History
AFRICVILLE: A Canadian Station for the Underground Railroad
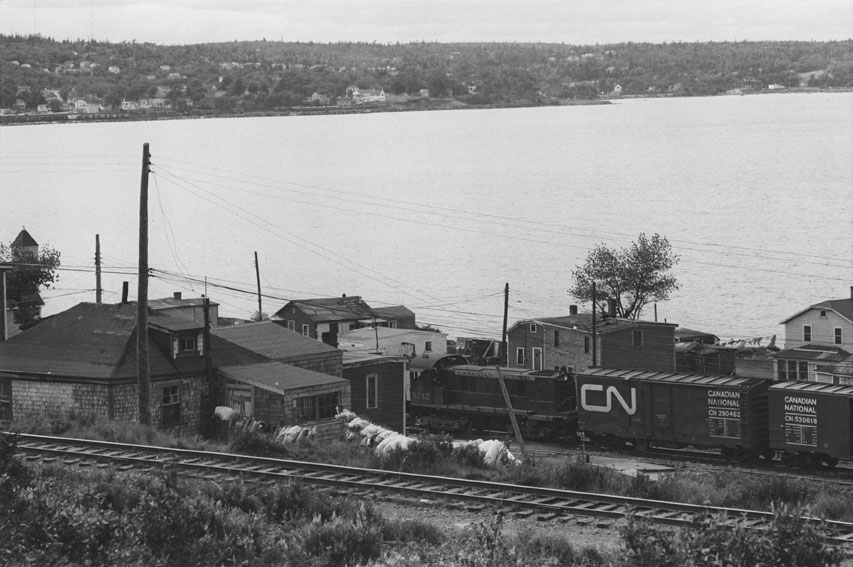
Africville was an African-Canadian village located just north of Halifax and founded in the mid-18th century. The City of Halifax demolished the once-prosperous seaside community in the 1960s in what many said was an act of racism. The mayor of the Halifax Regional Municipality apologized for the action in 2010. For many people, Africville represents the oppression faced by Black Canadians, and the efforts to right historic wrongs.
Halifax was founded in 1749, when African people held as slaves dug out roads and built much of the city. Some evidence indicates that this early Black community lived a few miles north of the city on the southern shore of the Bedford Basin—an area that became Africville. Other evidence suggests that some of the Maroons of Jamaica (Africans who escaped enslavement), resettled to Nova Scotia by the British government, moved to the basin in 1796.
The first official record of Africville is from 1761, when the land was granted to several white families, including the families of men who imported and sold enslaved African men and women.
In 1848, William Arnold and William Brown, both Black settlers, bought land in Africville. Other families followed and in 1849 Seaview African United Baptist Church was opened to serve the village’s 80 residents. After much petitioning by Africvillians, a school opened in 1883. A local resident had taught many of the children in Africville before the City school opened.
Africville residents ran fishing businesses from the Bedford Basin, selling their catch locally and in Halifax. Other residents ran farms, and several opened small stores toward the end of the 19th century. It was a haven from the anti-Black racism they faced in Halifax.
The City of Halifax collected taxes in Africville, but did not provide services such as paved roads, running water or sewers.
The City of Halifax continued to place undesirable services in Africville in the second half of the 19th century, including: a fertilizer plant, slaughterhouses, Rockhead Prison (1854), the “night-soil disposal pits” (human waste) and the Infectious Diseases Hospital (1870s). In 1915, Halifax City Council declared that Africville “will always be an industrial district.” Many Africville residents believed anti-Black racism was behind these decisions.
Multi-Ethnic Sports Hall of Fame to Tour Africville’s Black Loyalist Museum
Before the end of slavery in the United States, some freed and escaped slaves headed north to Canada’s Africville. In continuance of tradition, each July hundreds of former residents and their children head to the Africville Reunion on the former site—located on Bedford Basin’s shore on the northwestern end of Halifax Harbour in Nova Scotia—to reminisce, to re-acquaint, and re-establish themselves as a community.
