Black History
Descendants of Enslaved Africans to Receive $50 Million as Part of Wealth-Building Initiative
An ambitious wealth-building initiative will provide 800 Black residents of Minnesota, South Dakota and North Dakota with $50,000 grants over the next eight years to support economic justice and financial well-being for descendants of enslaved Africans during the trans-Atlantic slave trade.

By Niara Savage, published in the Minnesota Spokesman-Recorder, an NNPA member
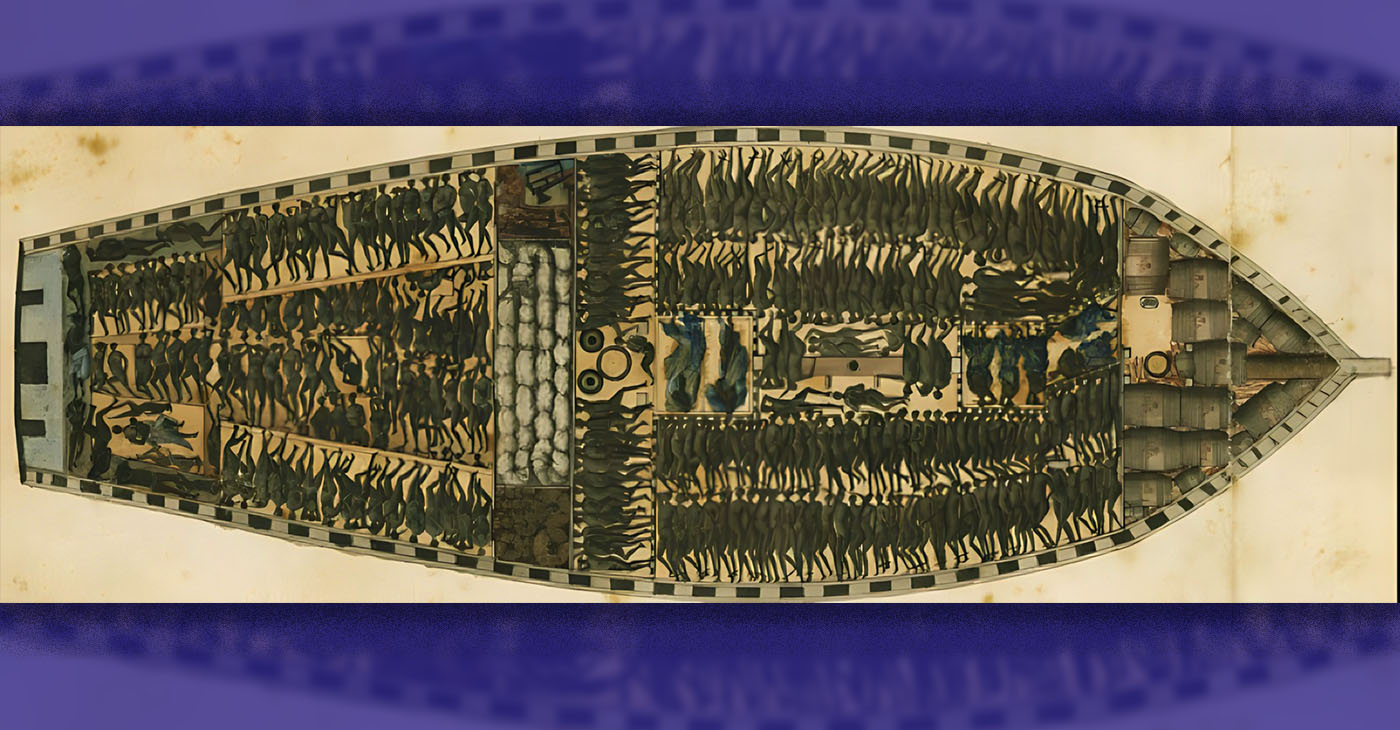
The promise of 40 acres and a mule
An ambitious wealth-building initiative will provide 800 Black residents of Minnesota, South Dakota and North Dakota with $50,000 grants over the next eight years to support economic justice and financial well-being for descendants of enslaved Africans during the trans-Atlantic slave trade.
The $50 million Open Road Fund, financed by the Bush Foundation headquartered in St. Paul, is intended to address race-based economic disparities and cultivate Black wealth. Indeed, the grants should not be labeled as “reparations” because the funds are simply not enough to repair the generational harms inflicted by the institution of slavery, said Danielle Mkali, senior director of community wealth-building at Nexus Community Partners. The nonprofit is stewarding the funds through community engagement and disbursement.
“It shares a lot of the spirit of what people think of when they think about reparations, and the reason why we are being so clear about distinguishing the Open Road Fund from reparations is that, as it’s designed now…it’s not nearly enough in terms of reparations for what is owed to Black descendants of enslaved African people,” Mkali said.
“What reparations should do and will do is impact every descendant of enslaved African people. It would be a profound and significant apology from our state governments, from our national governments. There would be a profound investment financially, educationally, with all kinds of different resources that attempt to acknowledge what descendants of enslaved African people have endured, and what our ancestors have endured,” Mkali added, noting that the fund will only reach about 100 people each year through 2031.
A 2022 study by WalletHub found that Minnesota has the third-largest racial wealth gap in the country behind Wisconsin and Washington, D.C. In 2018, White Minnesotans’ median household income was $73,027 while the median Black household income was less than half that figure at $36,849.
“We don’t want people to think, ‘Oh well, the Black folks in Minnesota, North and South Dakota are good now.’ We aren’t,” Mkali said.
Earlier this year, the St. Paul City Council took a step toward addressing racial disparities in the city when it established the Saint Paul Recovery Act Community Reparations Commission to serve as an advisory body to the city council and mayor on repairing damage caused by systemic racism in the city that led to racial disparities in generational wealth, homeownership, health care, education, employment and fairness within the criminal justice system among Black descendants of enslaved Africans.
Recipients of the $50,000 Open Road Fund grants can use the money for a variety of wealth-building projects, including buying a home, paying off debt, estate planning, investing in life insurance, covering tuition costs or starting a business. People can apply for the grants as individuals or as a part of a group on the Nexus Community Partners website (https://www.nexuscp.org/open-road-fund/).
Applicants’ goals must be aligned with one of five categories of wealth-building including housing and housing stability, education, financial well-being, health and healing and ownership and economic justice.
The application for the Open Road Fund opened on June 19 (Juneteenth) and will close on July 28. To be eligible, applicants must be aged 14 or older, a resident of Minnesota, South Dakota, or North Dakota, and a descendant of an African person enslaved during the trans-Atlantic slave trade. There are no income caps or minimums. A separate $50 million trust aims to support Native and Indigenous people in the region.
In a two-part process, applicants will first complete initial registration that confirms eligibility for the grant and then discuss how they hope to use the money to achieve their wealth-building goals. A diverse panel composed of individuals who also meet the eligibility requirements for applicants will review applications.
After passing the initial application phase, 100 applicants will be selected at random to receive the awards. “If you’ve completed the application fully, and you’ve said what your wealth-building project will be, you will be put into the randomization tool,” Mkali said. “We’re not saying one wealth-building project has more merit than another wealth-building project.”
Single parents, people with disabilities, formerly incarcerated individuals, senior citizens, and members of the LGBT community are especially encouraged to apply. Recipients will be required to attend orientation and training workshops and complete an evaluation survey one year after receiving the funds. They’ll also have access to educational wealth-building webinars.
Nexus Community Partners hopes the Open Road Fund will encourage more funders to release dollars directly into the Black community.
“The stipulation from the beginning from the Bush Foundation was that the dollars needed to go directly into individual’s hands and not be granted to nonprofit organizations. The purpose of the fund would be to directly impact people’s individual wealth-building,” Mkali said.
Activism
Oakland Post: Week of April 24 – 30, 2024
The printed Weekly Edition of the Oakland Post: Week of April 24 – 30, 2024

