Black History
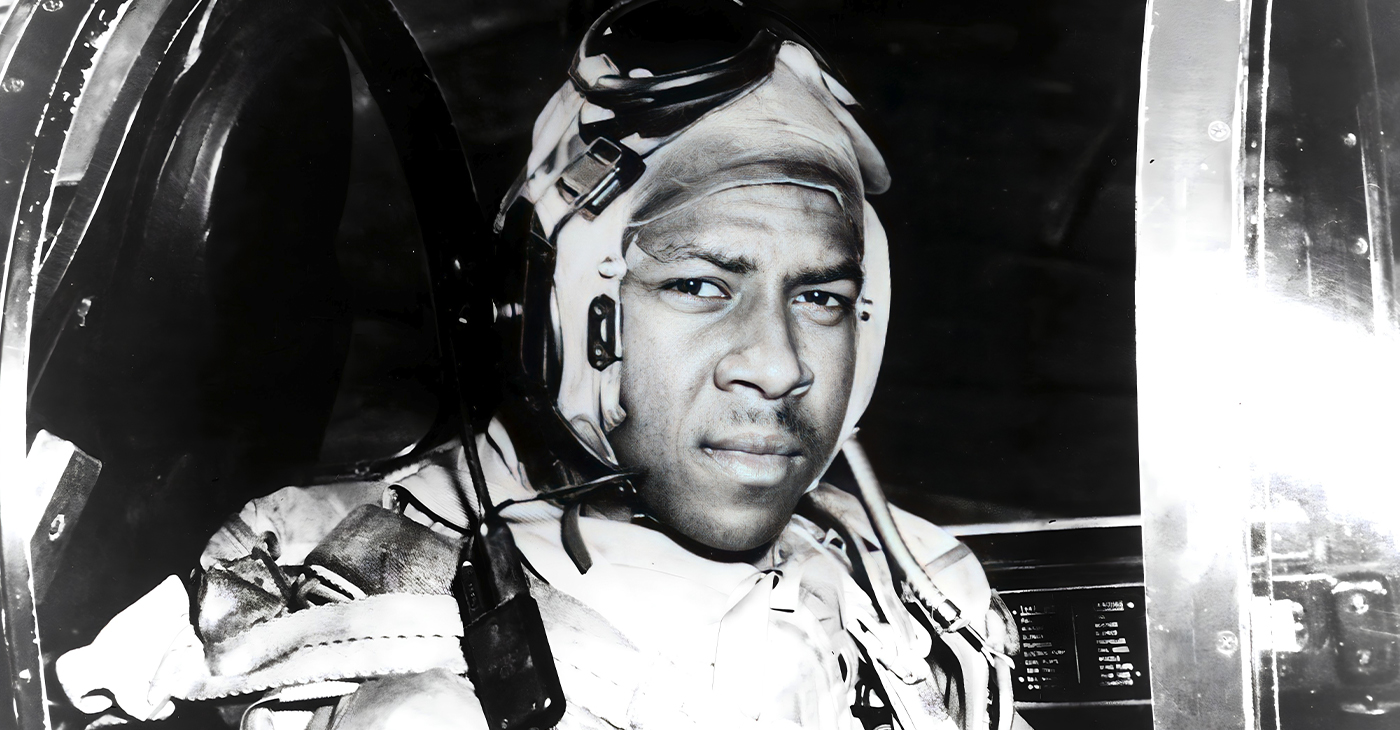
Jesse Leroy Brown: Proof of Persistence
From his days as a sharecropper in Hattiesburg, Mississippi, James Leroy Brown (1926−1950) dreamed of becoming a pilot. In school, he excelled at math and became a top athlete. This level of determination was his ticket to enter Ohio State University in 1944

