Health
More Children at Risk of Measles in Wake of Ebola Epidemic

In this Monday, Jan. 19, 2015 file photo, a health care worker, right, takes the temperatures of school children for signs of the Ebola virus before they enter their school in the city of Conakry, Guinea. (AP Photo/Youssouf Bah, File)
LAURAN NEERGAARD, AP Medical Writer
WASHINGTON (AP) — Ebola’s toll moved beyond 10,000 deaths Thursday even as researchers warned of yet another threat to hard-hit West Africa: On the heels of the unprecedented devastation, large outbreaks of measles and other vaccine-preventable diseases could move into the region.
Ebola derailed child immunizations in the three countries hardest hit by Ebola — Liberia, Sierra Leone and Guinea, leaving hundreds of thousands more children vulnerable to the more routine infections, researchers said Thursday. Already, worrisome clusters of measles cases are cropping up.
The new study warns that it’s crucial to restart the shots quickly, citing math models that estimate thousands could die if a large enough measles outbreak were to strike before the battered health care system has a chance to recover.
Measles epidemics often follow humanitarian crises because “measles is so incredibly contagious,” explained Johns Hopkins University epidemiologist Justin Lessler, who led the study published in the journal Science.
“Measles is not the only health threat that has been made worse by the Ebola crisis, and may not even be the most dire, but it is one we can do something about,” he added.
The Ebola death milestone announced by the World Health Organization on Thursday had been expected for weeks, even though overall the epidemic is waning. Liberia has begun the 42-day countdown toward being declared Ebola-free if no new cases arise. Guinea and Sierra Leone still are struggling to end new infections, although cases aren’t nearly as high as in the fall.
A side effect of hospitals closed in the outbreak zone, and a population frightened of what health care remained, is that unnecessary deaths occurred from malaria, childbirth and other common conditions.
Now the question is whether measles and other vaccine-preventable childhood diseases will be the next post-Ebola problem.
In Guinea, UNICEF has reports of 339 suspected measles cases, 27 of them confirmed, agency spokesman Patrick Moser said in New York.
Doctors Without Borders said it has reports of 182 suspected measles cases in Liberia, plus some suspected cases in Sierra Leone, too.
Health services are slowly resuming in areas where Ebola’s grip has lessened. In Liberia, routine childhood vaccinations are being given in health facilities again, said Tolbert Nyenswah, an assistant health minister.
In addition, UNICEF and Doctors Without Borders are working with Liberian officials for a measles and polio vaccination campaign in May that will target more than 600,000 children under age 5, Moser said. Similar campaigns also are planned for Sierra Leone, depending on the continuing Ebola situation.
Measles remains a leading killer of children in developing countries, and it’s far more contagious than Ebola. There have been some huge epidemics when vaccinations were disrupted. Hopkins’ Lessler noted that between 2010 and 2013, about 294,000 cases of measles spread through the Congo, with more than 5,000 deaths, after a period of political instability.
His team set out to model what might happen if a large measles outbreak spread across Liberia, Sierra Leone and Guinea.
At the start of the Ebola crisis there already were about 778,000 unvaccinated children ages 9 months to 5 years in the three countries, the study estimated. For every month that Ebola disrupted regular health care, an extra 20,000 children became susceptible to measles, the researchers calculated.
In a worst-case regional outbreak, about 127,000 people would have gotten sick before Ebola but, after 18 months of vaccine disruption, an additional 100,000 illnesses could be expected, the researchers calculated. Anywhere from 2,000 to 16,000 more deaths could occur.
That estimate assumed that vaccinations dropped by 75 percent during the Ebola crisis, and Lessler said recent information suggests the decreases weren’t that severe. Even if vaccinations dropped by just 25 percent, Lessler said that still could mean tens of thousands more illnesses and anywhere from 500 to 4,000 additional deaths than before the recent Ebola outbreak.
Models are just that, and there’s no way to know if the region really is poised for a post-Ebola measles outbreak. But health groups say it’s urgent to restart vaccinations.
“There is a threat,” Dr. Estrella Lasry of Doctors Without Borders said in a phone interview from Liberia.
Health workers will have to make sure parents understand the need for resuming routine childhood immunizations, and the difference from studies of experimental Ebola vaccines that are being conducted in the region.
“There’s a need to rebuild trust in the health system,” she said.
___
Associated Press writers Maria Cheng in Geneva and Jonathan Paye-Layleh in Monrovia, Liberia, contributed to this report.
Copyright 2015 The Associated Press. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.
Alameda County
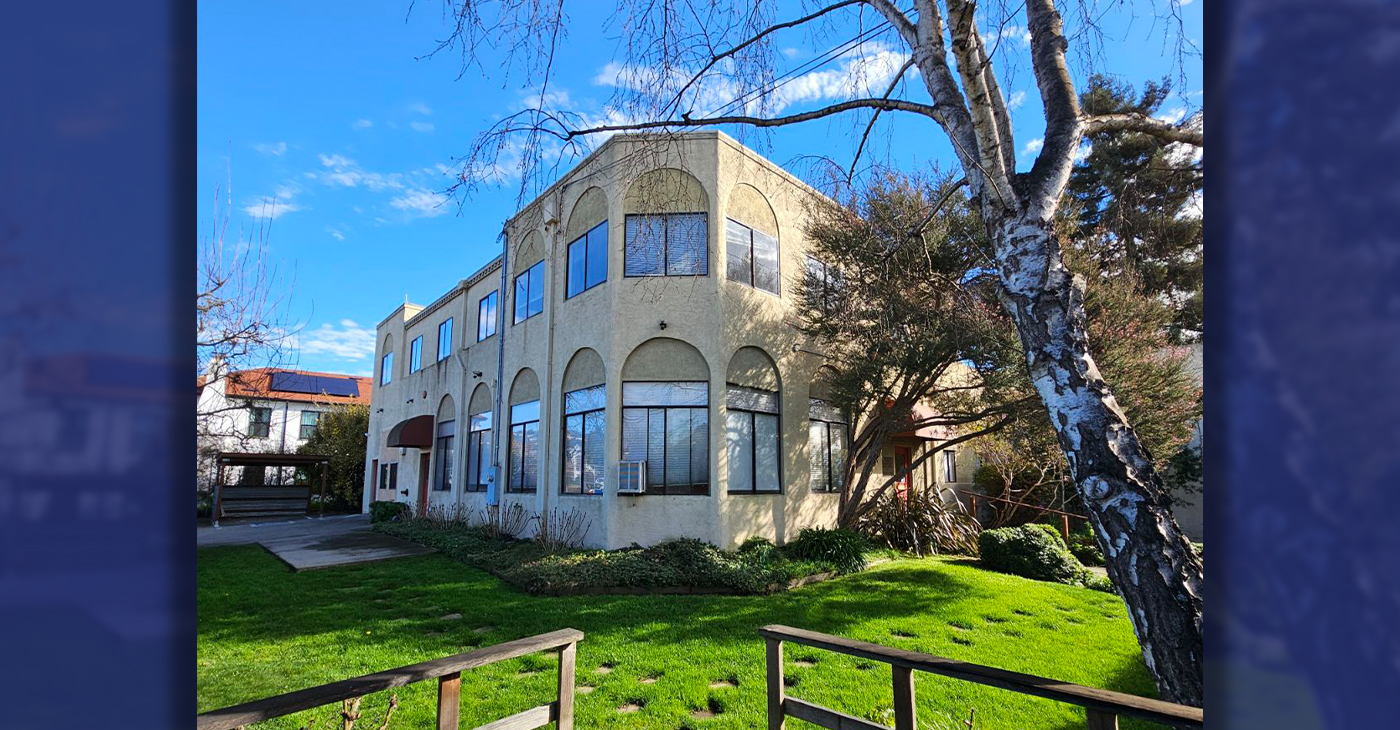
A Safe Place, Bay Area Domestic Violence Community Organization, Opens New Service Center in Oakland
Oakland-Bay Area non-profit, A Safe Place, announces the grand opening of its newly purchased building in Oakland that will be a service center for families that have suffered from domestic violence. The new, two-story building has over six new service rooms for counseling, mental health support groups, legal services, children’s treatment, safe space for community engagement, and partnership activities.

