#NNPA BlackPress
Cincinnati’s First Black Female Juvenile Court Judge Faces Jail Time After Sham Trial Exposes Racism, Cronyism and Corruption
NNPA NEWSWIRE — Tracie Hunter, Cincinnati’s first African-American female Juvenile Court Judge in Hamilton County’s 110-year history, who’s also a church pastor in Cincinnati, remains buoyed by the support of so many including The Coalition for a Just Hamilton County which is composed of members from the Interdenominational Ministry Alliance; the Cincinnati Chapter of the NAACP; the local chapter of Al Sharpton’s National Action Network; the Black United Front; the Southern Christian Leadership Council; the Nation of Islam and others.
By Stacy M. Brown, NNPA Newswire Correspondent
@StacyBrownMedia
Cincinnati, the third largest city in Ohio, sits on a hilly landscape along the Ohio River at the Kentucky border just opposite Covington and Newport.
It’s ice cold temperatures during the winter is only surpassed by the cold-blooded racial history of the Queen City.
Nearly 20 years after a race riot wreaked destruction downtown and many of the city’s already worn neighborhoods, the City Council called for a study to identify practices that might contribute to institutional racism.
What they haven’t addressed is the travesty of a racially- and politically-motivated conviction of Tracie Hunter, Cincinnati’s first African-American female Juvenile Court Judge in Hamilton County’s 110-year history.
Hunter was also the first Democrat to serve in that capacity.
However, on July 22, Hunter is scheduled to begin a six-month jail sentence.
She was convicted for “securing a public contract” – she says that she still doesn’t know what that means.
Shockingly, the jury was mostly comprised of wives of her political foes, and friends, attorneys and neighbors of the prosecutor.
One juror worked for WCPO Television, a station that has filed numerous lawsuits against Hunter.
Another juror was a lawyer who worked at the firm that represented WCPO.
Court documents revealed that the jury foreman contributed $500 to state Sen. Bill Seitz, the father of county jury coordinator Brad Seitz, who was responsible for compiling the panel of jurors.
Three black jurors, none of whom had known ties to prosecutors and all of whom held out for acquittal, ultimately succumbed to pressure by other panelists and a judge who refused to allow defense lawyers to poll the jury after announcing the verdict.
In all American trials, particularly those that end in guilty verdicts, it’s the right of attorneys to request the judge to poll all 12 jurors to ensure each were in agreement with the verdict.
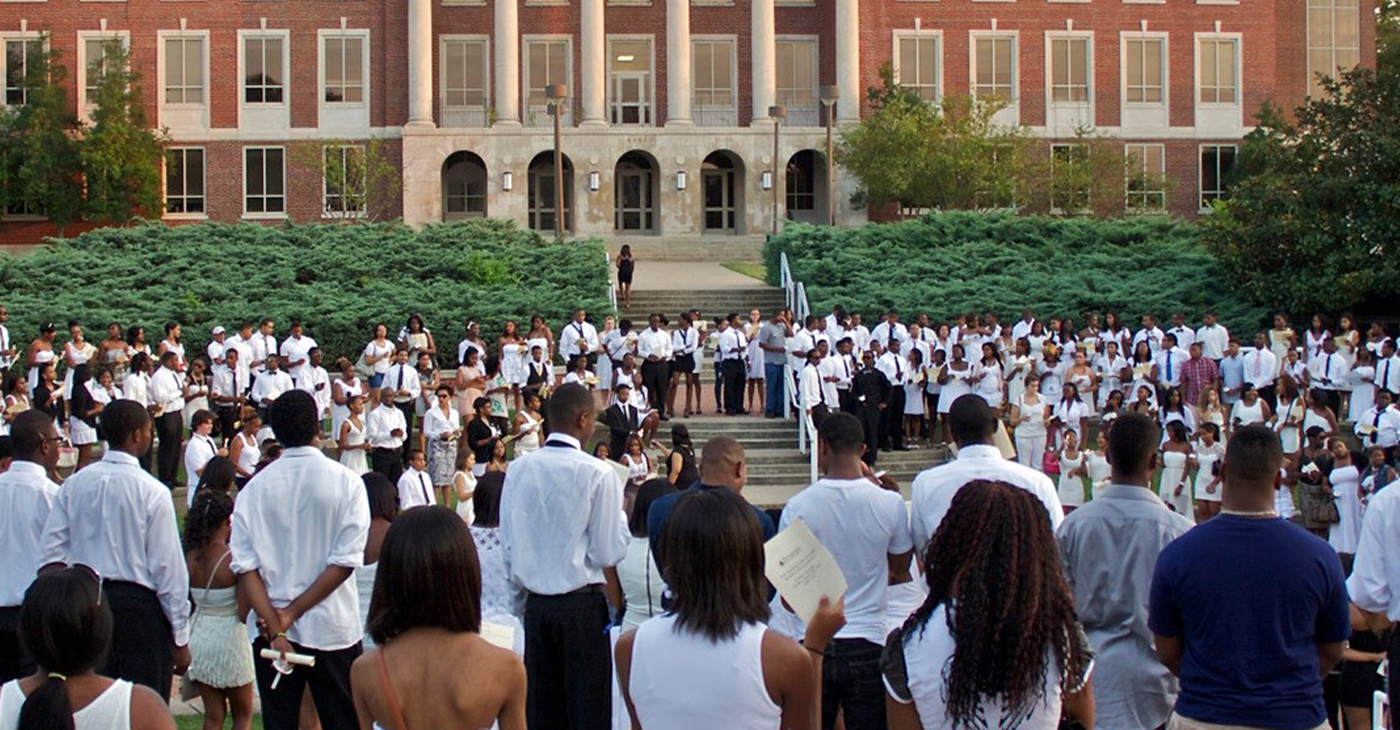
“The judge refused a motion for a retrial after he refused to poll the jury, in clear violation of the law and at the request of my attorney,” Hunter told NNPA Newswire during the annual National Newspaper Publishers Association (NNPA) annual convention in Cincinnati.
Hunter was joined by a large group of supporters sporting black T-shirts imprinted with the logo, “Justice for Judge Tracie Hunter.”
“At the close of the trial, three jurors came forward and said that their finding was ‘not guilty’ and if Judge Norbert Nadel had polled the jury, they would have said so,” Hunter said.
After being convicted on one of 10 counts filed against her, Hunter lost her appeal.
However, she and her supporters were quick to point out that the judge presiding over the appeal was none other than Prosecutor Joe Deters’ mother-in-law, Judge Sylvia Hendon.
Representatives for Deters and Hendon declined to comment to NNPA Newswire.
Hunter, who earned her undergraduate degree from Miami University in 1988 and her Juris Doctorate from the University of Cincinnati College of Law in 1992, won election in 2010, stunning the Republican-led city by defeating GOP contender John Williams.
Williams and the GOP contested Hunter’s victory and a heated court battle and numerous appeals by the Hamilton County Board of Elections which refused to count more than 800 votes from majority Democrat and Black precincts, ensued.
Hunter then filed a federal lawsuit to have those voted counted.
While the court finally ordered those votes to be counted, election officials still certified Williams as the victor.
However, once the votes were counted, the election was overturned in Hunter’s favor.
The 18-month period proved pivotal because then-Gov. John Kasich appointed Williams to the bench and the state Supreme Court changed the rules giving Williams administrative authority over the court.
As the senior judge and the only one elected, Hunter would have received the position of administrative judge.
Still, Hunter worked behind the bench to protect the rights of children including refusing to allow their names and faces to appear in news coverage.
Among other things, she instilled a system that focused on rehabilitation instead of incarceration.
Hunter mandated prosecutors turn over all critical evidence to defense lawyers.