By Tamara Shiloh
From his days as a sharecropper in Hattiesburg, Mississippi, James Leroy Brown (1926−1950) dreamed of becoming a pilot. In school, he excelled at math and became a top athlete. This level of determination was his ticket to enter Ohio State University in 1944.
On leaving Hattiesburg, Brown’s high school principal penned a letter to him saying: “As the first of our graduates to enter a predominantly white university, you are our hero.” And that hero worked even harder to remain there. To earn money to pay for his education, Brown worked a midnight shift on the Pennsylvania Railroad. After loading boxcars all night, he worked on maintaining a high GPA during the day.
To help pay his tuition, Brown joined the Naval Reserve after seeing a recruitment poster on campus. Students were being sought for a new naval aviation program. People around him only offered discouraging remarks, telling Brown that he would “never make it to the cockpit of a Navy aircraft.” But the comments only fueled his desire to not only apply but be accepted. It took persistence, but he was finally permitted to take the qualification exams.
Brown underwent five hours of written tests, several oral tests, and a physical that proved rigorous. Yet he made it through every step. Afterwards, he wrote to a childhood friend: “I’m not sure the Navy really wants me.” But in March of 1947, he received orders to Selective Flight Training in Glenview, Ill., and later to additional training at Naval Air Station Ottumwa and Naval Air Station Pensacola.
On Oct. 21, 1948, Brown became the first African American man to complete Navy flight training. A story with the headline First Negro Naval Aviator was published the following day. It was quickly picked up by the Associated Press, and Brown’s photo appeared in Life magazine.
Assigned to fighter squadron VF-32 aboard USS Wright where he served as section leader, Brown flew a Vought F4U-4 Corsair. In Oct. of 1950, the squad was a part of Fast Carrier Task Force 77 and deployed to Korea to assist U.N. forces.
It was Dec. 4, 1950, when Brown’s voice was heard over the radio: “I think I may have been hit. I’ve lost my oil pressure.” Soon after, he crash-landed his Corsair on the side of a snowy mountain. His wingman, Lt. Thomas J. Hudner Jr., realized something was wrong — Brown hadn’t emerged from the cockpit.
Hudner brought his Corsair down, where he discovered Brown trapped in his aircraft, bleeding and in pain. Trapped in his cockpit by a damaged instrument panel, Brown could not be rescued. He asked Hudner to tell his wife, Daisy, how much he loved her before he died.
Brown’s shipmates honored him with a warrior’s funeral. He posthumously received the Distinguished Flying Cross, the Air Medal, and the Purple Heart.
Learn more about Brown, Hunder, and their friendship during the Korean War in the YA adaptation “Devotion: An Epic Story of Heroism and Friendship,” by Adam Makos.
Activism
Oakland Post: Week of April 24 – 30, 2024
The printed Weekly Edition of the Oakland Post: Week of April 24 – 30, 2024

To enlarge your view of this issue, use the slider, magnifying glass icon or full page icon in the lower right corner of the browser window. ![]()
Activism
Oakland Post: Week of April 17 – 23, 2024
The printed Weekly Edition of the Oakland Post: Week of April 17 – 23, 2024

To enlarge your view of this issue, use the slider, magnifying glass icon or full page icon in the lower right corner of the browser window. ![]()
Black History
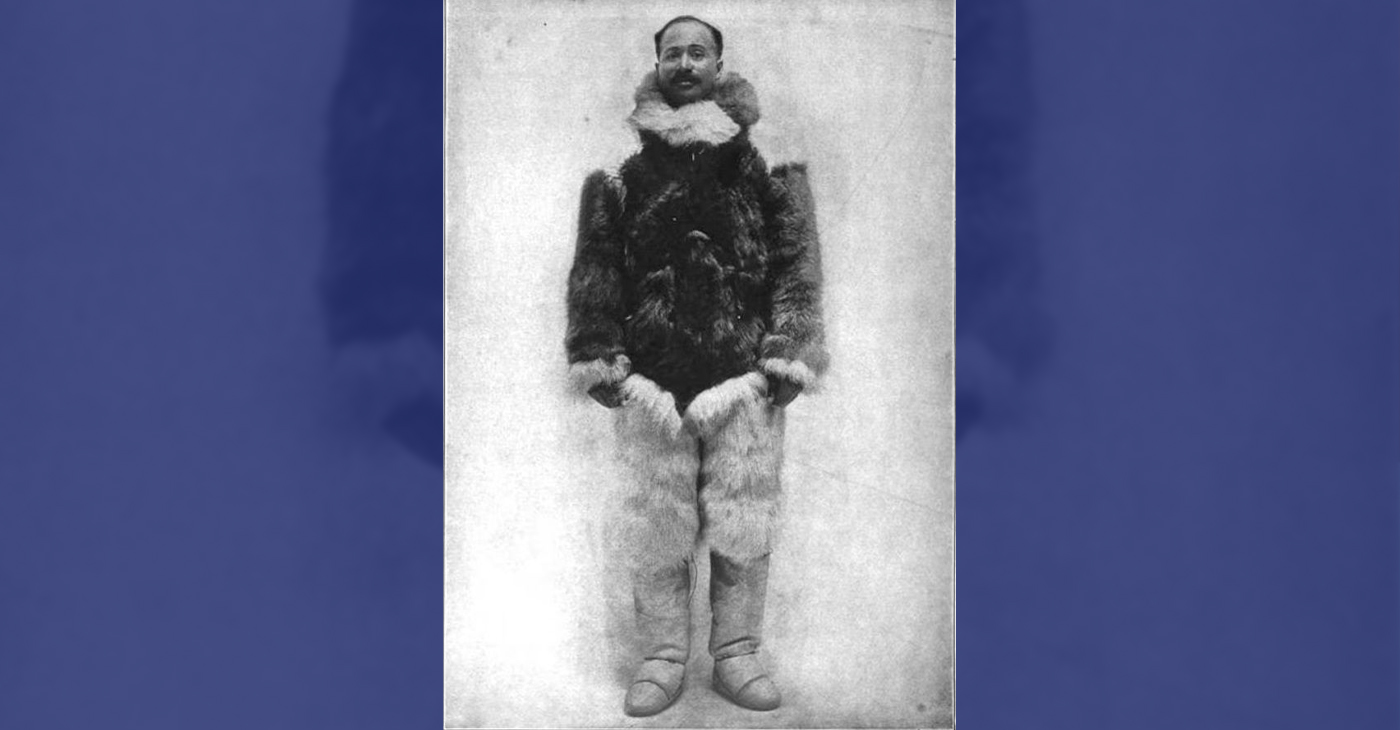
Matthew Henson: Explorer Extraordinaire
Matthew Henson, a trailblazing explorer who overcame countless obstacles to leave an incredible mark on history. Born on August 8, 1866, in Charles County, Maryland, his journey is a testament to the power of determination and the spirit of adventure.