While Africville as a town no longer exists, its spirit continues in the unity of its people.
The Multi-Ethnic Sports Hall of Fame (MESHOF) and its Nova Scotia partners have collaborated to tour the Black Loyalist Museum, July5 – 28, 2019. The museum was featured in the film Book of Negroes.
Arif Khatib, MESHOF founder, said the complete travel package includes a tour of several Black cities including the Black Loyalist Museum.
“Nova Scotia is considered the birthplace of modern ice hockey,” said Khatib, “Through the years MESHOF has presented educational sessions about the establishment of Colored Hockey, its upstanding role models, and an organizational talent never seen in Black sport.”
Bay Area
BART to Retire Legacy Trains in Public Ceremony April 20

The Richmond Standard
Bay Area Rapid Transit’s final dispatch of legacy trains will take place on Saturday, April 20, and will be accompanied by a retirement ceremony and a final legacy ride.
At 1 p.m., the public is invited to celebrate the last run of BART’s legacy trains during a ceremony that will take place in the free area of the plaza at MacArthur Station in Oakland.
Following the ceremony, the public is invited to board a legacy train and ride from MacArthur to Fremont Station, mirroring the initial service BART provided when it opened Sept. 11, 1972.
“It’s a 45-minute trip that travels along approximately 24 miles of the original section of tracks,” BART officials said.
Multiple legacy trains will run for the event, and all will make station stops and may turn around at Bay Fair depending on the number of attendees waiting to ride. Regular fares will apply.
“These train cars are part of the history of the Bay Area,” said Bob Powers, BART general manager. “While we are excited to modernize the system, we recognize the profound cultural importance of these cars, and we want to celebrate their rich history and give them a proper send off.”
BART is now running train cars from its Fleet of the Future project.
Those nostalgic for the older trains will be able to view three of them soon at Western Railway Museum in Suisun City.
A handful of other legacy cars will be transferred to be repurposed for short-term rentals, entertainment venues, and training facilities, according to BART. Most of the legacy cars have been recycled.
Activism
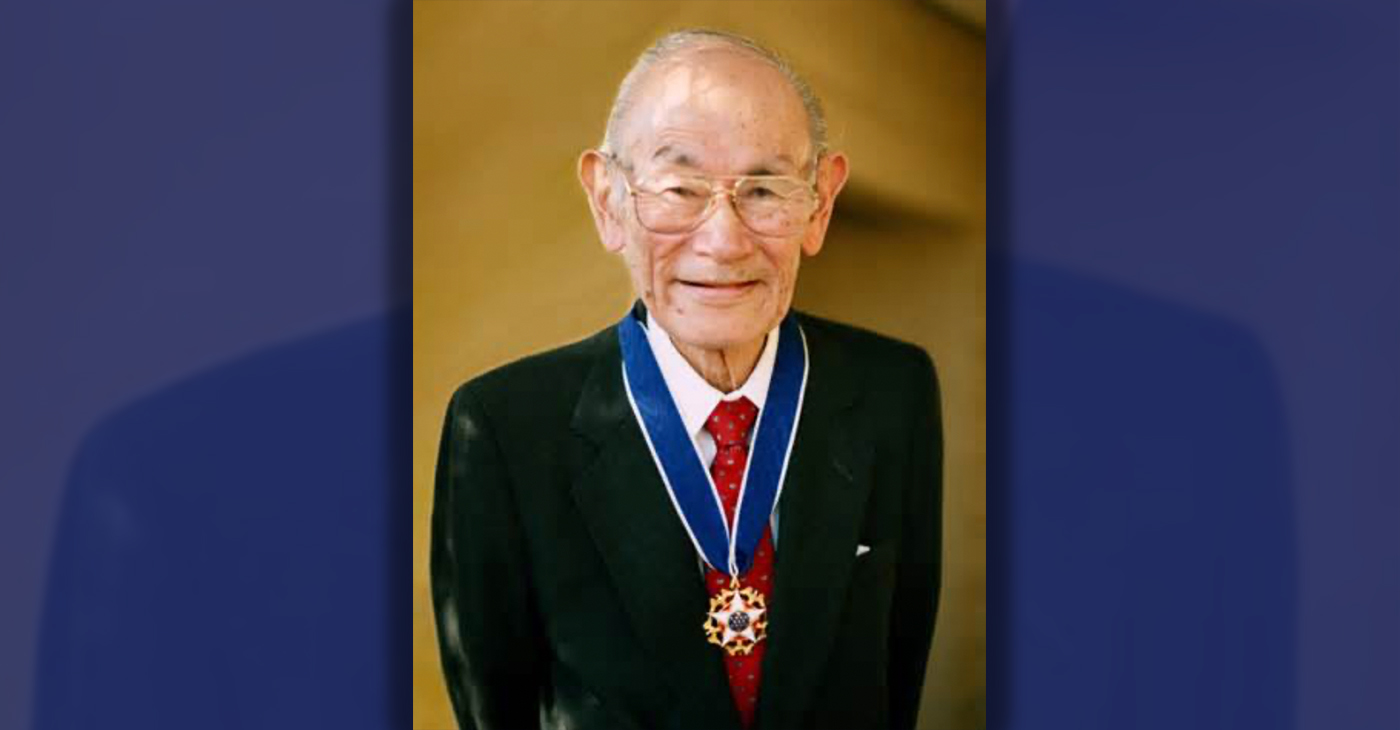
Oakland Schools Honor Fred Korematsu Day of Civil Liberties
