Berkeley
Federal Grants, Loans Available to Those Affected By January Storms
Berkeley homeowners, renters, and businesses can apply for federal funding to help pay for essential repairs or serious disaster-related needs resulting from the January storms that were not covered by insurance. Apply by phone, online, using an app, or in person.
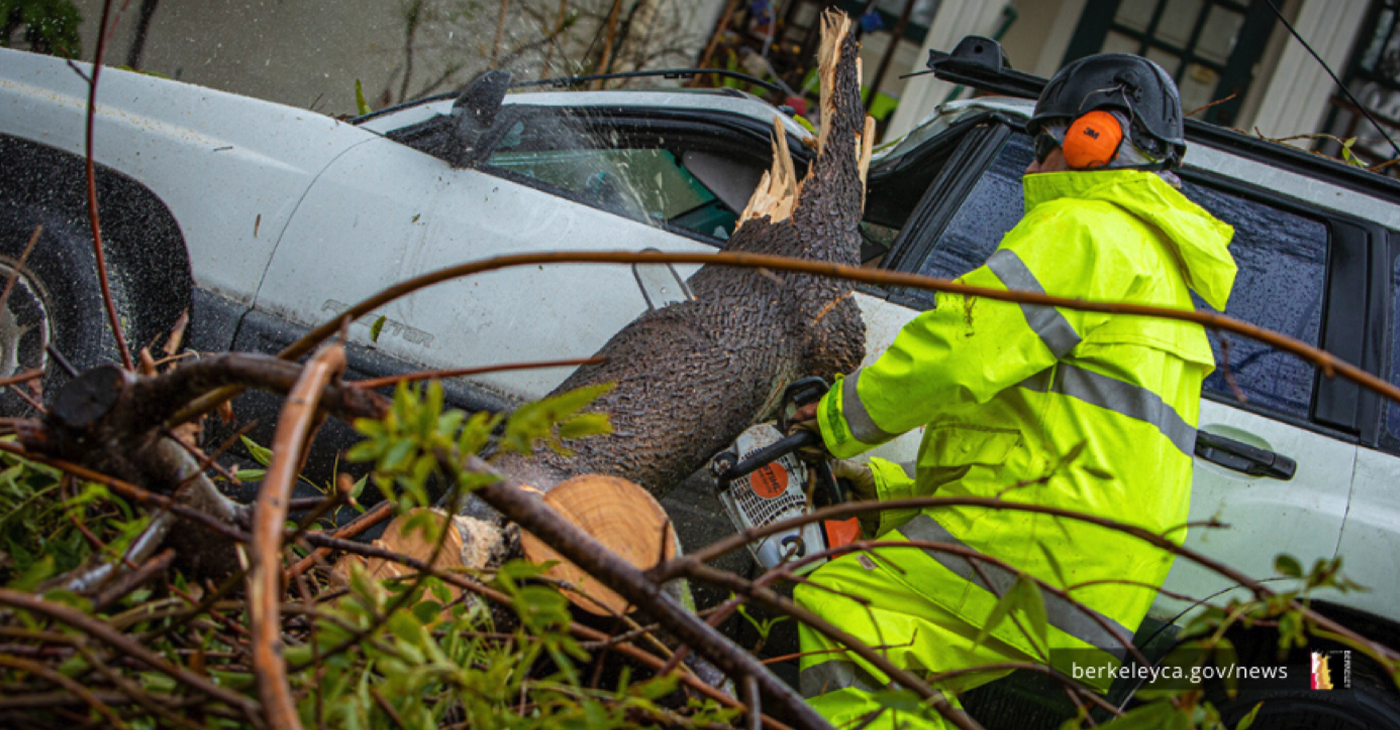

