#NNPA BlackPress
For People of Color, Gentrification is More a Curse than a Blessing
NNPA NEWSWIRE — According to a March 2019 study by the National Community Reinvestment Coalition (NCRC), more than 135,000 Black and Hispanics around the nation were displaced between 2000 and 2012. Gentrification and displacement of long-time residents were most intense from 2000 to 2013 in the nation’s biggest cities, and rare in most other places, according to the study. During those years, gentrification was concentrated in larger cities with vibrant economies but also appeared in smaller cities where it often impacted areas with the most amenities near central business districts.
By Stacy M. Brown, NNPA Newswire Senior Correspondent
@StacyBrownMedia
From a dowdy provincial city in the 1980s, Philadelphia has become a world-class urban center through gentrification – primarily through landmark architecture that now sets the city center and University City, apart.
“Over 50, and retirees, are moving back from the suburbs where they raised their children into Center City and the Italian Market where I have lived since 1980,” stated Dr. Margaret J. King, the director of The Center for Cultural Studies & Analysis in Philadelphia.
“Of course, gentrification brings money into the city, while it also drives up home prices – some houses have multiplied their asking prices 15 times over 40 years,” King noted.
“Housing is being restored and renovated, making more of the city habitable and in fact desirable. Now the suburbs have flipped into a working-class magnet as well as a market for Millennials who can’t afford center-city prices yet,” King stated.
Gentrification isn’t just an issue in Philadelphia – not by a long shot.
According to a March 2019 study by the National Community Reinvestment Coalition (NCRC), more than 135,000 Black and Hispanics around the nation were displaced between 2000 and 2012.
Gentrification and displacement of long-time residents were most intense from 2000 to 2013 in the nation’s biggest cities, and rare in most other places, according to the study.
During those years, gentrification was concentrated in larger cities with vibrant economies but also appeared in smaller cities where it often impacted areas with the most amenities near central business districts.
In Washington, D.C., 20,000 Black residents were displaced, and in Portland, Oregon, 13 percent of the Black community was displaced over the more than decade period that was studied.
Seven cities accounted for nearly half of the gentrification nationally: New York City, Los Angeles, Washington, D.C., Philadelphia, Baltimore, San Diego, and Chicago.
Washington, D.C., was the most gentrified city by percentage of eligible neighborhoods that experienced gentrification; New York City was the most gentrified by sheer volume, study authors noted.
According to the Merriam-Webster Dictionary, gentrification is defined as the process of repairing and rebuilding homes and businesses in a deteriorating area, such as an urban neighborhood, accompanied by an influx of middle-class or affluent people and that often results in the displacement of earlier, usually poorer residents.
“Gentrification is rich people deciding they want a specific neighborhood as their own, and they get municipal backing, pay some money, and get all of the poor people out of there,” stated Mark Love, a New York realtor.
Neighborhoods were considered to be eligible to gentrify if, in 2000, they were in the lower 40 percent of home values and family incomes in that metropolitan area.
During the study, researchers found that most low- to moderate-income neighborhoods did not gentrify or revitalize.
Instead, they remained impoverished, untouched by investments and building booms that occurred in major cities, and vulnerable to future gentrification and displacement.
“When a neighborhood gentrifies, the cost of living increases, and it’s harder for low-income families to find housing, and that’s one of the biggest downsides,” stated Melanie Musson, a writer for ExpertInsuranceReviews.com.
“In a city like Philadelphia, neighborhoods are part of your identity. If you grow up in a neighborhood, you often want to remain living there your whole life because it’s who you are,” Musson stated.
“Unfortunately, sometimes, after several generations living in the same zip code, the newest generation has to find housing elsewhere because it’s too expensive to live where their home has always been,” she said.
Bruce Mirken, the media relations director for the nonprofit public, policy, and advocacy organization, The Greenlining Institute, said he lives in San Francisco and works in Oakland – two cities that are ground zero for the gentrification crisis in California.
“We see the most obvious results among the very low-income, who increasingly cannot keep a roof over their heads, leading to a growing homeless population,” Mirken stated.