Every Jan. 30, OUSD commemorates the legacy of Fred Korematsu, an Oakland native, a Castlemont High School graduate, and a national symbol of resistance, resilience, and justice. His defiant stand against racial injustice and his unwavering commitment to civil rights continue to inspire the local community and the nation. Tuesday was “Fred Korematsu Day of Civil Liberties and the Constitution” in the state of California and a growing number of states across the country.

By Post Staff
Every Jan. 30, OUSD commemorates the legacy of Fred Korematsu, an Oakland native, a Castlemont High School graduate, and a national symbol of resistance, resilience, and justice.
His defiant stand against racial injustice and his unwavering commitment to civil rights continue to inspire the local community and the nation. Tuesday was “Fred Korematsu Day of Civil Liberties and the Constitution” in the state of California and a growing number of states across the country.
One OUSD school is named in his honor: Fred T. Korematsu Discovery Academy (KDA) elementary in East Oakland.
Several years ago, founding KDA Principal Charles Wilson, in a video interview with anti-hate organization “Not In Our Town,” said, “We chose the name Fred Korematsu because we really felt like the attributes that he showed in his work are things that the children need to learn … that common people can stand up and make differences in a large number of people’s lives.”
Fred Korematsu was born in Oakland on Jan. 30, 1919. His parents ran a floral nursery business, and his upbringing in Oakland shaped his worldview. His belief in the importance of standing up for your rights and the rights of others, regardless of race or background, was the foundation for his activism against racial prejudice and for the rights of Japanese Americans during World War II.
At the start of the war, Korematsu was turned away from enlisting in the National Guard and the Coast Guard because of his race. He trained as a welder, working at the docks in Oakland, but was fired after the bombing of Pearl Harbor in 1941. Fear and prejudice led to federal Executive Order 9066, which forced more than 120,000 Japanese Americans out of their homes and neighborhoods and into remote internment camps.
The 23-year-old Korematsu resisted the order. He underwent cosmetic surgery and assumed a false identity, choosing freedom over unjust imprisonment. His later arrest and conviction sparked a legal battle that would challenge the foundation of civil liberties in America.
Korematsu’s fight culminated in the Supreme Court’s initial ruling against him in 1944. He spent years in a Utah internment camp with his family, followed by time living in Salt Lake City where he was dogged by racism.