To enlarge your view of this issue, use the slider, magnifying glass icon or full page icon in the lower right corner of the browser window. ![]()
Activism
Oakland Post: Week of April 17 – 23, 2024
The printed Weekly Edition of the Oakland Post: Week of April 17 – 23, 2024

To enlarge your view of this issue, use the slider, magnifying glass icon or full page icon in the lower right corner of the browser window. ![]()
Black History
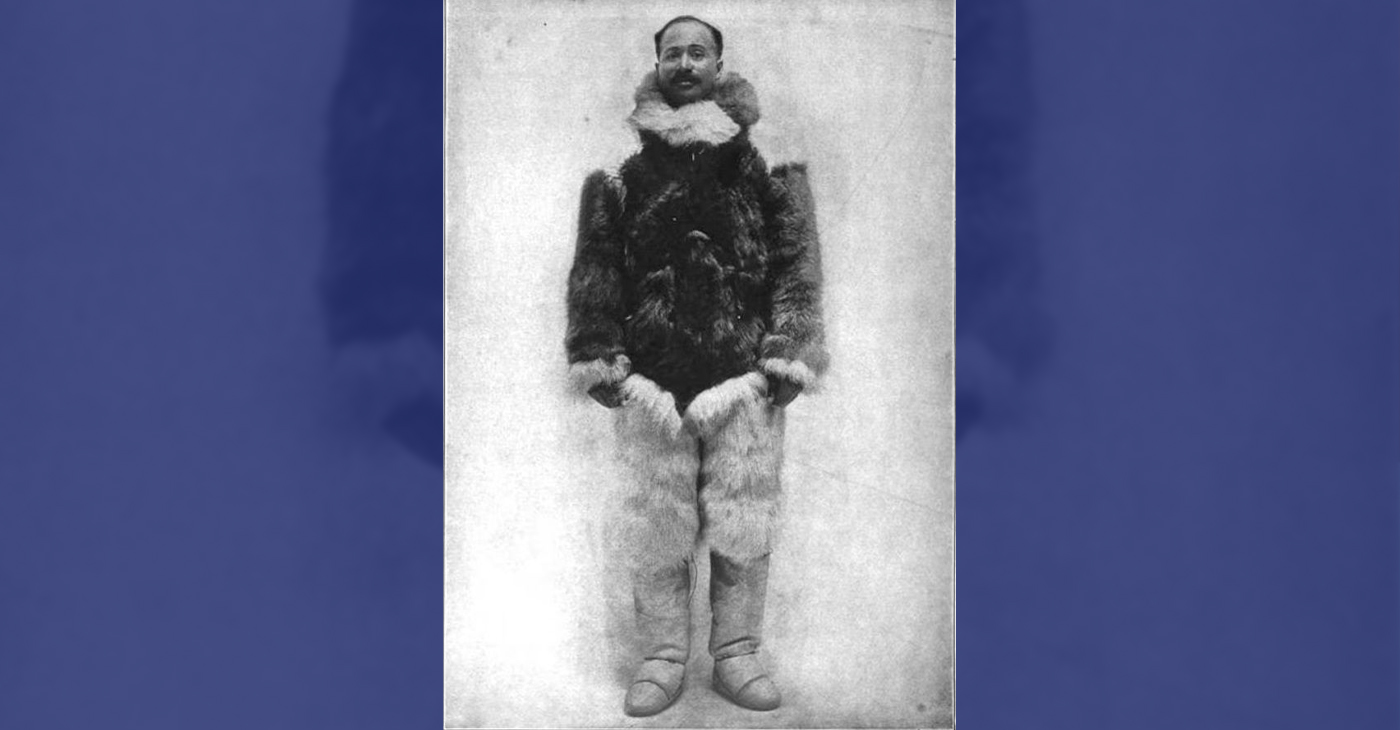
Matthew Henson: Explorer Extraordinaire
Matthew Henson, a trailblazing explorer who overcame countless obstacles to leave an incredible mark on history. Born on August 8, 1866, in Charles County, Maryland, his journey is a testament to the power of determination and the spirit of adventure.