Homeowners, renters, businesses, and nonprofits can apply by March 16 for up to $37,900 in grants to cover property damage and a similar amount for other needs not covered by insurance. Small Business Administration loans can also help cover costs.
Berkeley homeowners, renters, and businesses can apply for federal funding to help pay for essential repairs or serious disaster-related needs resulting from the January storms that were not covered by insurance. Apply by phone, online, using an app, or in person. Serious disaster-related needs include medical and dental expenses, transportation, childcare, and moving and storage expenses.
These FEMA grants apply to those eligible Berkeleyans who had storm-related property damage between Dec. 31, 2022 to Jan. 30, 2023. Those who apply will be considered for two types of grants:
- up to $37,900 for property damages to a primary residence.
- up to $37,900 for other needs, such as a hotel stay while displaced, funds to replace damaged items, and increases to childcare or medical expenses during the disaster.
Loans for storm relief are also available to homeowners, renters, and businesses through the federal Small Business Administration. These loans can be paid off over thirty years and can have interest limits as low as 4 percent, depending on access to alternative credit. The loan types include:
- Homeowners: Up to $200,000 to repair or replace a primary residence
- Renters/Homeowners: Up to $40,000 to replace or repair personal property, like clothing, furniture, cars, or appliances
- Businesses: Up to $2 million to help meet financial obligations or operating expenses that would have been avoided had the disaster not happened.
Often, flood damages aren’t covered by typical homeowner’s insurance, so these can be very costly repairs. See if the grants and loans can help you and your household.
People can apply for the FEMA grants online, by phone (1-800-621-3362), via app, or at a disaster assistance center. To apply for a Small Business Administration loan, see their disaster loan website, their application portal, and a factsheet about their loan products.
APPLICANTS MUST MEET ELIGIBILITY GUIDELINES
In general, applicants for the FEMA grants must meet all of the following conditions to qualify:
- You or someone who lives with you is a U.S. citizen, a non-citizen national, or a qualified alien. If you have questions about FEMA’s citizenship and immigration requirements, please visit their website.
- You pass FEMA’s identity and occupancy verification if it applies to you.
- You have no insurance –or– have filed an insurance claim, but it does not cover all of your losses.
- You have serious needs or expenses due to losses in a Presidentially declared disaster area.
Alameda County was recently added to the major disaster declaration for California’s severe storms and flooding. The declaration allows FEMA and the Small Business Administration to provide direct support to individuals, households, nonprofits, and businesses in Alameda County and other counties in California.
FEMA DISASTER ASSISTANCE HELPS COVER UNINSURED OR UNDER-INSURED EXPENSES
Disaster assistance may include grants to help pay for temporary housing and essential home repairs as well as other serious disaster-related needs such as medical and dental expenses, transportation, childcare, and moving and storage expenses.
If you have insurance, first file a claim with your insurance provider. FEMA provides assistance to applicants for your uninsured or underinsured disaster-caused expenses and serious needs.
Applying does not guarantee that assistance will be awarded.
LEARN MORE ABOUT APPLYING
There are several ways you can apply for FEMA assistance under the Individual Assistance program:
- Online: http://www.disasterassistance.gov/
- FEMA mobile app(Google Play and iOS): https://www.fema.gov/about/news-multimedia/mobile-app-text-messages
- Phone: 1 (800) 621-3362
- In person:
Oakland Disaster Recovery Center
7001 Oakport Street, Oakland, CA 94566
Dublin Disaster Recovery Center
4825 Gleeson Drive, Dublin, CA 94568
Open February 10 until February 24, 2023, 10 am to 7pm daily.
Keep track of deadlines and apply as soon as you are able to meet the March 16 FEMA deadline.
Bay Area
Rich Lyons, Longtime Campus Business, Innovation Leader, Will Be UC Berkeley’s Next Chancellor
Rich Lyons, an established economist, former dean of the Haas School of Business and the campus’s current leader for innovation and entrepreneurship, will become the next chancellor at the University of California, Berkeley, the UC Board of Regents announced on April 10.