Tracie Hunter, Cincinnati’s first African-American female Juvenile Court Judge in Hamilton County’s 110-year history, who’s also a church pastor in Cincinnati, is surrounded by member publishers of the Black Press of America during the National Newspaper Publishers Association 2019 Annual Convention’s Welcome Reception on June 26 in Cincinnati, OH.
She forced juvenile court to change its entire reporting system; outlawed the routine shackling of juveniles in her courtroom; exposed that juvenile case statistics were being inaccurately reported and falsified to the Ohio Supreme Court; hired African Americans in key positions; reduced default judgments; and spearheaded the change of state election laws which paved the way for ex-felons to vote.
“I also bought in people from outside of Cincinnati who affirmed that shielding these 12-year-old kids faces and preventing their names from being in the media helped to reduce any chance that they’d have a repeat run-in with law enforcement,” Hunter said.
However, the Cincinnati Enquirer and WCPO Television joined Republican county officials in the prosecutors’ and commissioners’ offices in lawsuits challenging Hunter.
“They filed 30 lawsuits in less than 9 months that I was on the bench,” Hunter said.
After serving just 18 months, her enemies found a way to silence her and end her career.
Hunter was charged with theft for using her judicial credit card to appeal the lawsuits filed against her by Deters, the prosecutor.
Now, with her law license suspended and having exhausted any savings and appeals, Hunter is facing jail.
Further frustrating is that Hunter is the lone caregiver to her ailing and aging mother.
Hunter, who’s also a church pastor in Cincinnati, remains buoyed by the support of so many including The Coalition for a Just Hamilton County which is composed of members from the Interdenominational Ministry Alliance; the Cincinnati Chapter of the NAACP; the local chapter of Al Sharpton’s National Action Network; the Black United Front; the Southern Christian Leadership Council; the Nation of Islam and others.
“They’ve tried to stop me from telling my truth and all I have is my truth,” she said, noting that she’s mostly refrained from giving interviews because the local media has only used sound bites to try and embarrass her.
“I’ve lost hope in the justice system which is why I became a judge in the first place,” Hunter said. “I’ve not lost faith in God even though they’ve tried to drive me out of this city even with what the Ku Klux Klan did,” she said, alluding to when the hooded racist group threatened 12-year-olds and their families in front of North College Hill Elementary School after Hunter ruled that their faces and names couldn’t be used in the media.
“There is so much racism, so much nepotism and so much cronyism here in Cincinnati but I just hold on to the belief that the truth shall set you free and I will continue to stand on the truth,” she said.
#NNPA BlackPress
IN MEMORIAM: Ramona Edelin, Influential Activist and Education Advocate, Dies at 78
NNPA NEWSWIRE — Born on September 4, 1945, in Los Angeles, California, activist Ramona Edelin’s early years were marked by a commitment to education and social justice. According to her HistoryMakers biography, after graduating from Fisk University with a Bachelor’s degree in 1967, she pursued further studies at the University of East Anglia in England. She earned her master’s degree before completing her Ph.D. at Boston University in 1981.
The post IN MEMORIAM: Ramona Edelin, Influential Activist and Education Advocate, Dies at 78 first appeared on BlackPressUSA.