In 1976, President Gerald Ford overturned Executive Order 9066. Seven years later, the 9th Circuit Court of Appeals in San Francisco vacated Korematsu’s conviction. He said in court, “I would like to see the government admit that they were wrong and do something about it so this will never happen again to any American citizen of any race, creed, or color.”
Korematsu’s dedication and determination established him as a national icon of civil rights and social justice. He advocated for justice with Rosa Parks. In 1998, President Bill Clinton gave him the Presidential Medal of Freedom saying, “In the long history of our country’s constant search for justice, some names of ordinary citizens stand for millions of souls … To that distinguished list, today we add the name of Fred Korematsu.”
After Sept. 11, 2001, Korematsu spoke out against hatred and discrimination, saying what happened to Japanese Americans should not happen to people of Middle Eastern descent.
Korematsu’s roots in Oakland and his education in OUSD are a source of great pride for the city, according to the school district. His most famous quote, which is on the Korematsu elementary school mural, is as relevant now as ever, “If you have the feeling that something is wrong, don’t be afraid to speak up.”
Black History
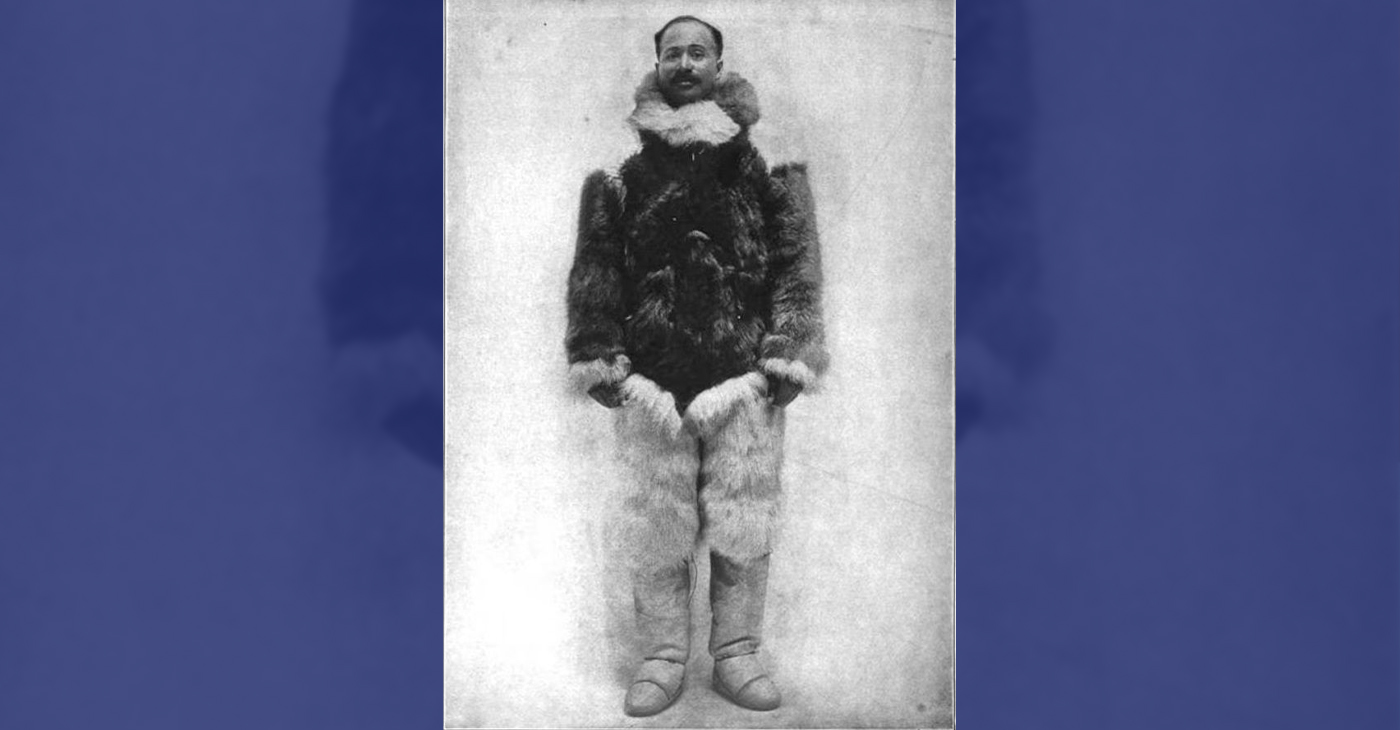
Matthew Henson: Explorer Extraordinaire
Matthew Henson, a trailblazing explorer who overcame countless obstacles to leave an incredible mark on history. Born on August 8, 1866, in Charles County, Maryland, his journey is a testament to the power of determination and the spirit of adventure.