By Jason Pohl
Rich Lyons, an established economist, former dean of the Haas School of Business and the campus’s current leader for innovation and entrepreneurship, will become the next chancellor at the University of California, Berkeley, the UC Board of Regents announced on April 10.
The board’s unanimous confirmation makes Lyons, 63, the first UC Berkeley undergraduate alumnus since 1930 to become the campus’s top leader. In an interview this week, Lyons said he credits his Berkeley roots and his campus mentors with encouraging him to ask big questions, advance institutional culture and enhance public education — all priorities of his for the years to come.
Lyons, who will be Berkeley’s 12th chancellor, will succeed Chancellor Carol Christ, who announced last year that she’d step down as chancellor on July 1.
“I am both thrilled and reassured by this excellent choice. In so many ways, Rich embodies Berkeley’s very best attributes, and his dedication to the university’s public mission and values could not be stronger,” Christ said. “I am confident he will bring to the office visionary aspirations for Berkeley’s future that are informed by, and deeply respectful of, our past.”
Rising through the Berkeley ranks
Born in 1961, Lyons grew up in Los Altos in the early days of the Silicon Valley start-up boom.
He attended Berkeley, where he graduated in 1982 with a Bachelor of Science degree in business and finance. Lyons went on to earn his Ph.D. in 1987 in economics from MIT. After six years teaching at Columbia Business School, Lyons returned west, where in 1993 he joined the Berkeley faculty as a professor of economics and finance, specializing in the study of international finance and global exchange rates.
He’s remained on campus since, with one notable exception.
Starting in 2006, Lyons spent two years working at Goldman Sachs as the chief learning officer. It was a period that instilled in him an appreciation for leadership and the importance of organizational culture.
He carried those lessons with him when he returned to campus in 2008 and became the dean of the Haas School of Business.
While dean, Lyons oversaw the construction of Connie & Kevin Chou Hall, a state-of-the-art academic building that opened in 2017 and is celebrated for its sustainability. He also helped establish two new degree programs, linking the business school with both the College of Engineering and the Department of Molecular and Cell Biology.
But it was his creation of four distinct defining leadership principles that spurred a sweeping culture initiative at the school that stands out in the minds of many. Those values — question the status quo, confidence without attitude, students always, and beyond yourself — became a creed of sorts for new students and alumni alike.
Those values are important, Lyons said, because they shape and support the cohesive structure of a strong, connected community — spanning science and technology to the arts and humanities. They also convey the story about what it means to be at Berkeley and to believe in the university’s public mission.
“When we are great as educators, it’s identity-making,” Lyons said. “We’re helping students and others see identities in themselves that they couldn’t see.”
Lyons in January 2020 became Berkeley’s first-ever chief officer of innovation and entrepreneurship.
Building on his research exploring how leaders drive innovation and set behavioral norms and culture, Lyons worked to expand and champion Berkeley’s rich portfolio of innovation and entrepreneurship activities for the benefit of students, faculty, staff, startups and external partners.
It was a major commitment to thinking outside the box, he said. One need only look to the Berkeley Changemaker program that he helped launch in 2020 to see innovation and entrepreneurship in action.
The campuswide program with some 30 courses tells the story of what Berkeley is — the story that members of the Berkeley community can tell long into the future. Berkeley Changemaker started as an idea and its courses quickly became among the most popular academic offerings on campus.
“Over 500 students showed up,” he said. “Why? Because it’s a narrative. It’s not just a name. It’s not just a curriculum. It’s not just a course. It’s a way of living, and it’s a way of living that Berkeley has occupied forever. This idea that there’s got to be a better way to do this, question the status quo.”
Activism
Oakland’s ‘Green the Church,’ Others, Host a Climate Revival
On April 20, Oakland’s Green The Church California (GTC) and the Center For Food, Faith and Justice will celebrate Earth Day and present a Climate Revival event titled “Growing Healthy Communities From Soil To The Soul” at McGee Avenue Baptist Church at 1640 Stuart St, Berkeley, CA. The day will include inspiring talks, interactive workshops, networking opportunities, and a special panel on Food Sovereignty and Global Food Resilience.