By Stacy M. Brown, NNPA Newswire Senior National Correspondent
@StacyBrownMedia
Once upon a time, Black Americans were simply known as colored people, or Negroes. That is until Ramona Edelin came along. The activist, renowned for her pivotal roles in advancing civil rights, education reform, and community empowerment, died at her D.C. residence last month at the age of 78. Her death, finally confirmed this week by Barnaby Towns, a communications strategist who collaborated with Dr. Edelin, was attributed to cancer.
Born on September 4, 1945, in Los Angeles, California, Edelin’s early years were marked by a commitment to education and social justice. According to her HistoryMakers biography, after graduating from Fisk University with a Bachelor’s degree in 1967, she pursued further studies at the University of East Anglia in England. She earned her master’s degree before completing her Ph.D. at Boston University in 1981.
Edelin’s contributions to academia and activism were manifold. She was pivotal in popularizing the term “African American” alongside Rev. Jesse L. Jackson in the late 1980s.
Jackson had announced the preference for “African American,” speaking for summit organizers that included Dr. Edelin. “Just as we were called Colored, but were not that, and then Negro, but not that, to be called Black is just as baseless,” he said, adding that “African American” “has cultural integrity” and “puts us in our proper historical context.”
Later, Edelin told Ebony magazine, “Calling ourselves African Americans is the first step in the cultural offensive,” while linking the name change to a “cultural renaissance” in which Black Americans reconnected with their history and heritage.
“Who are we if we don’t acknowledge our motherland?” she asked later. “When a child in a ghetto calls himself African American, immediately he’s international. You’ve taken him from the ghetto and put him on the globe.”
The HistoryMakers bio noted that Edelin’s academic pursuits led her to found and chair the Department of African American Studies at Northeastern University, where she established herself as a leading voice.
Transitioning from academia to advocacy, Edelin joined the National Urban Coalition in 1977, eventually ascending to president and CEO. During her tenure, she spearheaded initiatives such as the “Say Yes to a Youngster’s Future” program, which provided crucial support in math, science, and technology to youth and teachers of color in urban areas. Her biography noted that Edelin’s efforts extended nationwide through partnerships with organizations like the National Science Foundation and the United States Department of Education.
President Bill Clinton recognized Edelin’s expertise by appointing her to the Presidential Board on Historically Black Colleges and Universities in 1998. She also co-founded and served as treasurer of the Black Leadership Forum, solidifying her standing as a respected leader in African American communities.
Beyond her professional achievements, Edelin dedicated herself to numerous boards and committees, including chairing the District of Columbia Educational Goals 2000 Panel and contributing to the Federal Advisory Committee for the Black Community Crusade for Children.
Throughout her life, Edelin received widespread recognition for her contributions. Ebony magazine honored her as one of the 100 Most Influential Black Americans, and she received prestigious awards such as the Southern Christian Leadership Award for Progressive Leadership and the IBM Community Executive Program Award.
The post IN MEMORIAM: Ramona Edelin, Influential Activist and Education Advocate, Dies at 78 first appeared on BlackPressUSA.
#NNPA BlackPress
Tennessee State University Board Disbanded by MAGA Loyalists as Assault on DE&I Continues
NNPA NEWSWIRE — Recent legislative actions in Tennessee, such as repealing police reform measures enacted after the killing of Tyre Nichols, underscore a troubling trend of undermining local control and perpetuating racist agendas. The new law preventing local governments from restricting police officers’ authority disregards community efforts to address systemic issues of police violence and racial profiling.
The post Tennessee State University Board Disbanded by MAGA Loyalists as Assault on DE&I Continues first appeared on BlackPressUSA.