By Courtney Slocum Riley
Special to The Post
Oakland-Bay Area non-profit, A Safe Place, announces the grand opening of its newly purchased building in Oakland that will be a service center for families that have suffered from domestic violence.
The new, two-story building has over six new service rooms for counseling, mental health support groups, legal services, children’s treatment, safe space for community engagement, and partnership activities.
Domestic violence occurrences and offenses account for a considerable amount of all violent crimes in Alameda County. A Safe Place is attempting to provide a safe place for families to heal. A Safe Place is the only comprehensive domestic violence assistance program including a safehouse, in Oakland.
The grand opening celebration will also serve as a fundraiser to build out healing, therapeutic spaces for children and adult victims and survivors and survivors of domestic violence (male and female).
The new service center will expand the work of the organization, founded in 1976 when a group of women working in San Francisco came together to address the urgent need for a shelter in the East Bay. A year later, they founded A Safe Place (ASP) in Oakland. Run solely by volunteers, they set up a crisis line to offer crisis counseling and information to battered women and their children.
The organization serves over 500 adults and children annually through a host of services including crisis counseling via 24-hour crisis line, emergency motel and safehouse sheltering, mental health services (counseling and support groups).
Under the leadership of Executive Director, Carolyn Russell, the organization has grown from a single program into the comprehensive domestic violence and assistance program. ASP strives to meet the growing and diverse needs of our growing community.
The organization hopes to complete all the upgrades and therapeutic room improvements by August 2024. The public is invited to donate to the effort by using the website at www.asafeplace.org/donate. The organization also accepts in-kind gifts as well as items from the organization’s Amazon Wishlist.
Community
Swim to fight cancer