“And homelessness in California has a distinct racial dynamic, tracing back through a long history of redlining and discrimination: Black Californians represent about six and a half percent of our state’s population, but about 40 percent of its homeless,” he noted.
In New York, where many residents are still growing accustomed to the decades-long gentrification of Harlem, the Bronx has forever been known as the city’s most urban borough. That’s quickly changing due to gentrification.
In November 2019, officials announced a $950 million, 4.3 acre, multi-tower, and mixed-use development along the Mott Haven waterfront. More than 1,300 high-end apartments are among the upgrades that are certain to price many long-time residents out of the area.
Mychal Johnson, a co-founding member of South Bronx Unite, told The Bronx Times that gentrification isn’t good for economically oppressed communities of color.
“It seems like the community board, and Borough president isn’t looking out for the community,” Johnson stated.
Mitchell noted that, in 2016, Richmond had similar numbers of Black and White residents. From 2000 to 2016, the Black population decreased by seven percent, while the White population increased by 35 percent.
In 2000, Blacks were 57 percent of the population, and whites were 38 percent. In 2016, Blacks represented 47 percent and Whites were 46 percent of the population.
“This shift has come to the East End like a racialized wave crashing onto the shores of the neighborhood in currents of physical, cultural, and economic displacement. The Black community is drowning as we watch our land and culture swallowed up, block by block with no reprieve in sight,” Mitchell wrote in the report.
“Gentrification in the East End of Richmond is manifesting as a process of re-segregation,” she stated. “In Richmond, gentrification is colonization.”
In Portland, Oregon, an essay that accompanied the NCRC study noted that city as the “Whitest city of its size in the United States.”
The city’s White population currently stands at 77.4 percent while Blacks make up just 5.7 percent.
“Take a group of people who have been systematically denied wealth-building opportunities for generations, add low, stagnating incomes, throw in a subprime mortgage disaster, spiraling housing costs and wholesale community displacement, and you have a recipe for a severe economic backslide,” Cheryl Chandler-Roberts, executive director of Portland’s African American Alliance for Homeownership, said in the report.
“There is no African American community in Portland at this point,” Chandler-Roberts stated.
“It’s a scattered community.”
NEXT: Urban development and public policy experts from Carnegie Mellon University weigh-in on gentrification.
#NNPA BlackPress
