Activism
Black Californians Among Those Discovering American Indian Lineage
The Dawes Act of 1887 gave each tribal family head 160 acres of land and each single person 80 acres. The government would hold the land title in a trust for 25 years, after which each individual would receive United States citizenship and a “fee simple” land title. Under this law, Black tribal members, known as Freedmen, were granted approximately 2 million acres of land.

By Lila Brown, California Black Media
A growing number of Black Americans, relying on newly digitized federal records and other sources, are discovering direct bloodlines to Native American ancestors. These discoveries are inspiring individuals to trace and claim their Native ancestry, leading some to apply for citizenship with tribal nations.
When 32-year-old Daniel Bruce Kelly, an actor and minister, began researching his genealogy, he was sure that he would identify a family origin in Africa.
He identifies as African American and says he was determined to prove his parents wrong. They had begun discovering, exploring and embracing their European and Native American ancestry.
In his research, Kelly discovered that his great-great-great-grandfather was registered as Cherokee on the Dawes Roll, a United States government record listing individuals eligible for Indigenous tribal citizenship.
Kelly also identified other family members listed as Indian on U.S. Census Bureau records.
“At first, I was offended that my parents didn’t want to claim to be African, but then I had this awakening. You can’t talk about Native American history without talking about the Black American Indians,” Kelly said.
Similarly, Cameron Lewis, a truck driver from Sacramento, says he always heard family members talk about having “Indian in the family.” Delving into family documents, he found out that his great-great grandfather acquired land in the mid-1800s in areas of Florida inhabited by Seminoles.
“I found it hard to believe that whites would sell hundreds of acres of land to Blacks in the South during slavery,” he said. “This was when I started coming across terms I was not familiar with, describing my ancestors as ‘mulatto’ and ‘intransigent,’ and linking them to tribes such as the Yamasee, Catawba, and Creek — terms I’ve never even heard of.”
The Dawes Act of 1887 gave each tribal family head 160 acres of land and each single person 80 acres. The government would hold the land title in a trust for 25 years, after which each individual would receive United States citizenship and a “fee simple” land title. Under this law, Black tribal members, known as Freedmen, were granted approximately 2 million acres of land.
In Oklahoma’s Creek Nation, about a third of the land was Black-owned.
While the Emancipation Proclamation was signed by President Abraham Lincoln in 1863, slavery in the continental United States did not fully end as a legal institution until June 14, 1866, when the Creek Tribe agreed to abandon enslavement of African Americans. That was the day after Congress approved the Fourteenth Amendment.
Recent efforts to recognize historical injustices against Native Americans have seen progress. Last month, during Native American Heritage Month, Gov. Gavin Newsom issued a Proclamation celebrating the unveiling of a monument dedicated to California Native peoples at the State Capitol.
While this progress is appreciated, many Black Native Americans feel that the history of their Black freedman ancestors remains largely overlooked.
“We have to tell the whole of the story,” said Cherokee Nation Principal Chief Chuck Hoskin Jr. in 2022 during the 70th annual Cherokee National Holiday.
“We have to acknowledge that we enslaved African Americans under our own law. If we ignore or suppress that, we do to Freedmen and their descendants the same things that has been done to Cherokee people. Any nation is a stronger nation if they tell their whole story: the tragedy, the triumph, and the chapters that are dark and difficult,” added Hoskin.
According to the 2020 U.S. Census, approximately 1.4 million Californians identify as fully or partially American Indian and Alaskan Native. California also has the largest Native American population in the country, with close to 900,000 Native residents.
A population map commissioned by the Cherokee Nation in 2013 shows that California has the second-largest Cherokee population in the country after Oklahoma, where many displaced American Indians settled after the Trail of Tears in the 1830s.
In 2021, the Cherokee Nation Supreme Court removed the phrase “by blood” from its constitution. That change acknowledges that the descendants of Black people once enslaved by the tribe, the “Cherokee Freedmen,” have the right to citizenship, which means they are eligible to run for tribal office and to access other resources.
However, debates about who is — and who is not — Native continue.
For example, the great-great-great-grandmother of Kiori Jordan-Marquering, 46, of Santa Rosa, who was known as “Indian Julia,” was denied acceptance into the Choctaw Nation based on her appearance.
“She is visibly Negro,” the space reserved for “office use” on her application form noted.
“My ancestor’s application for citizenship was contested in court for more than three years before ultimately being denied,” says Jordan-Marquering.
Only the Cherokee Nation and the Seminole Tribe of Florida recognize Freedmen as eligible for citizenship.
This resource is supported in whole or in part by funding provided by the State of California, administered by the California State Library in partnership with the California Department of Social Services and the California Commission on Asian and Pacific Islander American Affairs as part of the Stop the Hate program. To report a hate incident or hate crime and get support, go to CA vs Hate.
Activism
Oakland Post: Week of April 24 – 30, 2024
The printed Weekly Edition of the Oakland Post: Week of April 24 – 30, 2024

