California Black Media
Reports Cast Shadows on the Economic Picture for Black Californians
Recent studies suggest that the economic picture for Black Californians is not looking rosy. The state is becoming less affordable for African Americans, leading many families to relocate to less expensive places both within and past the borders.

Bo Tefu
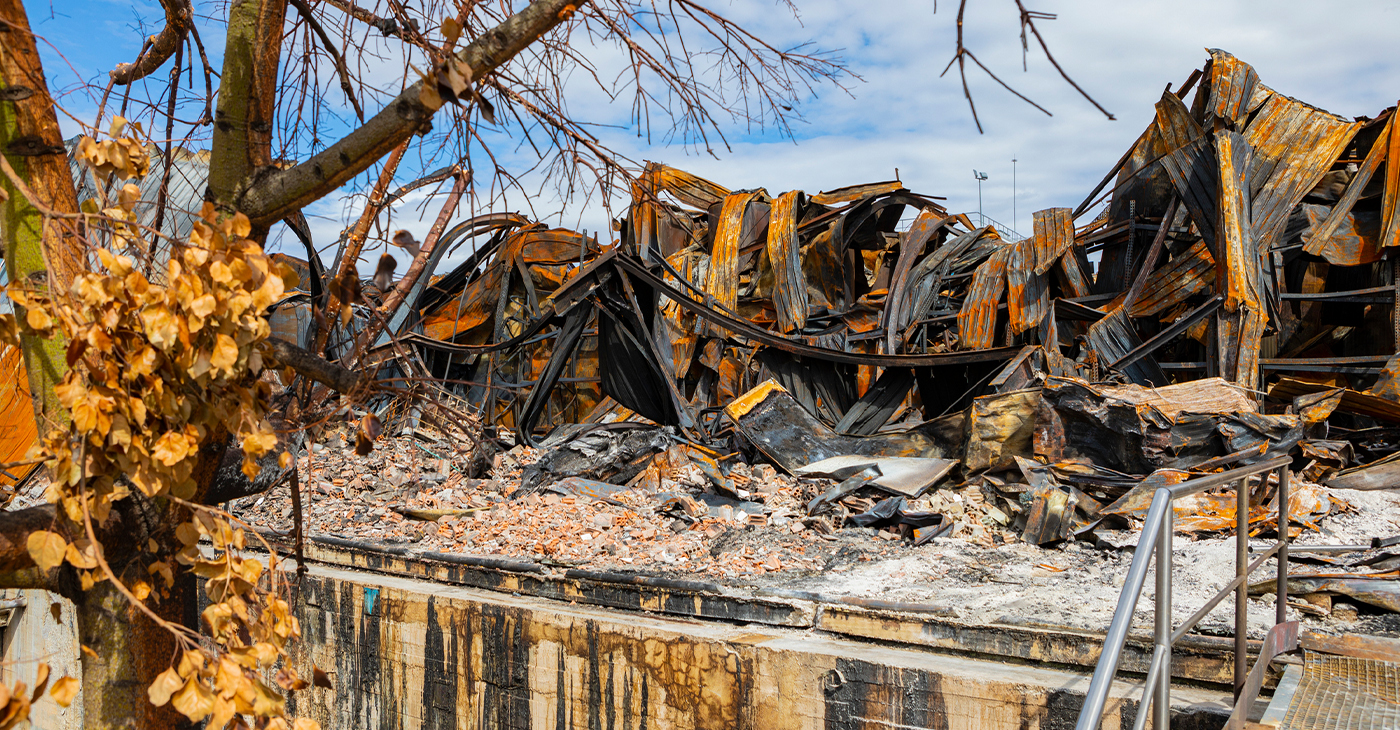
Trump’s White House Pushes to Control California Wildfire Recovery
The executive order signed Jan. 27 by President Donald Trump directs federal agencies to explore regulations that could override California and municipal permitting rules for homes and other structures destroyed in the fires. Land-use and rebuilding permits have traditionally been handled by cities and counties, making the move an unprecedented federal intervention into disaster recovery.
Bo Tefu
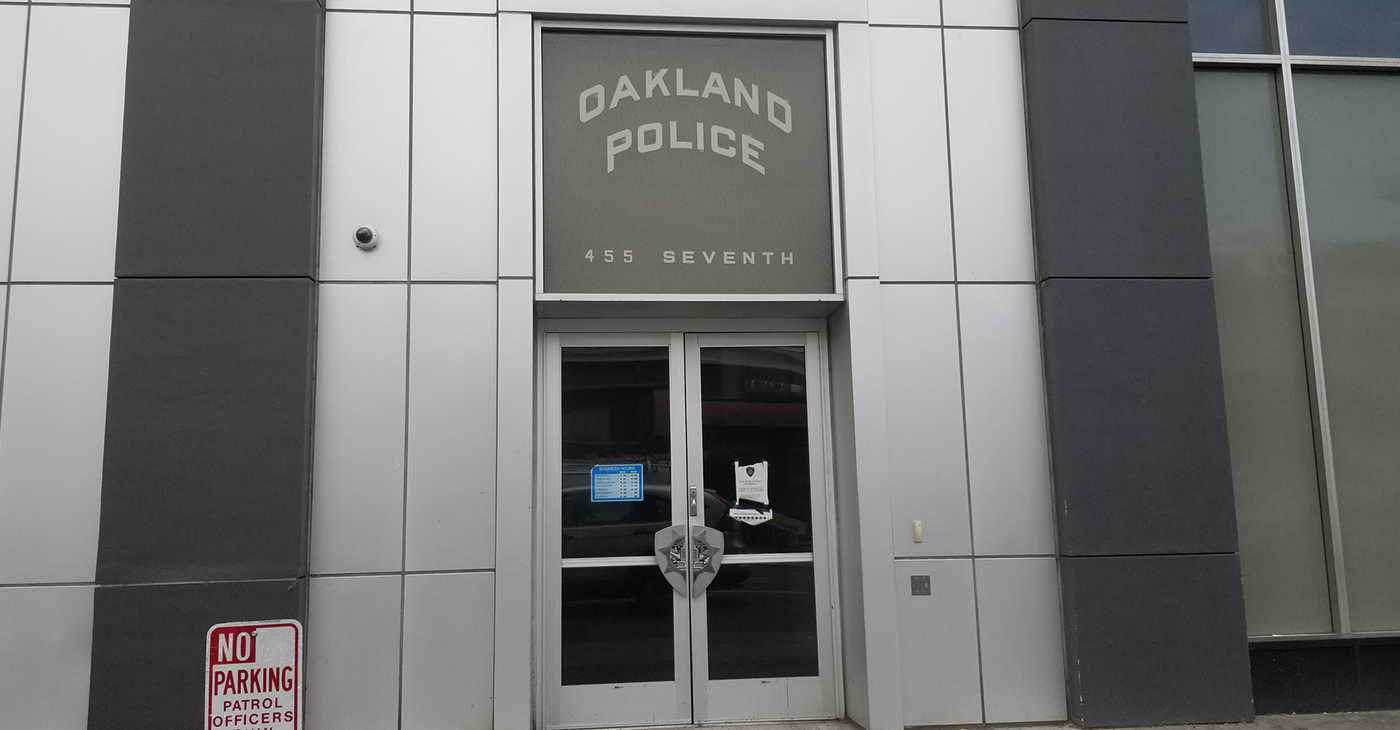