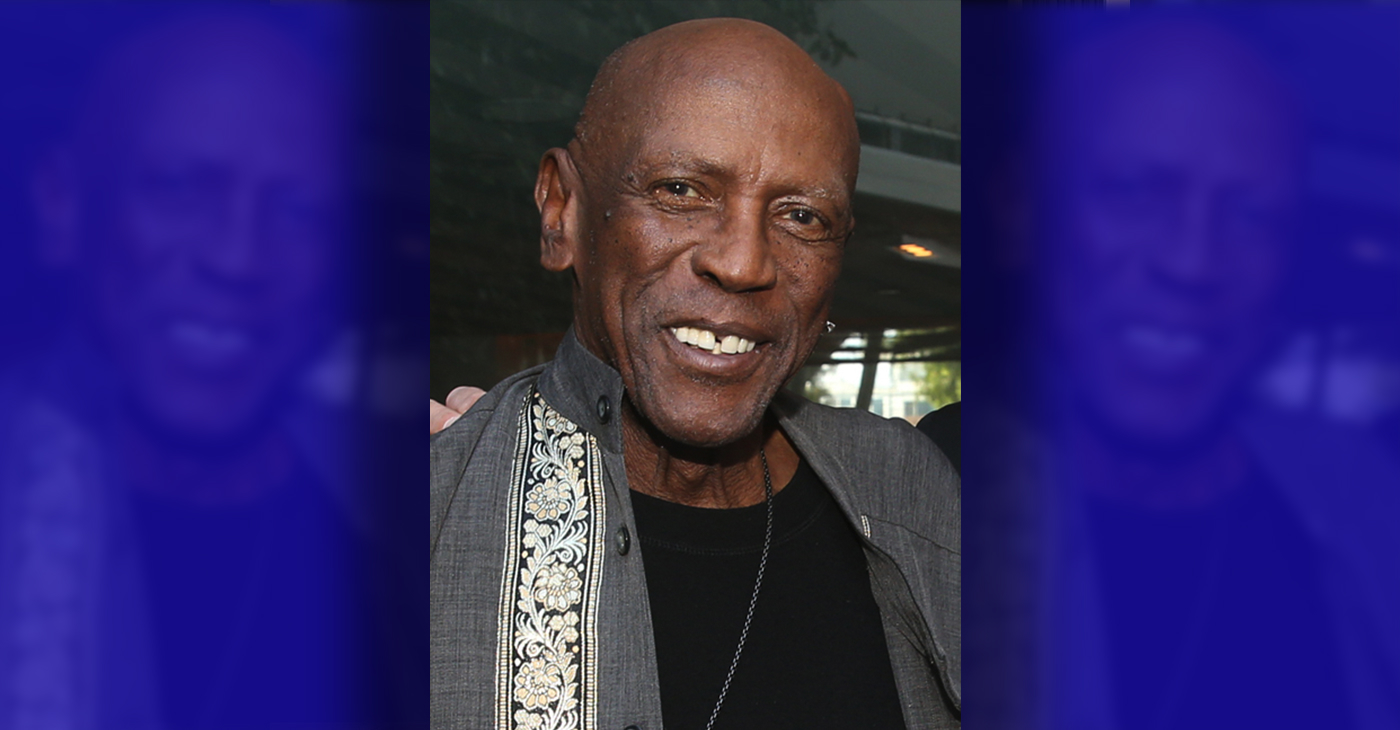
Beloved Actor and Activist Louis Cameron Gossett Jr. Dies at 87
NNPA NEWSWIRE — Louis Gossett Jr., the groundbreaking actor whose career spanned over five decades and who became the first Black actor to win an Academy Award as Best Supporting Actor for his memorable role in “An Officer and a Gentleman,” has died. Gossett, who was born on May 27, 1936, in Brooklyn, N.Y., was 87. Recognized early on for his resilience and nearly unmatched determination, Gossett arrived in Los Angeles in 1967 after a stint on Broadway.
The post Beloved Actor and Activist Louis Cameron Gossett Jr. Dies at 87 first appeared on BlackPressUSA.

By Stacy M. Brown
NNPA Newswire Senior National Correspondent
@StacyBrownMedia
Louis Gossett Jr., the groundbreaking actor whose career spanned over five decades and who became the first Black actor to win an Academy Award as Best Supporting Actor for his memorable role in “An Officer and a Gentleman,” has died. Gossett, who was born on May 27, 1936, in Brooklyn, N.Y., was 87. Recognized early on for his resilience and nearly unmatched determination, Gossett arrived in Los Angeles in 1967 after a stint on Broadway.
He sometimes spoke of being pulled over by law enforcement en route to Beverly Hills, once being handcuffed to a tree, which he remembered as a jarring introduction to the racial tensions of Hollywood. In his memoir “An Actor and a Gentleman,” Gossett recounted the ordeal, noting the challenges faced by Black artists in the industry. Despite the hurdles, Gossett’s talent shone brightly, earning him acclaim in groundbreaking productions such as “A Raisin in the Sun” alongside Sidney Poitier. His Emmy-winning portrayal of Fiddler in “Roots” solidified his status as a trailblazer, navigating a landscape fraught with racial prejudice.
According to the HistoryMakers, which interviewed him in 2005, Gossett’s journey into the limelight began during his formative years at PS 135 and Mark Twain Junior High School, where he demonstrated early leadership as the student body president. His passion for the arts blossomed when he starred in a “You Can’t Take It With You” production at Abraham Lincoln High School, catching the attention of talent scouts who propelled him onto Broadway’s stage in “Take A Giant Step.” His stellar performance earned him the prestigious Donaldson Award for Best Newcomer to Theatre in 1952. Though initially drawn to sports, Gossett’s towering 6’4” frame and athletic prowess led him to receive a basketball scholarship at New York University. Despite being drafted by the New York Knicks in 1958, Gossett pursued his love for acting, honing his craft at The Actors Studio under the tutelage of luminaries like John Sticks and Peggy Fury.