To enlarge your view of this issue, use the slider, magnifying glass icon or full page icon in the lower right corner of the browser window. ![]()
Activism
Oakland Post: Week of April 17 – 23, 2024
The printed Weekly Edition of the Oakland Post: Week of April 17 – 23, 2024

To enlarge your view of this issue, use the slider, magnifying glass icon or full page icon in the lower right corner of the browser window. ![]()
Activism
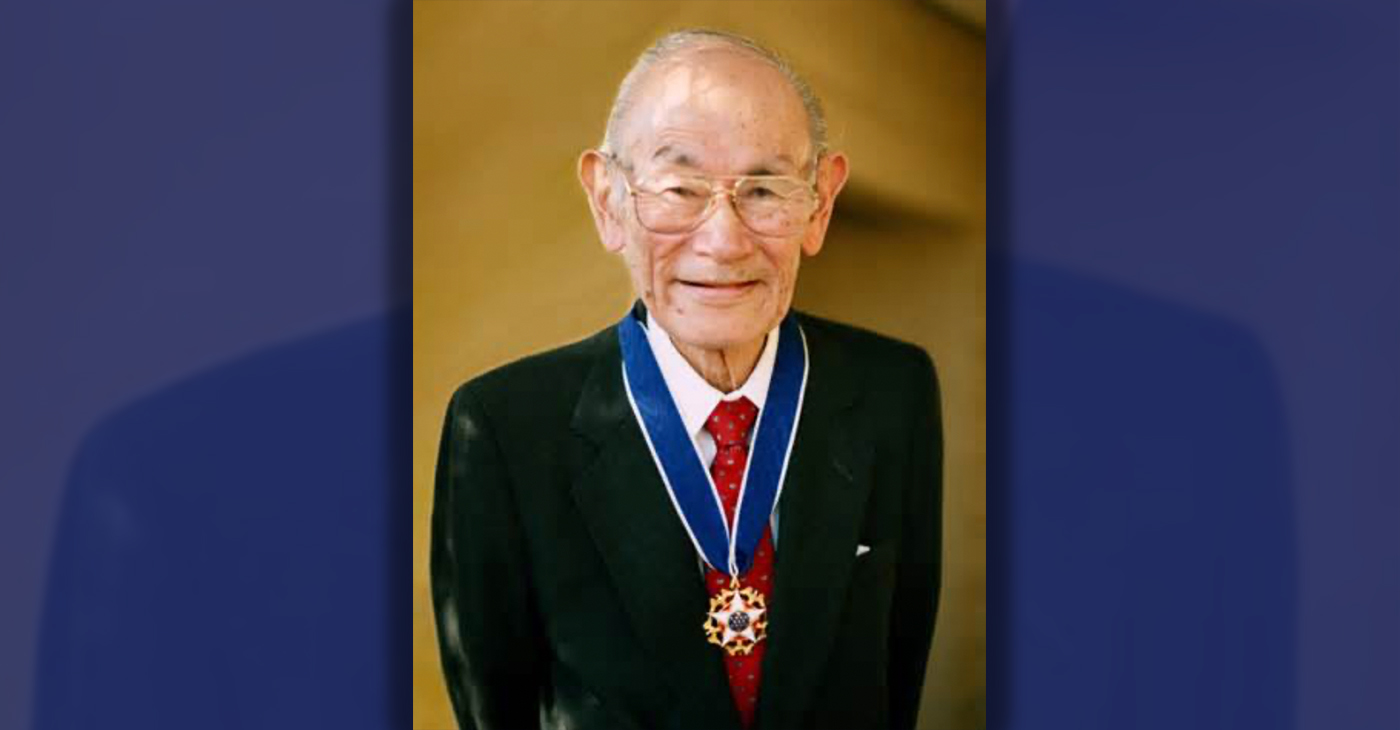
Oakland Schools Honor Fred Korematsu Day of Civil Liberties
Every Jan. 30, OUSD commemorates the legacy of Fred Korematsu, an Oakland native, a Castlemont High School graduate, and a national symbol of resistance, resilience, and justice. His defiant stand against racial injustice and his unwavering commitment to civil rights continue to inspire the local community and the nation. Tuesday was “Fred Korematsu Day of Civil Liberties and the Constitution” in the state of California and a growing number of states across the country.