By Tamara Shiloh
Matthew Henson, a trailblazing explorer who overcame countless obstacles to leave an incredible mark on history. Born on August 8, 1866, in Charles County, Maryland, his journey is a testament to the power of determination and the spirit of adventure.
Henson’s life began amidst the backdrop of post-Civil War America, where opportunities for African Americans were scarce. From a young age, he possessed an insatiable curiosity about the world beyond his small town. At the age of 12, he embarked on a journey that would change the course of his life forever when he joined a merchant ship as a cabin boy.
His most famous expedition was his journey to the Arctic with renowned explorer Robert E. Peary. In 1887, Henson joined Peary’s crew as a seaman and quickly proved himself to be invaluable with his skills as a navigator and craftsman. Over the course of several expeditions, Matthew endured extreme cold, treacherous terrain, and grueling conditions as he and Peary sought to reach the elusive North Pole.
In 1908–09, Peary set out on his eighth attempt to reach the North Pole. It was a big expedition, with Peary planning to leave supplies along the way. When he and Henson boarded their ship, the Roosevelt, leaving Greenland on August 18, 1909, they were joined by a large group. This included 22 Inuit men, 17 Inuit women, 10 children, 246 dogs, 70 tons of whale meat, blubber from 50 walruses, hunting gear, and tons of coal.
In February, Henson and Peary left their anchored ship at Ellesmere Island’s Cape Sheridan, along with the Inuit men and 130 dogs. They worked together to set up a trail and supplies along the way to the Pole.
Peary picked Henson and four Inuit people to join him in the final push to the Pole. However, before they reached their destination, Peary couldn’t walk anymore and had to ride in a dog sled. He sent Henson ahead to scout the way. In a later interview with a newspaper, Henson recalled being in the lead and realizing they had gone too far. The group turned back, and Henson noticed his footprints helped guide them to their destination. At that location, Henson planted the American flag.
Henson’s legacy extends far beyond his expeditions to the Arctic. He shattered racial barriers in the world of exploration and inspired countless individuals, regardless of race, to dream big and pursue their passions. In 1937, he was finally recognized for his achievements when he was inducted into The Explorers Club, an organization dedicated to promoting scientific exploration and field research.
Matthew Henson died in the Bronx, New York, on March 9, 1955, at the age of 88.
-

 Activism4 weeks ago
Activism4 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of March 27 – April 2, 2024
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoCOMMENTARY: D.C. Crime Bill Fails to Address Root Causes of Violence and Incarceration
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoMayor, City Council President React to May 31 Closing of Birmingham-Southern College
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoBeloved Actor and Activist Louis Cameron Gossett Jr. Dies at 87
-

 Community1 week ago
Community1 week agoFinancial Assistance Bill for Descendants of Enslaved Persons to Help Them Purchase, Own, or Maintain a Home
-

 Activism3 weeks ago
Activism3 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of April 3 – 6, 2024
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoV.P. Kamala Harris: Americans With Criminal Records Will Soon Be Eligible for SBA Loans
-

 Activism2 weeks ago
Activism2 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of April 10 – 16, 2024