In 1961, Gossett’s talent caught the eye of Broadway directors, leading to roles in acclaimed productions such as “Raisin in the Sun” and “The Blacks,” alongside legends like James Earl Jones, Cicely Tyson, Roscoe Lee Brown, and Maya Angelou. Transitioning seamlessly to television, Gossett graced small screens with appearances in notable shows like “The Bush Baby” and “Companions in Nightmare.” Gossett’s silver screen breakthrough came with his role in “The Landlord,” paving the way for a prolific filmography that spanned over 50 movies and hundreds of television shows. From “Skin Game” to “Lackawanna Blues,” Gossett captivated audiences with his commanding presence and versatile performances.
However, his portrayal of “Fiddler” in Alex Haley’s groundbreaking miniseries “Roots” earned Gossett critical acclaim, including an Emmy Award. The HistoryMakers noted that his golden touch extended to the big screen, where his role as Sergeant Emil Foley in “An Officer and a Gentleman” earned him an Academy Award for Best Supporting Actor, making him a trailblazer in Hollywood history.
Beyond the glitz and glamour of Hollywood, Gossett was deeply committed to community activism. In 1964, he co-founded a theater group for troubled youth alongside James Earl Jones and Paul Sorvino, setting the stage for his lifelong dedication to mentoring and inspiring the next generation. Gossett’s tireless advocacy for racial equality culminated in the establishment of Eracism, a nonprofit organization dedicated to combating racism both domestically and abroad. Throughout his illustrious career, Gossett remained a beacon of strength and resilience, using his platform to uplift marginalized voices and champion social change. Gossett is survived by his children, Satie and Sharron.
The post Beloved Actor and Activist Louis Cameron Gossett Jr. Dies at 87 first appeared on BlackPressUSA.
#NNPA BlackPress
COMMENTARY: D.C. Crime Bill Fails to Address Root Causes of Violence and Incarceration
WASHINGTON INFORMER — The D.C. crime bill and so many others like it are reminiscent of the ‘94 crime bill, which produced new and harsher criminal sentences, helped deploy thousands of police and surveilling methods in Black and brown communities, and incentivized more states to build prisons through a massive infusion of federal funding. While it is not at the root of mass incarceration, it significantly accelerated it, forcing a generation of Black and brown families into a never-ending cycle of state-sanctioned violence and incarceration.
The post COMMENTARY: D.C. Crime Bill Fails to Address Root Causes of Violence and Incarceration first appeared on BlackPressUSA.
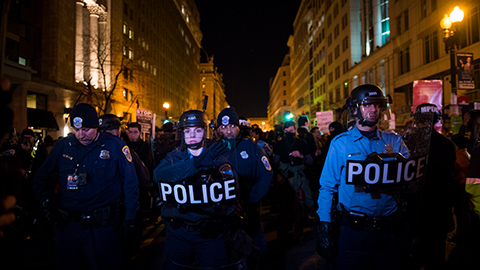
By Kaili Moss and Jillian Burford | Washington Informer
Mayor Bowser has signed the “Secure DC” omnibus bill passed by the D.C. Council last month. But we already know that this bill will be disastrous for all of D.C., especially for Black and brown residents.
While proponents claim that this legislation “will make D.C. residents safer and more secure,” it actually does nothing to address the root of the harm in the first place and instead maintains a cycle of violence, poverty, and broken community ties. The omnibus bill calls for increased surveillance, drug-free zones, and will expand pre-trial detention that will incarcerate people at a significantly higher rate and for an indeterminate amount of time before they are even tried. This bill will roll back decades of nationwide policy reform efforts and initiatives to keep our communities safe and whole, which is completely contradictory to what the “Secure” D.C. bill claims it will do.