By Tamara Shiloh
Matthew Henson, a trailblazing explorer who overcame countless obstacles to leave an incredible mark on history. Born on August 8, 1866, in Charles County, Maryland, his journey is a testament to the power of determination and the spirit of adventure.
Henson’s life began amidst the backdrop of post-Civil War America, where opportunities for African Americans were scarce. From a young age, he possessed an insatiable curiosity about the world beyond his small town. At the age of 12, he embarked on a journey that would change the course of his life forever when he joined a merchant ship as a cabin boy.
His most famous expedition was his journey to the Arctic with renowned explorer Robert E. Peary. In 1887, Henson joined Peary’s crew as a seaman and quickly proved himself to be invaluable with his skills as a navigator and craftsman. Over the course of several expeditions, Matthew endured extreme cold, treacherous terrain, and grueling conditions as he and Peary sought to reach the elusive North Pole.
In 1908–09, Peary set out on his eighth attempt to reach the North Pole. It was a big expedition, with Peary planning to leave supplies along the way. When he and Henson boarded their ship, the Roosevelt, leaving Greenland on August 18, 1909, they were joined by a large group. This included 22 Inuit men, 17 Inuit women, 10 children, 246 dogs, 70 tons of whale meat, blubber from 50 walruses, hunting gear, and tons of coal.
In February, Henson and Peary left their anchored ship at Ellesmere Island’s Cape Sheridan, along with the Inuit men and 130 dogs. They worked together to set up a trail and supplies along the way to the Pole.
Peary picked Henson and four Inuit people to join him in the final push to the Pole. However, before they reached their destination, Peary couldn’t walk anymore and had to ride in a dog sled. He sent Henson ahead to scout the way. In a later interview with a newspaper, Henson recalled being in the lead and realizing they had gone too far. The group turned back, and Henson noticed his footprints helped guide them to their destination. At that location, Henson planted the American flag.
Henson’s legacy extends far beyond his expeditions to the Arctic. He shattered racial barriers in the world of exploration and inspired countless individuals, regardless of race, to dream big and pursue their passions. In 1937, he was finally recognized for his achievements when he was inducted into The Explorers Club, an organization dedicated to promoting scientific exploration and field research.
Matthew Henson died in the Bronx, New York, on March 9, 1955, at the age of 88.
-

 Activism4 weeks ago
Activism4 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of March 27 – April 2, 2024
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoBeloved Actor and Activist Louis Cameron Gossett Jr. Dies at 87
-

 Community1 week ago
Community1 week agoFinancial Assistance Bill for Descendants of Enslaved Persons to Help Them Purchase, Own, or Maintain a Home
-

 Activism3 weeks ago
Activism3 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of April 3 – 6, 2024
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoV.P. Kamala Harris: Americans With Criminal Records Will Soon Be Eligible for SBA Loans
-

 Activism2 weeks ago
Activism2 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of April 10 – 16, 2024
-

 Community1 week ago
Community1 week agoAG Bonta Says Oakland School Leaders Should Comply with State Laws to Avoid ‘Disparate Harm’ When Closing or Merging Schools
-

 Community6 days ago
Community6 days agoOakland WNBA Player to be Inducted Into Hall of Fame