Alameda County
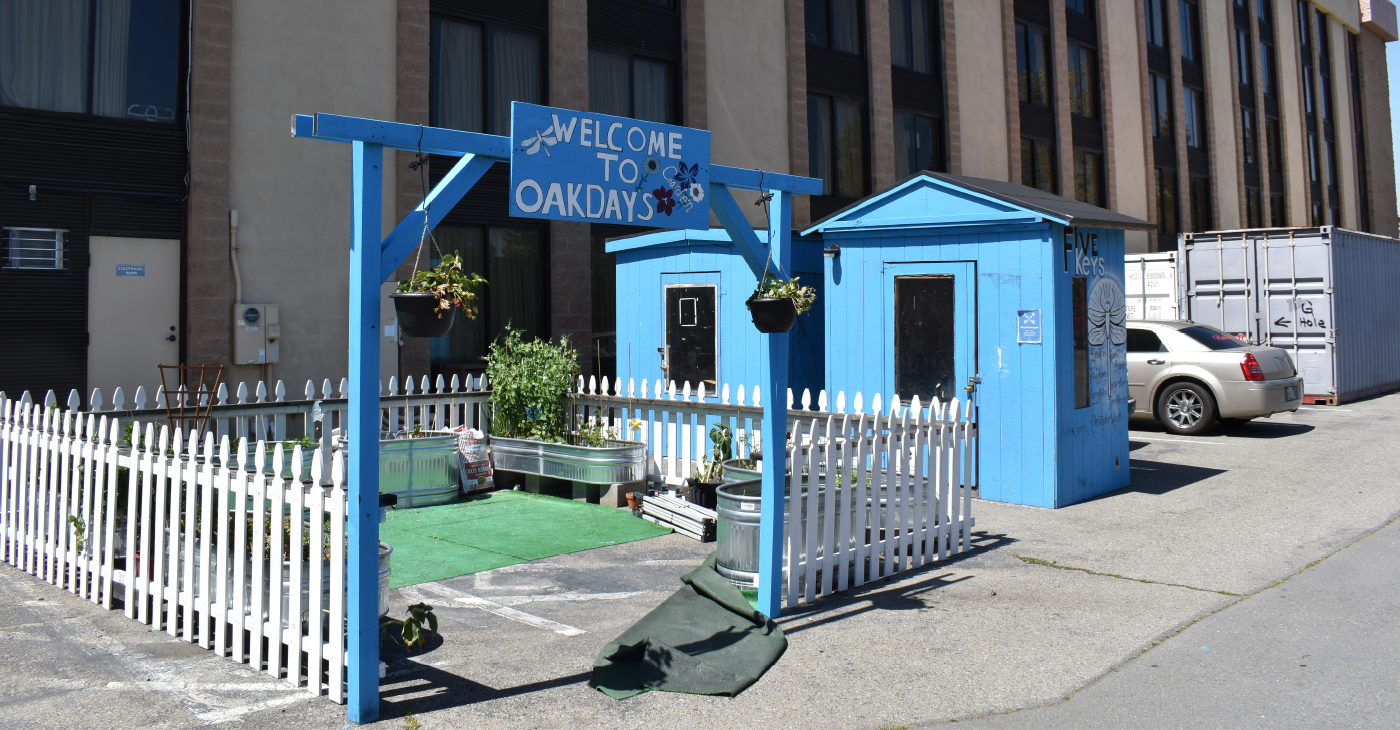
An Oakland Homeless Shelter Is Showing How a Housing and Healthcare First Approach Can Work: Part 1
Hundreds of tents and abandoned vehicles now dot major streets and neighborhoods of the Bay Area. Unfortunately, this problem is expected to worsen as the housing market skyrockets and the cost of living becomes unattainable for most Americans.