What is unfolding in Washington, D.C., is part of a dangerous national trend. We have seen a resurrection of bad crime bills in several jurisdictions across the country — a phenomenon policy experts have named “zombie laws,” which are ineffective, costly, dangerous for communities of color and, most importantly, will not create public safety. Throwing more money into policing while failing to fund preventative measures does not keep us safe.
The D.C. crime bill and so many others like it are reminiscent of the ‘94 crime bill, which produced new and harsher criminal sentences, helped deploy thousands of police and surveilling methods in Black and brown communities, and incentivized more states to build prisons through a massive infusion of federal funding. While it is not at the root of mass incarceration, it significantly accelerated it, forcing a generation of Black and brown families into a never-ending cycle of state-sanctioned violence and incarceration. Thirty years later, despite spending billions each year to enforce these policies with many of these provisions remaining in effect, it has done very little to create long-term preventative solutions. Instead, it placed a permanent moving target on the backs of Black people, and the D.C. crime bill will do the same.
The bill calls for more pretrial detention. When our loved ones are held on pretrial detention, they are held on the presumption of guilt for an indeterminate amount of time before ever seeing a judge, which can destabilize people and their families. According to experts at the Malcolm Weimer Center for Social Policy at Harvard University, just one day in jail can have “devastating consequences.” On any given day, approximately 750,000 people are held in jails across the nation — a number that beats our nation’s capital population by about 100,000. Once detained, people run the risk of losing wages, jobs, housing, mental and health treatments, and time with their families. Studies show that pretrial detention of even a couple of days makes it more likely for that person to be rearrested.
The bill also endangers people by continuing a misguided and dangerous War on Drugs, which will not get drugs off the street, nor will it deter drug use and subsequent substance use disorders (SUDs). Drug policies are a matter of public health and should be treated as such. Many states such as Alabama, Iowa and Wisconsin are treating the current fentanyl crisis as “Crack 2.0,” reintroducing a litany of failed policies that have sent millions to jails and prisons instead of prioritizing harm reduction. Instead, we propose a simple solution: listen to members of the affected communities. Through the Decrim Poverty D.C. Coalition, community members, policy experts and other stakeholders formed a campaign to decriminalize drugs and propose comprehensive legislation to do so.
While there are many concerning provisions within the omnibus bill, car chases pose a direct physical threat to our community members. In July 2023, NBC4 reported that the D.C. Council approved emergency legislation that gave MPD officers the ability to engage in vehicular pursuits with so-called “limited circumstances.” Sgt. Val Barnes, the head of MPD’s carjacking task force, even expressed concern months before the decision, saying, “The department has a pretty strict no-chase policy, and obviously for an urban setting and a major metropolitan city, that’s understandable.” If our law enforcement officers themselves are operating with more concern than our elected officials, what does it say about the omnibus bill’s purported intention to keep us safe?
And what does it mean when the risk of bodily harm is posed by the pursuit itself? On Saturday, Feb. 10, an Eckington resident had a near-miss as a stolen car barreled towards her and her dog on the sidewalk with an MPD officer in pursuit. What responsibility does the city hold if this bystander was hit? What does restitution look like? Why are our elected officials pushing for MPD officers to contradict their own policies?
Just a few summers ago during the uprisings of 2020, we saw a shift in public perspectives on policing and led to legislation aimed at limiting police power after the highly-publicized murders of loved ones Breonna Taylor and George Floyd — both victims of War on Drugs policing and the powers gained from the ’94 crime bill. And yet here we are. These measures do not keep us safe and further endanger the health of our communities. Studies show that communities that focus on harm reduction and improving material conditions have a greater impact on public safety and community health. What’s missing in mainstream conversations about violent crime is the violence that stems from state institutions and structures that perpetuate racial and class inequality. The people of D.C. deserve to feel safe, and that includes feeling safe from the harms enacted by the police.
Kaili Moss is a staff attorney at Advancement Project, a national racial justice and legal organization, and Jillian Burford is a policy organizer at Harriet’s Wildest Dreams.