Gov. Newsom, AG Bonta to Local Law Enforcement: You Have Authority to Investigate Federal Agents
The guidance, released by the California Department of Justice (DOJ), emphasizes that local and state police have concurrent jurisdiction in cases involving federal officers and are not required to defer to federal investigations. The bulletin follows recent federal officer-involved shooting deaths in Minnesota and California.
Activism
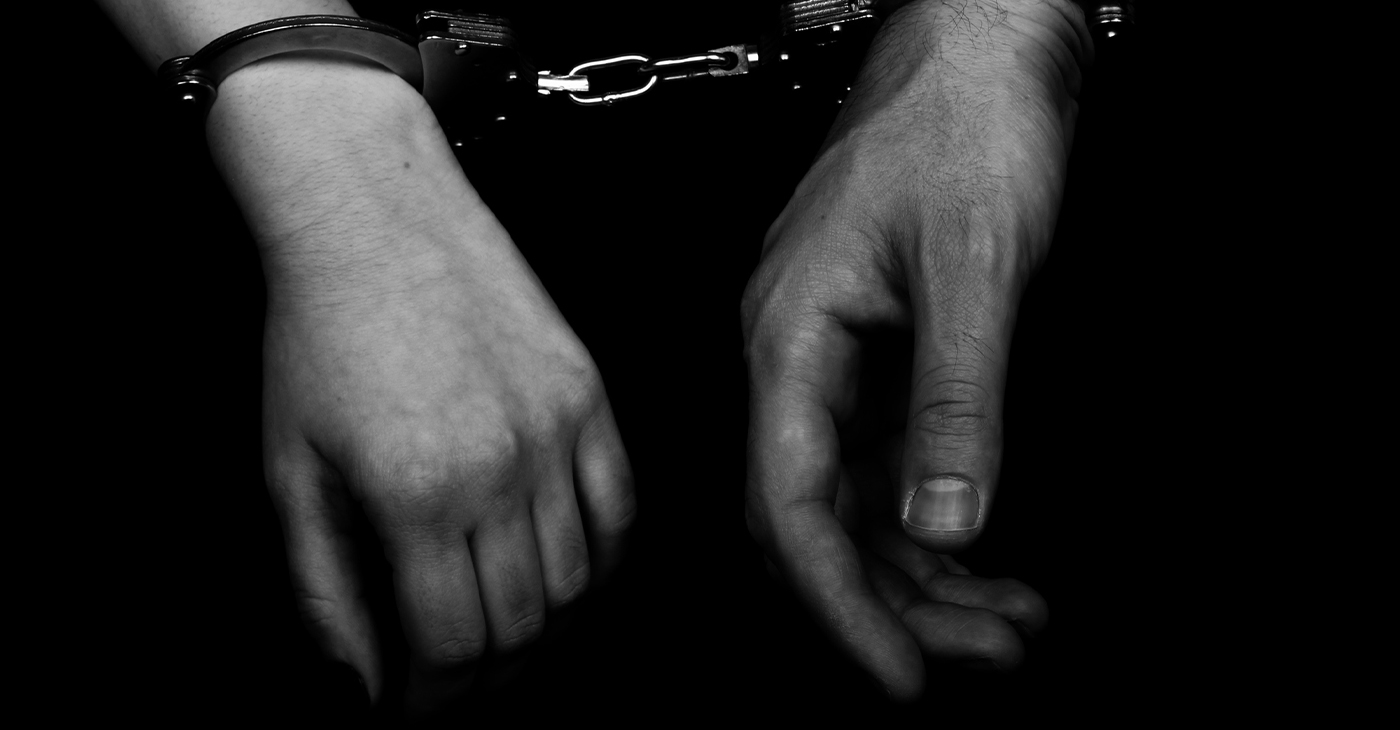
Cracking Down on Human Trafficking, California DOJ Announces 120 Arrests
According to the California DOJ, 87 arrests were made for loitering, 25 for solicitation, and eight for pimping and pandering. Officials said the operation focused on reducing demand for commercial sexual exploitation while prioritizing a survivor-centered approach.
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoOP-ED: The Dream Cannot be Realized Without Financial Freedom
-

 #NNPA BlackPress4 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress4 weeks agoFour Stolen Futures: Will H-E-B Do The Right Thing?
-

 Activism2 weeks ago
Activism2 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of January 28, 2025 – February 3, 2026
-

 Activism2 weeks ago
Activism2 weeks agoLife Expectancy in Marin City, a Black Community, Is 15-17 Years Less than the Rest of Marin County
-

 Activism3 weeks ago
Activism3 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of January 21 – 27, 2026
-

 Activism2 weeks ago
Activism2 weeks agoMedi-Cal Cares for You and Your Baby Every Step of the Way
-
Uncategorized2 weeks ago
Homegoing Service for Education Advocate Oscar Wright, 101
-

 Activism7 days ago
Activism7 days agoAfter Don Lemon’s Arrest, Black Officials Raise Concerns About Independent Black Media