By Tamara Shiloh
Matthew Henson, a trailblazing explorer who overcame countless obstacles to leave an incredible mark on history. Born on August 8, 1866, in Charles County, Maryland, his journey is a testament to the power of determination and the spirit of adventure.
Henson’s life began amidst the backdrop of post-Civil War America, where opportunities for African Americans were scarce. From a young age, he possessed an insatiable curiosity about the world beyond his small town. At the age of 12, he embarked on a journey that would change the course of his life forever when he joined a merchant ship as a cabin boy.
His most famous expedition was his journey to the Arctic with renowned explorer Robert E. Peary. In 1887, Henson joined Peary’s crew as a seaman and quickly proved himself to be invaluable with his skills as a navigator and craftsman. Over the course of several expeditions, Matthew endured extreme cold, treacherous terrain, and grueling conditions as he and Peary sought to reach the elusive North Pole.
In 1908–09, Peary set out on his eighth attempt to reach the North Pole. It was a big expedition, with Peary planning to leave supplies along the way. When he and Henson boarded their ship, the Roosevelt, leaving Greenland on August 18, 1909, they were joined by a large group. This included 22 Inuit men, 17 Inuit women, 10 children, 246 dogs, 70 tons of whale meat, blubber from 50 walruses, hunting gear, and tons of coal.
In February, Henson and Peary left their anchored ship at Ellesmere Island’s Cape Sheridan, along with the Inuit men and 130 dogs. They worked together to set up a trail and supplies along the way to the Pole.
Peary picked Henson and four Inuit people to join him in the final push to the Pole. However, before they reached their destination, Peary couldn’t walk anymore and had to ride in a dog sled. He sent Henson ahead to scout the way. In a later interview with a newspaper, Henson recalled being in the lead and realizing they had gone too far. The group turned back, and Henson noticed his footprints helped guide them to their destination. At that location, Henson planted the American flag.
Henson’s legacy extends far beyond his expeditions to the Arctic. He shattered racial barriers in the world of exploration and inspired countless individuals, regardless of race, to dream big and pursue their passions. In 1937, he was finally recognized for his achievements when he was inducted into The Explorers Club, an organization dedicated to promoting scientific exploration and field research.
Matthew Henson died in the Bronx, New York, on March 9, 1955, at the age of 88.
-

 Activism4 weeks ago
Activism4 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of March 27 – April 2, 2024
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoCOMMENTARY: D.C. Crime Bill Fails to Address Root Causes of Violence and Incarceration
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoMayor, City Council President React to May 31 Closing of Birmingham-Southern College
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoBeloved Actor and Activist Louis Cameron Gossett Jr. Dies at 87
-

 Community1 week ago
Community1 week agoFinancial Assistance Bill for Descendants of Enslaved Persons to Help Them Purchase, Own, or Maintain a Home
-

 Activism3 weeks ago
Activism3 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of April 3 – 6, 2024
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoV.P. Kamala Harris: Americans With Criminal Records Will Soon Be Eligible for SBA Loans
-

 Activism2 weeks ago
Activism2 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of April 10 – 16, 2024