The post COMMENTARY: D.C. Crime Bill Fails to Address Root Causes of Violence and Incarceration first appeared on BlackPressUSA.
#NNPA BlackPress
Mayor, City Council President React to May 31 Closing of Birmingham-Southern College
THE BIRMINGHAM TIMES — “This is a tragic day for the college, our students, our employees, and our alumni, and an outcome so many have worked tirelessly to prevent,” Rev. Keith Thompson, chairman of the BSC Board of Trustees said in an announcement to alumni. “We understand the devastating impact this has on each of you, and we will now direct our efforts toward ensuring the smoothest possible transition for everyone involved.”
The post Mayor, City Council President React to May 31 Closing of Birmingham-Southern College first appeared on BlackPressUSA.

By Barnett Wright | The Birmingham Times
Birmingham-Southern College will close on May 31, after more than a century as one of the city’s most respected institutions.
“This is a tragic day for the college, our students, our employees, and our alumni, and an outcome so many have worked tirelessly to prevent,” Rev. Keith Thompson, chairman of the BSC Board of Trustees said in an announcement to alumni. “We understand the devastating impact this has on each of you, and we will now direct our efforts toward ensuring the smoothest possible transition for everyone involved.”
There are approximately 700 students enrolled at BSC this semester.
“Word of the decision to close Birmingham Southern College is disappointing and heartbreaking to all of us who recognize it as a stalwart of our community,” Birmingham Mayor Randall Woodfin said in a statement. “I’ve stood alongside members of our City Council to protect this institution and its proud legacy of shaping leaders. It’s frustrating that those values were not shared by lawmakers in Montgomery.”
Birmingham City Council President Darrell O’Quinn said news of the closing was “devastating” on multiple levels.
“This is devastating for the students, faculty members, families and everyone affiliated with this historic institution of higher learning,” he said. “It’s also profoundly distressing for the surrounding community, who will now be living in close proximity to an empty college campus. As we’ve seen with other institutions that have shuttered their doors, we will be entering a difficult chapter following this unfortunate development … We’re approaching this with resilience and a sense of hope that something positive can eventually come from this troubling chapter.”
The school first started as the merger of Southern University and Birmingham College in 1918.
The announcement comes over a year after BSC officials admitted the institution was $38 million in debt. Looking to the Alabama Legislature for help, BSC did not receive any assistance.
This past legislative session, Sen. Jabo Waggoner sponsored a bill to extend a loan to BSC. However, the bill subsequently died on the floor.
Notable BSC alumni include former New York Times editor-in-chief Howell Raines, former U.S. Sen. Howell Heflin and former Alabama Supreme Court Chief Justice Perry O. Hooper Sr.
This story will be updated.
The post Mayor, City Council President React to May 31 Closing of Birmingham-Southern College first appeared on BlackPressUSA.
-

 Activism4 weeks ago
Activism4 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of March 20 – 26, 2024
-

 #NNPA BlackPress3 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress3 weeks agoCOMMENTARY: D.C. Crime Bill Fails to Address Root Causes of Violence and Incarceration
-

 #NNPA BlackPress3 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress3 weeks agoMayor, City Council President React to May 31 Closing of Birmingham-Southern College
-

 #NNPA BlackPress3 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress3 weeks agoFrom Raids to Revelations: The Dark Turn in Sean ‘Diddy’ Combs’ Saga
-

 #NNPA BlackPress3 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress3 weeks agoCOMMENTARY: Lady Day and The Lights!
-

 #NNPA BlackPress3 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress3 weeks agoBaltimore Key Bridge Catastrophe: A City’s Heartbreak and a Nation’s Alarm
-

 #NNPA BlackPress3 weeks ago
#NNPA BlackPress3 weeks agoBaltimore’s Key Bridge Struck by Ship, Collapses into Water
-

 Activism3 weeks ago
Activism3 weeks agoOakland Post: Week of March 27 – April 2, 2024














































