. His defiant stand against racial injustice and his unwavering commitment to civil rights continue to inspire the local community and the nation. Tuesday was “Fred Korematsu Day of Civil Liberties and the Constitution” in the state of California and a growing number of states across the country.

By Post Staff
Every Jan. 30, OUSD commemorates the legacy of Fred Korematsu, an Oakland native, a Castlemont High School graduate, and a national symbol of resistance, resilience, and justice.
His defiant stand against racial injustice and his unwavering commitment to civil rights continue to inspire the local community and the nation. Tuesday was “Fred Korematsu Day of Civil Liberties and the Constitution” in the state of California and a growing number of states across the country.
One OUSD school is named in his honor: Fred T. Korematsu Discovery Academy (KDA) elementary in East Oakland.
Several years ago, founding KDA Principal Charles Wilson, in a video interview with anti-hate organization “Not In Our Town,” said, “We chose the name Fred Korematsu because we really felt like the attributes that he showed in his work are things that the children need to learn … that common people can stand up and make differences in a large number of people’s lives.”
Fred Korematsu was born in Oakland on Jan. 30, 1919. His parents ran a floral nursery business, and his upbringing in Oakland shaped his worldview. His belief in the importance of standing up for your rights and the rights of others, regardless of race or background, was the foundation for his activism against racial prejudice and for the rights of Japanese Americans during World War II.
At the start of the war, Korematsu was turned away from enlisting in the National Guard and the Coast Guard because of his race. He trained as a welder, working at the docks in Oakland, but was fired after the bombing of Pearl Harbor in 1941. Fear and prejudice led to federal Executive Order 9066, which forced more than 120,000 Japanese Americans out of their homes and neighborhoods and into remote internment camps.
The 23-year-old Korematsu resisted the order. He underwent cosmetic surgery and assumed a false identity, choosing freedom over unjust imprisonment. His later arrest and conviction sparked a legal battle that would challenge the foundation of civil liberties in America.
Korematsu’s fight culminated in the Supreme Court’s initial ruling against him in 1944. He spent years in a Utah internment camp with his family, followed by time living in Salt Lake City where he was dogged by racism.
In 1976, President Gerald Ford overturned Executive Order 9066. Seven years later, the 9th Circuit Court of Appeals in San Francisco vacated Korematsu’s conviction. He said in court, “I would like to see the government admit that they were wrong and do something about it so this will never happen again to any American citizen of any race, creed, or color.”
Korematsu’s dedication and determination established him as a national icon of civil rights and social justice. He advocated for justice with Rosa Parks. In 1998, President Bill Clinton gave him the Presidential Medal of Freedom saying, “In the long history of our country’s constant search for justice, some names of ordinary citizens stand for millions of souls … To that distinguished list, today we add the name of Fred Korematsu.”
After Sept. 11, 2001, Korematsu spoke out against hatred and discrimination, saying what happened to Japanese Americans should not happen to people of Middle Eastern descent.
Korematsu’s roots in Oakland and his education in OUSD are a source of great pride for the city, according to the school district. His most famous quote, which is on the Korematsu elementary school mural, is as relevant now as ever, “If you have the feeling that something is wrong, don’t be afraid to speak up.”
Activism
WOMEN IMPACTING THE CHURCH AND COMMUNITY
Juanita Matthews, better known as “Sister Teacher,” is a walking Bible scholar. She moved to California from the great state of Arkansas in 1971. Sister Teacher has a passion for teaching. She has been a member of Bible Fellowship Missionary Baptist Church since 1971.

Sister Juanita Matthews
55 Years with Oakland Public School District
The Teacher, Mother, Community Outreach Champion, And Child of God
Juanita Matthews, better known as “Sister Teacher,” is a walking Bible scholar. She moved to California from the great state of Arkansas in 1971. Sister Teacher has a passion for teaching. She has been a member of Bible Fellowship Missionary Baptist Church since 1971. She followed her passion for teaching, and in 1977 became the lead teacher for Adult Class #6. Her motto still today is “Once My Student, Always My Student”.
Beyond her remarkable love for the Lord, Sister Teacher has showcased her love for teaching by working for the Oakland Unified School District for 55 years, all but four of those years spent at Emerson Elementary and Child Development School. She truly cares about her students, making sure they have the tools/supplies needed to learn either at OUSD or Bible Fellowship Missionary Baptist Church.
She’s also had a “Clothes Closet Ministry” for 51 years, making sure her students have sufficient clothing for school. The Clothes Closet Ministry extends past her students, she has been clothing the community for over 50 years as well. She loves the Lord and is a servant on a mission. She is a loving mother to two beautiful children, Sandra and Andre. This is the impact this woman of God has on her church and the community.
-

 Activism4 weeks ago
Activism4 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of March 27 – April 2, 2024
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoCOMMENTARY: D.C. Crime Bill Fails to Address Root Causes of Violence and Incarceration
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoMayor, City Council President React to May 31 Closing of Birmingham-Southern College
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoBeloved Actor and Activist Louis Cameron Gossett Jr. Dies at 87
-

 Community1 week ago
Community1 week agoFinancial Assistance Bill for Descendants of Enslaved Persons to Help Them Purchase, Own, or Maintain a Home
-

 Activism3 weeks ago
Activism3 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of April 3 – 6, 2024
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoV.P. Kamala Harris: Americans With Criminal Records Will Soon Be Eligible for SBA Loans
-

 Activism2 weeks ago
Activism2 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of April 10 – 16, 2024