Growing Healthy Communities from Soil to the Soul in Berkeley
By Y’Anad Burrell
On April 20, Oakland’s Green The Church California (GTC) and the Center For Food, Faith and Justice will celebrate Earth Day and present a Climate Revival event titled “Growing Healthy Communities From Soil To The Soul” at McGee Avenue Baptist Church at 1640 Stuart St, Berkeley, CA,
The day will include inspiring talks, interactive workshops, networking opportunities, and a special panel on Food Sovereignty and Global Food Resilience.
The keynote speaker is Rev. Danté R. Quick, PhD, senior pastor of First Baptist Church of Lincoln Gardens in Somerset, N.J. Quick is well known in the Bay Area, having served for more than 10 years as pastor of Friendship Missionary Baptist Church in Vallejo, CA.
Green The Church, founded in 2010 by Rev. Dr. Ambrose Carroll, Sr., and headquartered in Oakland, helps galvanize Black churches and their local communities and leaders to address issues critical to populations historically disengaged from conversations around pollution and health, climate change, and sustainability and energy efficiency.
The organization collaborates with major environmental, sustainability, food security, faith, and community-based non-profit organizations, and is committed to “creation justice”—care and justice for God’s people and the planet—and building the Beloved Community.
Environmental justice has long been a pressing concern for communities of color who bear the brunt of pollution and ecological degradation. Climate change exacerbates these issues, disproportionately impacting vulnerable communities. Recognizing this urgency, Black churches across the country are taking action.
With deep roots in the African American community and its commitment to social justice, the Black Church has become an essential advocate for sustainable practices and policies.
Over the past 14 years, in a powerful collaboration with significant environmental, sustainability, food security, faith, and community-based non-profit organizations, GTC has created a cadre of Black churches engaging in the environmental justice, climate, and sustainability movement.
GTC presently works with more than 1,000 pastors and congregations across the U.S., and groups in the Bahamas, Ghana, Nigeria, and the UK, showing that we can make a difference together.
The partnership between environmental justice advocates and the Black Church extends beyond individual congregations. Green The Church provides resources and support for faith communities seeking to address climate change and promote environmental justice.
Through collaboration, initiatives such as energy efficiency programs, solar installations, and environmental education have been implemented in Black churches nationwide. These efforts reduce the carbon footprint and save money on energy bills, benefiting the congregations and their communities.
The involvement of the Black Church in the fight against climate change is not just a participation, it’s a powerful message that galvanizes action across communities.
By integrating environmental justice into their ministry, Black churches are demonstrating that addressing climate change is not only a matter of science but also of social and moral responsibility, inspiring change at a grassroots level.
For more information, go to: www.greenthechurch.org.
Activism
Who are the Alameda County District 4 Supervisor Candidates’ Top Campaign Contributors?
Below, we’ve listed each candidate’s 10 highest campaign contributors. For Miley, two of his top campaign donors also bought their own advertisements to support him and/or oppose Esteen through independent expenditures. Such expenditures, though separate from campaign donations, are also public record, and we listed them. Additionally, the National Organization of Realtors has spent about $70,500 on their own independent expenditures to support Miley.