By Post Staff
Every Jan. 30, OUSD commemorates the legacy of Fred Korematsu, an Oakland native, a Castlemont High School graduate, and a national symbol of resistance, resilience, and justice.
His defiant stand against racial injustice and his unwavering commitment to civil rights continue to inspire the local community and the nation. Tuesday was “Fred Korematsu Day of Civil Liberties and the Constitution” in the state of California and a growing number of states across the country.
One OUSD school is named in his honor: Fred T. Korematsu Discovery Academy (KDA) elementary in East Oakland.
Several years ago, founding KDA Principal Charles Wilson, in a video interview with anti-hate organization “Not In Our Town,” said, “We chose the name Fred Korematsu because we really felt like the attributes that he showed in his work are things that the children need to learn … that common people can stand up and make differences in a large number of people’s lives.”
Fred Korematsu was born in Oakland on Jan. 30, 1919. His parents ran a floral nursery business, and his upbringing in Oakland shaped his worldview. His belief in the importance of standing up for your rights and the rights of others, regardless of race or background, was the foundation for his activism against racial prejudice and for the rights of Japanese Americans during World War II.
At the start of the war, Korematsu was turned away from enlisting in the National Guard and the Coast Guard because of his race. He trained as a welder, working at the docks in Oakland, but was fired after the bombing of Pearl Harbor in 1941. Fear and prejudice led to federal Executive Order 9066, which forced more than 120,000 Japanese Americans out of their homes and neighborhoods and into remote internment camps.
The 23-year-old Korematsu resisted the order. He underwent cosmetic surgery and assumed a false identity, choosing freedom over unjust imprisonment. His later arrest and conviction sparked a legal battle that would challenge the foundation of civil liberties in America.
Korematsu’s fight culminated in the Supreme Court’s initial ruling against him in 1944. He spent years in a Utah internment camp with his family, followed by time living in Salt Lake City where he was dogged by racism.
In 1976, President Gerald Ford overturned Executive Order 9066. Seven years later, the 9th Circuit Court of Appeals in San Francisco vacated Korematsu’s conviction. He said in court, “I would like to see the government admit that they were wrong and do something about it so this will never happen again to any American citizen of any race, creed, or color.”
Korematsu’s dedication and determination established him as a national icon of civil rights and social justice. He advocated for justice with Rosa Parks. In 1998, President Bill Clinton gave him the Presidential Medal of Freedom saying, “In the long history of our country’s constant search for justice, some names of ordinary citizens stand for millions of souls … To that distinguished list, today we add the name of Fred Korematsu.”
After Sept. 11, 2001, Korematsu spoke out against hatred and discrimination, saying what happened to Japanese Americans should not happen to people of Middle Eastern descent.
Korematsu’s roots in Oakland and his education in OUSD are a source of great pride for the city, according to the school district. His most famous quote, which is on the Korematsu elementary school mural, is as relevant now as ever, “If you have the feeling that something is wrong, don’t be afraid to speak up.”
-

 Activism4 weeks ago
Activism4 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of March 27 – April 2, 2024
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoBeloved Actor and Activist Louis Cameron Gossett Jr. Dies at 87
-

 Community1 week ago
Community1 week agoFinancial Assistance Bill for Descendants of Enslaved Persons to Help Them Purchase, Own, or Maintain a Home
-

 Activism3 weeks ago
Activism3 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of April 3 – 6, 2024
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoV.P. Kamala Harris: Americans With Criminal Records Will Soon Be Eligible for SBA Loans
-

 Activism2 weeks ago
Activism2 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of April 10 – 16, 2024
-

 Community1 week ago
Community1 week agoAG Bonta Says Oakland School Leaders Should Comply with State Laws to Avoid ‘Disparate Harm’ When Closing or Merging Schools
-

 Community6 days ago
Community6 days agoOakland WNBA Player to be Inducted Into Hall of Fame