By Magaly Muñoz
Hundreds of tents and abandoned vehicles now dot major streets and neighborhoods of the Bay Area. Unfortunately, this problem is expected to worsen as the housing market skyrockets and the cost of living becomes unattainable for most Americans.
As one of California’s biggest public policy challenges, over the past four years, the state has allocated nearly $20 billion to housing and homelessness initiatives. Despite this substantial investment, the issue does not seem to be easing. Instead, the number of people without stable housing is surging.
A 2022 Point In Time (PIT) Count showed that there were 9,747 homeless individuals living on the streets in Alameda County, an almost 22% increase from the 2019 count of 8,022 homeless individuals. Many reports estimate that this number will rise once the 2024 data is released.
Amongst the many initiatives to end homelessness, the 2016 Senate Bill 1380 established California as a “housing first” state that would provide assistance, programs and funding to those experiencing homelessness. The bill recognized that the evidence-based model of prioritizing housing could end all types of homelessness and is the most effective approach to ending chronic homelessness.
In the years following the passage of the law, doctors, county officials and a community organization came together to create a first of its kind shelter to combat homelessness with housing and healthcare: the Oak Days shelter. Located in the Hegenberger corridor of Oakland, this facility, once a Days Hotel, now houses 60 individuals, some who are medically fragile.
As local counties navigated how to isolate people during the start of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, the state obtained federal funding to begin Project Roomkey, an initiative providing non-congregate shelter options, such as hotels and motels for people experiencing homelessness, to protect life and minimize strain on the healthcare system.
Dr. Alexis Chettiar, a medical director in Alameda County, witnessed firsthand how the coronavirus disease took over the lives of the most vulnerable populations who were too sick to remain stable unless they had hands-on supportive health care and permanent housing.
She also noticed a trend of medically vulnerable individuals with psychiatric illnesses or substance abuse issues being expelled from nursing homes, often ending up in encampments or unsheltered conditions.
This observation would inspire her, along with fellow medical director Catherine Hayes, to start Cardea Health, supported by county funding.
“What we really wanted to do was to be able to layer on the medical services to a permanent supportive housing environment so that people could age in place, they could stay there, no matter how their care needs change over time. They could stay there through the end of their life,” Chettiar said.
Cardea Health provides medical and personal care for almost 60 patients across two sites. One of these sites is an Old Comfort Inn that was also transformed into a shelter for those experiencing homelessness and chronic illnesses. The medical team assists with tasks such as injecting insulin, administering dialysis, helping patients use the restroom or get dressed.
Chettiar shared that she’s seen people as young as 40 years old with health-related issues mimicking that of an 80-year-old. Some individuals had untreated wounds that led to infections or chronic illnesses that went untreated for years, leading to immense suffering before they were able to receive medical attention.
The harsh conditions of living on the streets have exacerbated what could’ve been manageable situations, into a full-blown health crisis that ultimately put them on the priority list for Cardea’s health assistance.
UCSF Benioff Homelessness and Housing Initiative conducted a survey of 3,200 people to study who is experiencing homelessness, how they became homeless, what their experiences are and what is preventing them from exiting homelessness.
Data from those surveys showed that 45% of those experiencing homelessness reported poor or fair health and 60% reported having a chronic illness. Participants also reported that being homeless worsened their physical and mental health.
Of those experiencing health problems, 23% couldn’t access necessary healthcare in the prior six months. Additionally, 38% visited emergency departments without hospitalization and 21% reported a hospitalization for a physical health concern.
Chettiar stated that the work at Cardea is intended to reduce hospital visits for those living on the streets, providing essential care where it’s needed most.
-

 Community2 weeks ago
Community2 weeks agoFinancial Assistance Bill for Descendants of Enslaved Persons to Help Them Purchase, Own, or Maintain a Home
-

 Activism4 weeks ago
Activism4 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of April 3 – 6, 2024
-

 Business3 weeks ago
Business3 weeks agoV.P. Kamala Harris: Americans With Criminal Records Will Soon Be Eligible for SBA Loans
-

 Activism3 weeks ago
Activism3 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of April 10 – 16, 2024
-

 Community3 weeks ago
Community3 weeks agoAG Bonta Says Oakland School Leaders Should Comply with State Laws to Avoid ‘Disparate Harm’ When Closing or Merging Schools
-

 Community2 weeks ago
Community2 weeks agoOakland WNBA Player to be Inducted Into Hall of Fame
-

 Community2 weeks ago
Community2 weeks agoRichmond Nonprofit Helps Ex-Felons Get Back on Their Feet
-

 Community2 weeks ago
Community2 weeks agoRPAL to Rename Technology Center for Retired Police Captain Arthur Lee Johnson