By Zack Haber
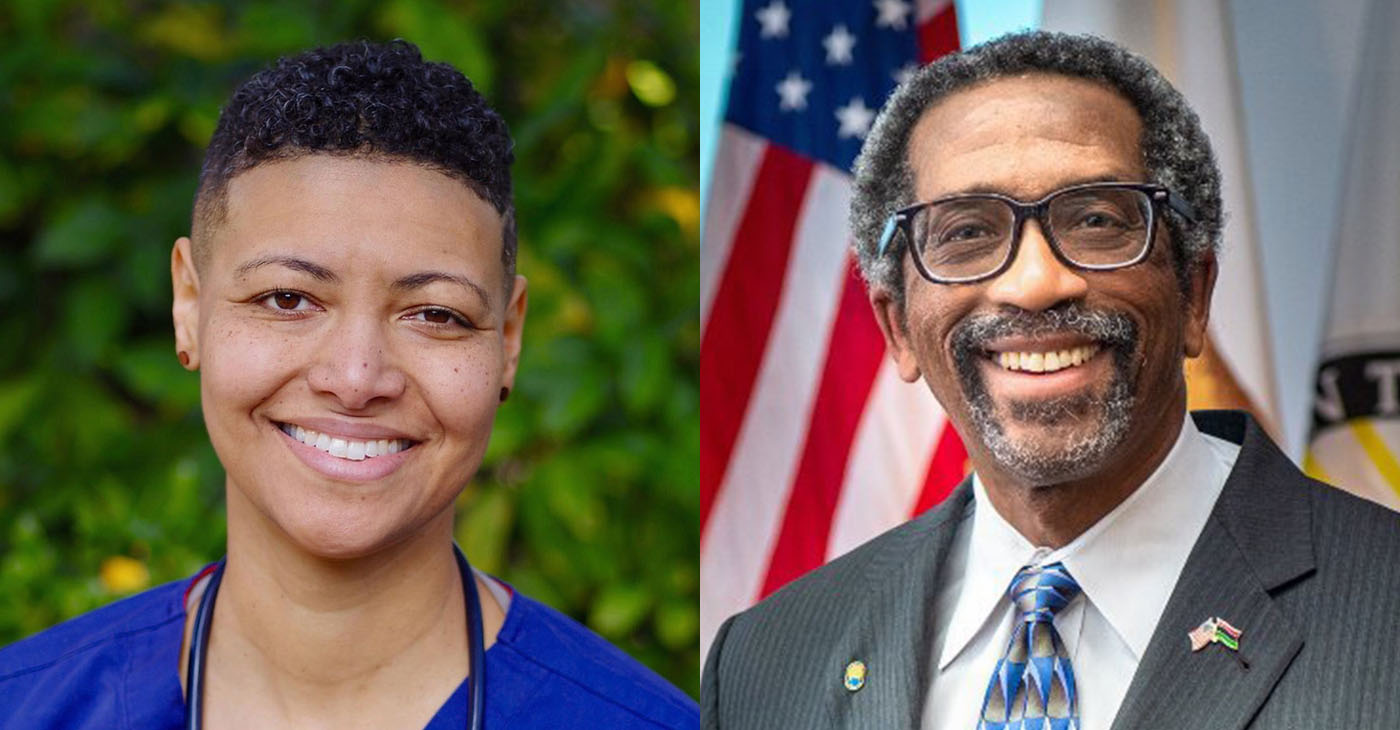
Nate Miley, who has served on Alameda County’s Board of Supervisors since 2000, is running for reelection to the District 4 supervisor seat.
Jennifer Esteen, a nurse and activist, is seeking to unseat him and become one of the five members of the powerful board that sets the county’s budget, governs its unincorporated areas, and oversees the sheriff, Alameda Health System, and mental health system.
District 4 includes most of East Oakland’s hills and flatlands beyond Fruitvale, part of Pleasanton and unincorporated areas south of San Leandro like Ashland and Castro Valley.
Voting is open and will remain open until March 5.
In California, campaign donations of $100 or more are public record. The records show that Miley has received about $550,000 in total campaign donations since he won the previous District 4 election in March 2020. Esteen has raised about $255,000 in total campaign donations since she started collecting them last July. All figures are accurate through Feb. 20.
While Miley has raised more money, Esteen has received donations from more sources. Miley received donations of $100 or more from 439 different sources. Esteen received such donations from 507 different sources.
Below, we’ve listed each candidate’s 10 highest campaign contributors. For Miley, two of his top campaign donors also bought their own advertisements to support him and/or oppose Esteen through independent expenditures. Such expenditures, though separate from campaign donations, are also public record, and we listed them. Additionally, the National Organization of Realtors has spent about $70,500 on their own independent expenditures to support Miley.
Nate Miley’s top campaign contributors:
The California Apartment Association, a trade group representing landlords and investors in California’s rental housing business, has spent about $129,500 supporting Miley’s election bid through about $59,500 in ads against Esteen, $55,000 in ads supporting Miley, and $15,000 in campaign donations.
The independent expenditure committee Preserve Agriculture in Alameda County has spent about $46,025 supporting Miley through about $27,200 in their own ads, and $18,825 in donations to his campaign. Preserve Agriculture has supported reelection efforts for former Alameda County DA Nancy O’Malley, and Sheriff Greg Ahern, a republican. It’s received funding from Chevron, PG&E, and a the California Apartment Association.
Organizations associated with the Laborers’ International Union of North America, or LiUNA, have donated about $35,000 in total. Construction and General Laborers Local 304, a local chapter of the union representing which represents over 4,000 workers, donated $20,000.
Laborers Pacific Southwest Regional Organizing Coalition, which represents 70,000 LiUNA members in Arizona, California, Hawaii and New Mexico, donated $15,000.
William ‘Bill’ Crotinger and the East Oakland-based company Argent Materials have donated $26,000. Crotinger is the president and founder of Argent, a concrete and asphalt recycling yard. Argent’s website says it is an eco-friendly company that diverts materials from landfills. In 2018, Argent paid the EPA $27,000 under a settlement for committing Clean Water Act violations.
Michael Morgan of Hayward, owner of We Are Hemp, a marijuana dispensary in Ashland, has donated $21,500.