By Stacy M. Brown, NNPA Newswire Senior National Correspondent
@StacyBrownMedia
Tennessee State University (TSU), the state’s only public historically Black college and university (HBCU), faces a tumultuous future as Gov. Bill Lee dissolved its board, a move supported by racist conservatives and MAGA Republicans in the Tennessee General Assembly, who follow the lead of the twice-impeached, four-times indicted, alleged sexual predator former President Donald Trump. Educators and others have denounced the move as an attack on diversity, equity, and inclusion (DE&I) and a grave setback for higher education.
Critics argue that TSU’s purported financial mismanagement is a manufactured crisis rooted in decades of underinvestment by the state government. They’ve noted that it continues a trend by conservatives and the racist MAGA movement to eliminate opportunities for Blacks in education, corporate America, and the public sector.
Gevin Reynolds, a former speechwriter for Vice President Kamala Harris, emphasizes in an op-ed that TSU’s financial difficulties are not the result of university leadership because a recent audit found no evidence of fraud or malfeasance.
Reynolds noted that the disbanding of TSU’s board is not an isolated incident but part of a broader assault on DE&I initiatives nationwide. Ten states, including Tennessee, have enacted laws banning DE&I policies on college campuses, while governors appointing MAGA loyalists to university trustee positions further undermine efforts to promote inclusivity and equality.
Moreover, recent legislative actions in Tennessee, such as repealing police reform measures enacted after the killing of Tyre Nichols, underscore a troubling trend of undermining local control and perpetuating racist agendas. The new law preventing local governments from restricting police officers’ authority disregards community efforts to address systemic issues of police violence and racial profiling.
The actions echo historical efforts to suppress Black progress, reminiscent of the violent backlash against gains made during the Reconstruction era. President Joe Biden warned during an appearance in New York last month that Trump desires to bring the nation back to the 18th and 19th centuries – in other words, to see, among other things, African Americans back in the chains of slavery, women subservient to men without any say over their bodies, and all voting rights restricted to white men.
The parallels are stark, with white supremacist ideologies used to justify attacks on Black institutions and disenfranchise marginalized communities, Reynolds argued.
In response to these challenges, advocates stress the urgency of collective action to defend democracy and combat systemic racism. Understanding that attacks on institutions like TSU are symptomatic of broader threats to democratic norms, they call for increased civic engagement and voting at all levels of government.
The actions of people dedicated to upholding the principles of inclusivity, equity, and justice for all will determine the outcome of the ongoing fight for democracy, Reynolds noted. “We are in a war for our democracy, one whose outcome will be determined by every line on every ballot at every precinct,” he stated.
The post Tennessee State University Board Disbanded by MAGA Loyalists as Assault on DE&I Continues first appeared on BlackPressUSA.
#NNPA BlackPress
Braxton Haulcy and the Expansion of Walker|West Music Academy
May 24, 2023 – Walker West Music Academy gets an early start on expansion. Join us for a Wednesday episode of The …
The post Braxton Haulcy and the Expansion of Walker|West Music Academy first appeared on BlackPressUSA.

May 24, 2023 – Walker West Music Academy gets an early start on expansion. Join us for a Wednesday episode of The …
The post Braxton Haulcy and the Expansion of Walker|West Music Academy first appeared on BlackPressUSA.
-

 Activism4 weeks ago
Activism4 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of March 27 – April 2, 2024
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoCOMMENTARY: D.C. Crime Bill Fails to Address Root Causes of Violence and Incarceration
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoMayor, City Council President React to May 31 Closing of Birmingham-Southern College
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoBeloved Actor and Activist Louis Cameron Gossett Jr. Dies at 87
-

 Community1 week ago
Community1 week agoFinancial Assistance Bill for Descendants of Enslaved Persons to Help Them Purchase, Own, or Maintain a Home
-

 Activism3 weeks ago
Activism3 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of April 3 – 6, 2024
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoV.P. Kamala Harris: Americans With Criminal Records Will Soon Be Eligible for SBA Loans
-

 Activism2 weeks ago
Activism2 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of April 10 – 16, 2024
























































8 Comments