Alameda County District 1 Supervisor David Haubert has donated $21,250 from his 2024 reelection campaign. He’s running unopposed for the District 1 seat.
SEIU 1021, which represents over 60,000 workers in local governments, non-profit agencies, healthcare programs, and schools in Northern California, has donated $20,000.
UA Local 342, which represents around 4,000 pipe trades industry workers in Contra Costa and Alameda counties, donated $20,000.
The union representing the county’s deputy sheriffs, Deputy Sheriff’s Association of Alameda County, has donated $17,000.
Becton Healthcare Resources and its managers have donated $14,625. Becton’s mission statement says it provides “behavioral health management services to organizations and groups that serve the serious and persistent mentally ill population.”
Jennifer Esteen’s top campaign contributors:
Mary Quinn Delaney of Piedmont, founder of Akonadi Foundation, has donated $20,000. Akonadi Foundation gives grants to nonprofit organizations, especially focusing on racial justice organizing,
Bridget Galli of Castro Valley has donated $7,000. Galli is a yoga instructor and a co-owner of Castro Valley Yoga.
Rachel Gelman of Oakland has donated $5,000. Gelman is an activist who has vowed to redistribute her inherited wealth to working class, Indigenous and Black communities.
California Worker Families Party has donated $5,000. The organization’s website describes itself as a “grassroots party for the multiracial working class.”
David Stern of Albany has donated $5,000. Stern is a retired UC Berkeley Professor of Education.
Oakland Rising Committee—a collaborative of racial, economic, and environmental justice organizations—has donated about $3,050.
Fredeke Von Bothmer-Goodyear, an unemployed resident of San Francisco, has donated $2,600.
Robert Britton of Castro Valley has donated $2,500. Britton is retired and worked in the labor movement for decades.
Progressive Era PAC has donated about $2,400. Its mission statement says it “exists to elect governing majorities of leaders in California committed to building a progressive era for people of color.”
East Bay Stonewall Democrats Club has donated $2,250. The club was founded in 1982 to give voice to the East Bay LGBTQIA+ communities.
-

 Activism4 weeks ago
Activism4 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of March 20 – 26, 2024
-

 #NNPA BlackPress3 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress3 weeks agoCOMMENTARY: D.C. Crime Bill Fails to Address Root Causes of Violence and Incarceration
-

 #NNPA BlackPress3 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress3 weeks agoMayor, City Council President React to May 31 Closing of Birmingham-Southern College
-

 #NNPA BlackPress3 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress3 weeks agoCOMMENTARY: Lady Day and The Lights!
-

 #NNPA BlackPress3 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress3 weeks agoFrom Raids to Revelations: The Dark Turn in Sean ‘Diddy’ Combs’ Saga
-

 #NNPA BlackPress3 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress3 weeks agoBaltimore Key Bridge Catastrophe: A City’s Heartbreak and a Nation’s Alarm
-

 #NNPA BlackPress3 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress3 weeks agoBaltimore’s Key Bridge Struck by Ship, Collapses into Water
-

 Activism3 weeks ago
Activism3 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of March 27 – April 2, 2024